在这篇文章中,我们将带领您了解android–将OSMDroid与Fragments集成的全貌,包括android集成chromium的相关情况。同时,我们还将为您介绍有关AndroidFragmen
在这篇文章中,我们将带领您了解android – 将OSMDroid与Fragments集成的全貌,包括android集成chromium的相关情况。同时,我们还将为您介绍有关Android Fragment FragmentTabHost 问题、Android Fragments 详细使用、android Fragments 详解七:fragement 示例、android Fragments详解三:实现Fragment的界面的知识,以帮助您更好地理解这个主题。
本文目录一览:- android – 将OSMDroid与Fragments集成(android集成chromium)
- Android Fragment FragmentTabHost 问题
- Android Fragments 详细使用
- android Fragments 详解七:fragement 示例
- android Fragments详解三:实现Fragment的界面

android – 将OSMDroid与Fragments集成(android集成chromium)
public class POfflineMapView extends Activity implements LocationListener,MapViewConstants{
private MapView myOpenMapView;
private OsmMapsitemizedoverlay mitemizedoverlay;
private ResourceProxy mResourceProxy;
private OverlayItem overlayItem;
private ArrayList<OverlayItem> mItems = new ArrayList<OverlayItem>();
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
mResourceProxy = new DefaultResourceProxyImpl(getApplicationContext());
setContentView(R.layout.offline_map_activity);
myOpenMapView = (MapView) findViewById(R.id.openmapview);
myOpenMapView.getTileProvider().clearTileCache();
//.... code continues
}
}
但是,我很难找到使用Fragments实现使用OSMDRoid Maptiles显示的示例(例如,SherlockMapFragment).有谁知道如何实现这一点,或者是否能够为我提供示例实施指南?
我需要这样做,因为我有一个Activity容器,当我点击某个按钮时,我想做一个片段.replace()来代替用OSMDRoid地图片段代替容器.
谢谢!
解决方法
要创建包含默认地图的片段,您可以执行以下操作:
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater,ViewGroup container,Bundle savedInstanceState) {
return new MapView(getActivity(),256);
}
在你的片段类中.
如果您想使用包含MapView的布局,您可以在片段中执行以下操作:
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater,Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View v = inflater.inflate(R.layout.offline_map_activity,null);
myOpenMapView = v.findViewById(R.id.openmapview);
return v;
}

Android Fragment FragmentTabHost 问题
今天需要做一个功能,实现 tab 切换功能,但是又不能向 viewpager 一样可以滑动,只能通过顶部的 tab 标签滑动,就是类似 ActionBar 的 tab 一样的切换。
然后我就去找例子,在 ApiDemos 中有 FragmentTabs(extends Activity),FragmentTabsFragment (extends Fragment),两个例子,特别说一下 FragmentTabsFragment,这个类中的 TabManager 是重写了 FragmentTabHost,自己实现的状态保存等等,值得参考一下,当然,这个类也参考了 FragmentTabHost 的实现。
在 Support4Demos 中,有 FragmentTabs (extends FragmentActivity),FragmentTabsFragmentSupport (extends Fragment);
我主要参考的是 FragmentTabsFragmentSupport,因为我想用 Fragment 去实现我的需求。
遇到的几个问题:
1.FragmentTabHost 的顶部 tab 样式是系统的,不符合我的要求,那么如何定制这个样式呢?
你一定是这样使用的:
mTabHost.addTab(mTabHost.newTabSpec("simple").setIndicator(“simple”), ArrayListFragment.class, null);
如果要改这个 tab 的样式,可以这样:
Button simple = new Button(getActivity());
simple.setText("xxx");
simple.setTextColor(this.getResources().getColor(R.color.green));
// simple.setBackgroundColor(R.color.indicate);
simple.setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.ic_star_p);
// set padding
// simple.setPadding(150, 150, 0, 0);
// set margin
LinearLayout.LayoutParams lp = new LinearLayout.LayoutParams(
0, LinearLayout.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, 1); // 1 是可选写的
lp.setMargins(150, 50, 0, 50);
simple.setLayoutParams(lp);
看到了吧,可以设置 padding, margin, background 等。。。
然后 -》setIndicator (View view), 看到了吧,有个方法是支持自定义 view 的,所以我们就可以自定义一个 view,比如,把上面定义的 Button simple 传进去就可以了。
还可以设置 TabWidget 的高度和背景:
mTabHost.getTabWidget().setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.ic_new_tab_p);
mTabHost.getTabWidget().setMinimumHeight(300);
mTabHost.getTabWidget().setDividerDrawable(null);
2. 多个 tab 切换的时候,每次都会从新执行:onCreateView,onDestroyView,导致比如 listview 这种无法保存浏览的位置?
