这篇文章主要围绕CSS:布局-水平垂直居中和css水平垂直居中的几种方法展开,旨在为您提供一份详细的参考资料。我们将全面介绍CSS:布局-水平垂直居中的优缺点,解答css水平垂直居中的几种方法的相关问
这篇文章主要围绕CSS:布局 - 水平垂直居中和css水平垂直居中的几种方法展开,旨在为您提供一份详细的参考资料。我们将全面介绍CSS:布局 - 水平垂直居中的优缺点,解答css水平垂直居中的几种方法的相关问题,同时也会为您带来-水平居中、垂直居中、水平垂直居中、ccs 之经典布局(一)(水平垂直居中)、css — 定位、背景图、水平垂直居中、CSS 介绍、什么是 CSS、为什么我们使用 CSS 以及 CSS 如何描述 HTML 元素的实用方法。
本文目录一览:- CSS:布局 - 水平垂直居中(css水平垂直居中的几种方法)
- -水平居中、垂直居中、水平垂直居中
- ccs 之经典布局(一)(水平垂直居中)
- css — 定位、背景图、水平垂直居中
- CSS 介绍、什么是 CSS、为什么我们使用 CSS 以及 CSS 如何描述 HTML 元素

CSS:布局 - 水平垂直居中(css水平垂直居中的几种方法)
1. 绝对定位 + 负 Margin
原理:首先利用 absolute 定位把容器块 左顶角 对准浏览器中心,然后再使用 负 margin 把容器块向左移动自身宽度的一半,向上移动自身高度的一半,即可以把容器块的中心移到浏览器中心。
优点:兼容性好
缺点:需要知道宽高,不够灵活
.container {
width: 600px;
height: 400px;
position: absolute;
left: 50%;
top: 50%;
margin-left: -300px; /* 宽度的一半 */
margin-top: -200px; /* 高度的一半 */
}2. 绝对定位 + Transform
原理:首先利用 absolute 定位把容器块 左顶角 对准浏览器中心,然后再使用 CSS3 transform 的 translate(x,y) 把容器块向左(x)移动自身宽度的一半,向上(y)移动自身高度的一半,即可以把容器块的中心移到浏览器中心。
优点:不需要知道宽高,灵活
缺点,兼容不好,在移动设备上建议使用
.container {
width: 600px;
height: 400px;
position: absolute;
left: 50%;
top: 50%;
transform: translate(-50%, -50%); /* 自身尺寸的一半 */
}3. 绝对定位 + 自动 Margin
原理:浏览器自动计算绝对定位的容器块上下左右外边距。
优点:灵活切兼容性好(IE8+)
缺点:适用于本身有尺寸的元素(比如图片),对于段落等必须显式设置其宽高
.container {
width: 600px;
height: 400px;
position: absolute;
top: 0;
right: 0;
bottom: 0;
left: 0;
margin: auto;
}4. CSS3 Flexbox
优点:不需要知道宽高
缺点:兼容性不好,在移动设备上建议使用
.container {
display: -webkit-flex;
display: -moz-flex;
display: -ms-flex;
display: -o-flex;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}5. Table display
优点:兼容性好
缺点:增加了无用的 HTML 结构
.vertical-wrapper {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
display: table;
.vertical {
display: table-cell;
vertical-align: middle;
& > * {
vertical-align: middle;
}
span {
display: inline-block;
}
img {
display: inline-block;
}
}
&.center {
.vertical {
text-align: center;
}
}
}
-水平居中、垂直居中、水平垂直居中
1、水平居中
水平居中可分为行内元素水平居中和块级元素水平居中
1.1 行内元素水平居中
这里行内元素是指文本text、图像img、按钮超链接等,只需给父元素设置text-align:center即可实现。
.center{
text-align:center;
}
<div>水平居中</div>
1.2 块级元素水平居中
-
定宽块级元素水平居中
只需给需要居中的块级元素加margin:0 auto即可,但这里需要注意的是,这里块状元素的宽度width值一定要有.center{
width:200px; margin:0 auto; } <div>水平居中</div> -
不定宽块级元素水平居中
不定宽,即块级元素宽度不固定
方法1:设置table通过给要居中显示的元素,设置display:table,然后设置margin:0 auto来实现
.center{ display:table; margin:0 auto; border:1px solid red; } <div>水平居中</div>方法2:设置inline-block(多个块状元素)
子元素设置inline-block,同时父元素设置text-align:center.center{ text-align:center; } .inlineblock-div{ display:inline-block; } <div> <div>1</div> <div>2</div> </div>方法3:设置flex布局