我是这样解决的:
if (rootView == null) {
rootView = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_pager_list, container, false);
}
ViewGroup parent = (ViewGroup) rootView.getParent();
if (parent != null) {
parent.removeView(rootView);
}
View tv = rootView.findViewById(R.id.text);
((TextView)tv).setText("Fragment #" + mNum);
return rootView;
测试代码下载地址:
http://download.csdn.net/detail/song_shi_chao/7168045
参考:
http://www.cnblogs.com/asion/archive/2013/09/25/3339313.html
http://ar.newsmth.net/thread-ffd9fb821607d1.html
http://www.eoeandroid.com/thread-322096-1-1.html
http://www.byywee.com/page/M0/S910/910755.html
http://blog.csdn.net/renpengben/article/details/12615487(我使用了这种方法)
http://www.2cto.com/kf/201309/242225.html
http://www.eoeandroid.com/thread-153696-1-1.html(ViewPager 与其中的子 View 滑动冲突该如何解决)

Android Fragments 详细使用
Fragments 诞生初衷
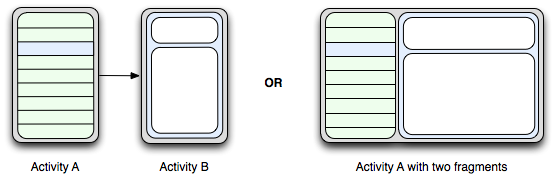
自从Android 3.0中引入fragments 的概念,根据词海的翻译可以译为:碎片、片段。其上的是为了解决不同屏幕分辩率的动态和灵活UI设计。大屏幕如平板小屏幕如手机,平板电脑的设计使得其有更多的空间来放更多的UI组件,而多出来的空间存放UI使其会产生更多的交互,从而诞生了fragments 。fragments 的设计不需要你来亲自管理view hierarchy 的复杂变化,通过将Activity 的布局分散到frament 中,可以在运行时修改activity 的外观,并且由activity 管理的back stack 中保存些变化。
Fragments 设计理念
在设计应用时特别是Android 应用 ,有众多的分辨率要去适应,而fragments 可以让你在屏幕不同的屏幕上动态管理UI。例如:通讯应用程序(QQ),用户列表可以在左边,消息窗口在右边的设计。而在手机屏幕用户列表填充屏幕当点击某一用户时,则弹出对话窗口的设计,如下图:
Fragments的生命周期
每一个fragments 都有自己的一套生命周期回调方法和处理自己的用户输入事件。 对应生命周期可参考下图:

其中大多数程序必须使用Fragments 必须实现的三个回调方法分别为:
onCreate
系统创建Fragments 时调用,可做执行初始化工作或者当程序被暂停或停止时用来恢复状态,跟Activity 中的onCreate相当。
onCreateView
用于首次绘制用户界面的回调方法,必须返回要创建的Fragments 视图UI。假如你不希望提供Fragments 用户界面则可以返回NULL。
onPause
当用户离开这个Fragments 的时候调用,这时你要提交任何应该持久的变化,因为用户可能不会回来。更多的事件可以参考上图的生命周期关系图。
Fragments 的类别
系统内置了三种Fragments ,这三种Fragments 分别有不同的应用场景分别为:
DialogFragment
对话框式的Fragments,可以将一个fragments 对话框并到activity 管理的fragments back stack 中,允许用户回到一个前曾摒弃fragments.
ListFragments
类似于ListActivity 的效果,并且还提供了ListActivity 类似的onListItemCLick和setListAdapter等功能。
PreferenceFragments
类似于PreferenceActivity .可以创建类似IPAD的设置界面。

android Fragments 详解七:fragement 示例
下例中实验了上面所讲的所有内容。此例有一个 activity,其含有两个 fragment。一个显示莎士比亚剧的播放曲目,另一个显示选中曲目的摘要。此例还演示了如何跟据屏幕大小配置 fragment。
主 activity 创建 layout。
@Override
protectedvoid onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.fragment_layout);
}主 activity 的 layoutxml 文档
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent">
<fragment android:id="@+id/titles" android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_width="0px" android:layout_height="match_parent" />
<FrameLayout android:id="@+id/details" android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_width="0px" android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="?android:attr/detailsElementBackground" />
</LinearLayout>系统在 activity 加载此 layout 时初始化 TitlesFragment(用于显示标题列表), TitlesFragment 的右边是一个 FrameLayout,用于存放显示摘要的 fragment,但是现在它还是空的, fragment 只有当用户选择了一项标题后,摘要 fragment 才会被放到 FrameLayout 中。
然而,并不是所有的屏幕都有足够的宽度来容纳标题列表和摘要。所以,上述 layout 只用于横屏,现把它存放于 ret/layout-land/fragment_layout.xml。
之外,当用于竖屏时,系统使用下面的 layout,它存放于 ret/layout/fragment_layout.xml:
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent">
<fragment android:id="@+id/titles"
android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" />
</FrameLayout>这个 layout 只包含 TitlesFragment。这表示当使用竖屏时,只显示标题列表。当用户选中一项时,程序会启动一个新的 activity 去显示摘要,而不是加载第二个 fragment。
下一步,你会看到 Fragment 类的实现。第一个是 TitlesFragment,它从 ListFragment 派生,大部分列表的功能由 ListFragment 提供。
当用户选择一个 Title 时,代码需要做出两种行为,一种是在同一个 activity 中显示创建并显示摘要 fragment,另一种是启动一个新的 activity。
public static class TitlesFragment extends ListFragment {
boolean mDualPane;
int mCurCheckPosition = 0;
@Override
public void onActivityCreated(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onActivityCreated(savedInstanceState);
// Populate list with our static array of titles.
setListAdapter(new ArrayAdapter<String>(getActivity(),
android.R.layout.simple_list_item_activated_1, Shakespeare.TITLES));
// Check to see if we have a frame in which to embed the details
// fragment directly in the containing UI.
View detailsFrame = getActivity().findViewById(R.id.details);
mDualPane = detailsFrame != null && detailsFrame.getVisibility() == View.VISIBLE;
if (savedInstanceState != null) {
// Restore last state for checked position.
mCurCheckPosition = savedInstanceState.getInt("curChoice", 0);
}
if (mDualPane) {
// In dual-pane mode, the list view highlights the selected item.
getListView().setChoiceMode(ListView.CHOICE_MODE_SINGLE);
// Make sure our UI is in the correct state.
showDetails(mCurCheckPosition);
}
}
@Override
public void onSaveInstanceState(Bundle outState) {
super.onSaveInstanceState(outState);
outState.putInt("curChoice", mCurCheckPosition);
}
@Override
public void onListItemClick(ListView l, View v, int position, long id) {
showDetails(position);
}
/**
* Helper function to show the details of a selected item, either by
* displaying a fragment in-place in the current UI, or starting a
* whole new activity in which it is displayed.
*/
void showDetails(int index) {
mCurCheckPosition = index;
if (mDualPane) {
// We can display everything in-place with fragments, so update
// the list to highlight the selected item and show the data.
getListView().setItemChecked(index, true);
// Check what fragment is currently shown, replace if needed.
DetailsFragment details = (DetailsFragment)
getFragmentManager().findFragmentById(R.id.details);
if (details == null || details.getShownIndex() != index) {
// Make new fragment to show this selection.
details = DetailsFragment.newInstance(index);
// Execute a transaction, replacing any existing fragment
// with this one inside the frame.
FragmentTransaction ft = getFragmentManager().beginTransaction();
ft.replace(R.id.details, details);
ft.setTransition(FragmentTransaction.TRANSIT_FRAGMENT_FADE);
ft.commit();
}
} else {
// Otherwise we need to launch a new activity to display
// the dialog fragment with selected text.