只需把要处理的块状元素的父元素设置display:flex,justify-content:center;.center{ display:flex; justify-content:center; } <div> <div>1</div> <div>2</div> </div>方法4:position + 负margin;
方法5:position + margin:auto;
方法6:position + transform;注:这里方法4、5、6同下面垂直居中一样的道理,只不过需要把top/bottom改为left/right,在垂直居中部分会详细讲述。
2、垂直居中
2.1 单行文本垂直居中
- 设置paddingtop=paddingbottom;或
- 设置line-height=height;
2.2 多行文本垂直居中
通过设置父元素table,子元素table-cell和vertical-align
vertical-align:middle的意思是把元素放在父元素的中部
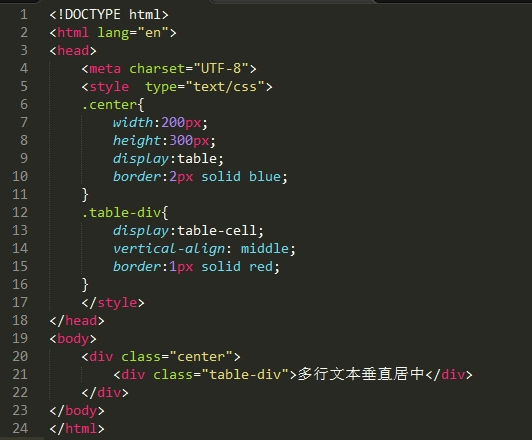

2.3 块级元素垂直居中
方法1:flex布局
在需要垂直居中的父元素上,设置display:flex和align-items:center
要求:父元素必须显示设置height值
显示效果:
方法2:利用position和top和负margin(需知宽高)
1、设置元素为absolute/relative/fixed
2、margin=负一半
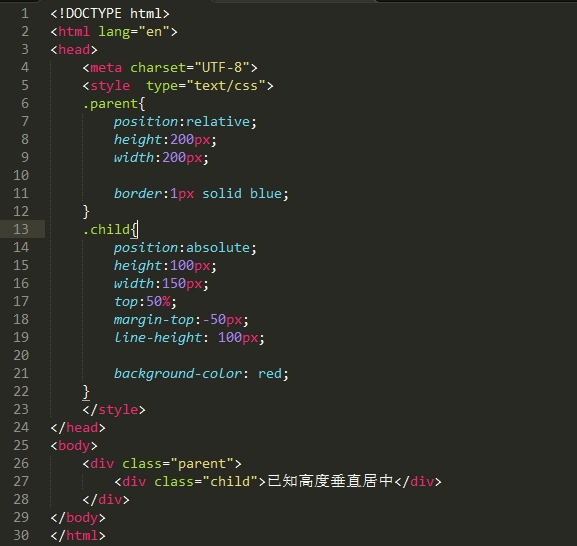
效果如下:
方法3:利用position和top/bottom和margin:auto(注意不是margin:0 auto)
1、position:absolute/relative/fixed
2、top/bottom:0
3、margin:auto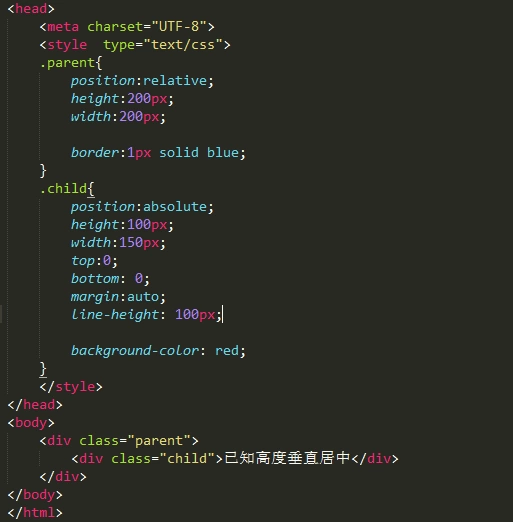
效果如下: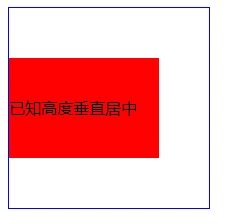
方法4:利用position和top和transform
transform中translate偏移的百分比就是相对于元素自身的尺寸而言的。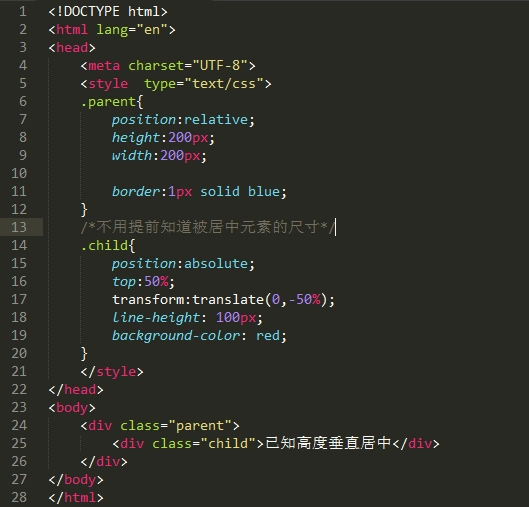
效果如下: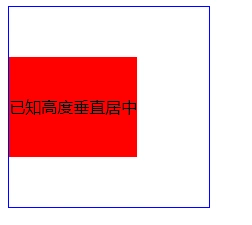
注:
- 上述的块级垂直居中方法,稍加改动,即可成为块级水平居中方法,如top/bottom换成left/right
- transform方法,可用于未知元素大小的居中
3、水平垂直居中
方法1:绝对定位+margin:auto
div{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background: green;
position:absolute;
left:0;
top: 0;
bottom: 0;
right: 0;
margin: auto;
}
方法2:绝对定位+负margin
div{
width:200px;
height: 200px;
background:green;
position: absolute;
left:50%;
top:50%;
margin-left:-100px;
margin-top:-100px;
}
方法3:绝对定位+transform
div{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background: green;
position:absolute;
left:50%; /* 定位父级的50% */
top:50%;
transform: translate(-50%,-50%); /*自己的50% */
}
方法4:flex布局
.box{
height:600px;
display:flex;
justify-content:center; //子元素水平居中
align-items:center; //子元素垂直居中
/* aa只要三句话就可以实现不定宽高水平垂直居中。 */
}
.box>div{
background: green;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
}
方法5:table-cell实现居中
.box{ display:table-cell;
vertical-align:middle;
text-align:center;
width:120px;
height:120px;
background:purple;
}

ccs 之经典布局(一)(水平垂直居中)
经典的 css 布局有以下几种,下面分别用不同的方法进行实现且进行对比。
一、水平居中
水平居中布局指的是当前元素在父级元素的容器中,水平方向上显示的是居中的,有以下几种方式来完成布局:
1、margin:0 auto; text-align:center 实现水平居中。
直接给子元素加上 margin:0 auto; text-align:center 来实现。实际中用的最多,但有一个小问题就是如果子元素里有文本内容,文本内容也会居中。
2、display:table 或者是 display:inline-block 配合 margin 来实现
3、相对定位实现居中
4、绝对定位实现居中,使用绝对定位有一点就是父元素要加上相对定位
5、flex 实现水平居中
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>css实现水平居中</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.box1 {
width: 100%;