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setClass(getActivity(), DetailsActivity.class);
intent.putExtra("index", index);
startActivity(intent);
}
}第二个 fragment, DetailsFragment 显示被选择的 Title 的摘要:
public static class DetailsFragment extends Fragment {
/**
* Create a new instance of DetailsFragment, initialized to
* show the text at ''index''.
*/
public static DetailsFragment newInstance(int index) {
DetailsFragment f = new DetailsFragment();
// Supply index input as an argument.
Bundle args = new Bundle();
args.putInt("index", index);
f.setArguments(args);
return f;
}
public int getShownIndex() {
return getArguments().getInt("index", 0);
}
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
if (container == null) {
// We have different layouts, and in one of them this
// fragment''s containing frame doesn''t exist. The fragment
// may still be created from its saved state, but there is
// no reason to try to create its view hierarchy because it
// won''t be displayed. Note this is not needed -- we could
// just run the code below, where we would create and return
// the view hierarchy; it would just never be used.
return null;
}
ScrollView scroller = new ScrollView(getActivity());
TextView text = new TextView(getActivity());
int padding = (int)TypedValue.applyDimension(TypedValue.COMPLEX_UNIT_DIP,
4, getActivity().getResources().getDisplayMetrics());
text.setPadding(padding, padding, padding, padding);
scroller.addView(text);
text.setText(Shakespeare.DIALOGUE[getShownIndex()]);
return scroller;
}
}如果当前的 layout 没有 R.id.detailsView(它被用于 DetailsFragment 的容器),那么程序就启动 DetailsActivity 来显示摘要。
下面是 DetailsActivity,它只是简单地嵌入 DetailsFragment 来显示摘要。
public static class DetailsActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
if (getResources().getConfiguration().orientation
== Configuration.ORIENTATION_LANDSCAPE) {
// If the screen is now in landscape mode, we can show the
// dialog in-line with the list so we don''t need this activity.
finish();
return;
}
if (savedInstanceState == null) {
// During initial setup, plug in the details fragment.
DetailsFragment details = new DetailsFragment();
details.setArguments(getIntent().getExtras());
getFragmentManager().beginTransaction().add(android.R.id.content, details).commit();
}
}
}注意这个 activity 在检测到是竖屏时会结束自己,于是主 activity 会接管它并显示出 TitlesFragment 和 DetailsFragment。这可以在用户在竖屏时显示在 TitleFragment,但用户旋转了屏幕,使显示变成了横屏。
原文链接: http://blog.csdn.net/nkmnkm/article/details/7197255

android Fragments详解三:实现Fragment的界面
为fragment添加用户界面
fragment一般作为activity的用户界面的一部分,把它自己的layout嵌入到activity的layout中。 一个
要为fragment提供layout,你必须实现onCreateView()回调方法,然后在这个方法中返回一个View对象,这个对象是fragment的layout的根。
注:如果你的fragment是从ListFragment中派生的,就不需要实现onCreateView()方法了,因为默认的实现已经为你返回了ListView控件对象。
要从onCreateView()方法中返回layout对象,你可以从layoutxml中生成layout对象。为了帮助你这样做,onCreateView()提供了一个LayoutInflater对象。
举例:以下代码展示了一个Fragment的子类如何从layoutxml文件example_fragment.xml中生成对象。
publicstaticclassExampleFragmentextendsFragment{
@Override
publicViewonCreateView(LayoutInflaterinflater,ViewGroupcontainer,BundlesavedInstanceState){
//Inflate the layout for this fragment