height: 100px;
background: beige;
/* position: relative; */
/* display: flex;
flex-direction: column; */
display: flex;
}
.box2 {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background: greenyellow;
/* margin:0 auto; 第1种方式来水平居中
text-align: center; */
/* display: table;
margin:0 auto; 第2种方式来水平居中 */
/* position: relative;
left: 50%;
transform: translateX(-50%); 第3种方式来水平居中 */
/* position: absolute;
left:50%;
transform: translateX(-50%); 第4种方式来水平居中 */
/* align-self: center; 第5种方式来水平居中 */
/* margin: auto; 第5种方式来水平居中,和display:flex配合使用 */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">
<div class="box2">box2</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>二、垂直居中
垂直居中布局指的是当前元素在父级元素的容器中,垂直方向显示是居中的,有以下几种方式来完成布局:
1、table-cell 和 vertical-align 属性配合使用
给父元素添加 display:table-cell; 显示的效果等同于表格中的单元格(单元格的内容允许水平或者是垂直方向的对齐设置)
vertical-align:center; 垂直方向上的居中
2、绝对定位和 transform 属性配合使用
这个要给父级一个相对定位
3、flex 实现垂直居中
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>垂直居中</title>
<style>
* {
padding:0;
margin: 0;
}
.box1{
width: 100px;
height: 500px;
background-color: rgb(223, 223, 241);
/* display: table-cell;
vertical-align: middle; 第1种方法实现垂直居中 */
/* position: relative; */
/* display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
justify-content: center; 第3种方法实现垂直居中 */
}
.box2{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background: greenyellow;
position: absolute;
/* top:50%;
transform: translateY(-50%); 第2种方法实现垂直居中 */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">
<div class="box2">box2</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>三、居中布局
居中布局就是即水平居中又垂直居中
1、绝对定位加上 transform 实现居中布局
要给父级加上相对定位,还有一点问题就是兼容性的问题
要给父级元素加上:position:relative;
子元素加上:position:absolute;top:50%;left:50% ;transform: translate (-50%,-50%);
2、table+margin 来实现水平居中,table-cell 和 vertical-align 实现垂直居中
有一点问题就是有可能会影响整体的布局效果没有绝对定位好
要给父级元素加上:display:table-cell;vertical-align:middle;
子元素加上:display:table;margin:0 auto;
3、flex 来实现水平垂直居中,它的作用最大
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>水平垂直居中</title>
<style>
*{
margin:0;
padding:0;
}
.box1{
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
background-color: greenyellow;
/* position: relative; 第1种水平垂直居中方式*/
/* display: table-cell; 第2种水平垂直居中方式
vertical-align: middle;
*/
/* display: flex;
justify-content: center; 第3种水平垂直居中方式 */
}
.box2{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: pink;
/* position: absolute; 第1种水平垂直居中方式
top:50%;
left: 50%;
transform: translate(-50%,-50%); */
/* display: table; 第2种水平垂直居中方式
margin: 0 auto; */