returninflater.inflate(R.layout.example_fragment,container,false);
}
}
onCreateView()参数中的container是存放fragment的layout的ViewGroup对象。savedInstanceState参数是一个Bundle,跟activity的onCreate()中Bundle差不多,用于状态恢复。但是fragment的onCreate()中也有Bundle参数,所以此处的Bundle中存放的数据与onCreate()中存放的数据还是不同的。至于详细信息,请参考“操控fragment的生命周期”一节。
Inflate()方法有三个参数:
1layout的资源ID。
2存放fragment的layout的ViewGroup。
3布尔型数据表示是否在创建fragment的layout期间,把layout附加到container上(在这个例子中,因为系统已经把layout插入到container中了,所以值为false,如果为true会导至在最终的layout中创建多余的ViewGroup(这句我看不明白,但我翻译的应该没错))。
现在你看到如何为fragment创建layout了,下面讲述如何把它添加到activity中。
把fragment添加到activity
一般情况下,fragment把它的layout作为activitiy的loyout的一部分合并到activity中,有两种方法将一个fragment添加到activity中:
方法一:在activity的layoutxml文件中声明fragment
如下代码,一个activity中包含两个fragment:
<?xmlversion="1.0"encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayoutxmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<fragmentandroid:name="com.example.news.ArticleListFragment"
android:id="@+id/list"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"/>
<fragmentandroid:name="com.example.news.ArticleReaderFragment"
android:id="@+id/viewer"
android:layout_weight="2"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"/>
</LinearLayout>
<fragment>中声明一个fragment。
当系统创建上例中的layout时,它实例化每一个fragment,然后调用它们的onCreateView()方法,以获取每个fragment的layout。系统把fragment返回的view对象插入到<fragment>元素的位置,直接代替<fragment>元素。
注:每个fragment都需要提供一个ID,系统在activity重新创建时用它来恢复fragment们,你也可以用它来操作fragment进行其它的事物,比如删除它。有三种方法给fragment提供ID:
1 为android:id属性赋一个数字。
2 为android:tag属性赋一个字符串。
3如果你没有使用上述任何一种方法,系统将使用fragment的容器的ID。
方法二:在代码中添加fragment到一个ViewGroup
这种方法可以在运行时,把fragment添加到activity的layout中。你只需指定一个要包含fragment的ViewGroup。
为了完成fragment的事务(比如添加,删除,替换等),你必须使用FragmentTransaction的方法。你可以从activity获取到FragmentTransaction,如下:
FragmentManagerfragmentManager =getFragmentManager()
FragmentTransactionfragmentTransaction =fragmentManager.beginTransaction();
然后你可以用add()方法添加一个fragment,它有参数用于指定容纳fragment的ViewGroup。如下:
ExampleFragmentfragment =newExampleFragment();
fragmentTransaction.add(R.id.fragment_container,fragment);
fragmentTransaction.commit();
Add()的第一个参数是容器ViewGroup,第二个是要添加的fragment。一旦你通过FragmentTransaction对fragment做出了改变,你必须调用方法commit()提交这些改变。
不仅在无界面的fragment中,在有界面的fragment中也可以使用tag来作为为一标志,这样在需要获取fragment对象时,要调用findFragmentTag()。
添加一个没有界面的fragment
上面演示了如何添加fragment来提供界面,然而,你也可以使用fragment为activity提供后台的行为而不用显示fragment的界面。
要添加一个没有界面的fragment,需在activity中调用方法add(Fragment,String)(它支持用一个唯一的字符串做为fragment的”tag”,而不是viewID)。这样添加的fragment由于没有界面,所以你在实现它时不需调用实现onCreateView()方法。
使用tag字符串来标识一个fragment并不是只能用于没有界面的fragment上,你也可以把它用于有界面的fragment上,但是,如果一个fragment没有界面,tag字符串将成为它唯一的选择。获取以tag标识的fragment,需使用方法findFragmentByTab()。
原文链接: http://blog.csdn.net/nkmnkm/article/details/7171697
我们今天的关于android – 将OSMDroid与Fragments集成和android集成chromium的分享已经告一段落,感谢您的关注,如果您想了解更多关于Android Fragment FragmentTabHost 问题、Android Fragments 详细使用、android Fragments 详解七:fragement 示例、android Fragments详解三:实现Fragment的界面的相关信息,请在本站查询。
本文标签:



![[转帖]Ubuntu 安装 Wine方法(ubuntu如何安装wine)](https://www.gvkun.com/zb_users/cache/thumbs/4c83df0e2303284d68480d1b1378581d-180-120-1.jpg)