/* align-self: center; 第3种水平垂直居中方式 */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">
<div class="box2">box2</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>

css — 定位、背景图、水平垂直居中
[TOC]
1. 定位
position:static | relative | absolute | fixed;
static 静态定位
relative 相对
absolute 绝对
fixed 固定
1.1 静态定位
静态定位意味着 “元素默认显示文档流的位置”。没有任何变化。
1.2 相对定位 relative
1. 特征:
- 给一个标准文档流下的盒子单纯的设置相对定位,与普通的盒子没有任何区别
- 留 “坑”,会影响页面布局
2. 作用:
- 1. 用于微调元素
- 2. 做 “子绝父相” 布局方案的参考
3. 参考点:
- 以原来的盒子为参考点
4. 相对定位的值:top 、bottom 、left 、right
<style>
.box {
width: 500px;
height: 600px;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
.box .a {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: red;
}
.box .b {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: green;
position: relative;
top: 30px;
left: 50px;
}
.box .c {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: blue;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="box">
<div class="a"></div>
<div class="b"></div>
<div class="c"></div>
</div>
1.3 绝对定位 absolute
1. 参考点:
判断是否有定位(相对定位,绝对定位,固定定位)的祖先盒子进行定位:
- 1. 如果没有定位的祖先盒子,以 body 为参考点
- 2. 如果单独设置了一个盒子为绝对定位:
- 1. 以 top 描述,它的参考点是以 body 的(0,0)为参考点
- 2. 以 bottom 描述,它的参考点是以浏览器的左下角为参考点
2. 子绝父相
以最近的父辈元素的左上角为参考点进行定位
3. 特征:
- 1. 脱标
- 2. 压盖
- 3. 子绝父相
<style>
.box {
width: 500px;
height: 600px;
border: 1px solid #000;
position: relative;
float: right;
}
.box .a {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: red;
}
.box .b {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: green;
position: absolute;
top: 20px;
left: 20px;
}
.box .c {
width: 300px;
height: 200px;
background-color: blue;
}
</style>
浮动和绝对定位的特征:
<style>
/*span {*/
/*background-color: red;*/
/*!*float: left;*!*/
/*position: absolute;*/
/*width: 200px;*/
/*height: 60px;*/
/*}*/
.container{
width: 1226px;
height: 100px;
margin: 0 auto;
background-color: #000;
}
.logo{
width: 55px;
height: 55px;
background-color: #ff6700;
float: left;
margin-top: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<span>
mjj
</span>
<div class="container">
<div class="logo"></div>
</div>
</body>
1.4 固定定位 fixed
它跟绝对定位基本相似,只有一个主要区别:绝对定位固定元素是相对于 html 根元素或其最近的定位祖先元素,而固定定位固定元素则是相对于浏览器视口本身。这意味着你可以创建固定的有用的网页效果,比如固定导航栏、回到顶部按钮,小广告等。
1. 特征:
- 1. 脱标
- 2. 固定不变
- 3. 提高层级
2. 参考点:
以浏览器的左上角为参考点
<style>
body{
padding-top: 100px;
}
.active{
position: relative;
background-color: yellowgreen;
}
.fix{
width: 100%;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
position: fixed;
top: 0;
left: 0;
}
</style>
<body>
<p>MJJwusir</p>
<p>wusir</p>
<p class="active">YAOwusir</p>
<div class="fix">固定不变</div>
<p>wusir</p>
<p>wusir</p>
</body>
1.5 z-index
1.z-index 只应用在定位的元素,默认 z-index:auto;(auto 相当于 0)
2.z-index 取值为整数,数值越大,它的层级越高
3. 如果元素设置了定位,没有设置 z-index,那么谁写在最后面的,表示谁的层级越高。(与标签的结构有关系)
4. 从父现象。通常布局方案我们采用子绝父相,比较的是父元素的 z-index 值,哪个父元素的 z-index 值越大,表示子元素的层级越高。
/*从父现象*/
<style>
.box1 {
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
width: 200px;
height: 60px;
border: 2px solid blue;
background-color: #000;
z-index: 10;
}
.box2 {
position: absolute;
top: 20px;
left: 0;
width: 200px;
height: 60px;
border: 2px solid red;
background-color: greenyellow;
z-index: 6;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="father1" style="position: relative;z-index: 2;">
<span class="box1"></span>
</div>
<div class="father2" style="position: relative;z-index: 3;">
<div class="box2"> </div>
</div>
</body>
2. 背景图
1. 背景图属性
- 1.background-image:url ("图片地址"); 给一个元素设置一个或多个背景图像
- 2.background-repeat:
- 定义背景图像的重复方式。 背景图像可以沿着水平轴,垂直轴,两个轴重复,或者根本不重复。
- 属性值:
- repeat 默认值。表示背景图水平和垂直方向都平铺
- no-repeat 表示背景图水平和处置方向都不平铺
- repeat-x 表示背景图只有水平方向上平铺
- repeat-y 表示背景图只有垂直方向上平铺
- 3.background-position
- 表示背景图定位初始位置。
background-position是background-position-x和background-position-y的综合属性。如果想使用background-position属性,那么必须先指定background-image属性。 - 语法:
- 1.background-position: 值 1 值 2;
- 2.background-position:position position;
- 表示背景图定位初始位置。
<style>
.bg{
width: 1200px;
height:1200px;
border: 1px solid #000;
/*设置背景图*/
background-image: url("xiaohua.jpg");
background-repeat: no-repeat;
/*调整背景图的位置*/
/*background-position: -164px -106px;*/
background-position: center center;
color: green;
font-weight: 700;
font-size: 30px;
}
</style>
2.CSS Sprite 雪碧图
CSS 雪碧图技术:即 CSS Sprite, 也有人叫它 CSS 精灵图,是一种图像拼合技术。该方法是将多个小图标和背景图像合并到一张图片上,然后利用 css 的背景定位来显示需要显示的图片部分。
使用雪碧图的使用场景:
-
静态图片,不随用户信息的变化而变化
-
小图片,图片容量比较小 (2~3k)
-
加载量比较大
一些大图不建议制作雪碧图
优点:
- 有效的减少 HTTP 请求数量
- 加速内容显示
雪碧图的实现原理:
- 它通过 css 的背景属性的 backrground-position 的来控制雪碧图的显示。
- 控制一个层,可显示的区域范围大消息,通过一个窗口,进行背景图的移动。
<style>
.swiper {
width: 100%;
height: 460px;
}
.container {
width: 1226px;
position: relative;
margin: 0 auto;
}
.swiper span {
display: inline-block;
width: 41px;
height: 69px;
background: url("icon-slides.png") no-repeat 0 0;
position: absolute;
margin-top: -34px;
top: 50%;
cursor: pointer;
}
.swiper span.prev {
background-position: -83px 0;
left: 234px;
}
.swiper span.next {
background-position: -124px 0;
right: 0;
}
.swiper span.prev:hover{
background-position: 0 0;
}
.swiper span.next:hover{
background-position: -42px 0;
}
</style>
<div class="swiper">
<div class="container">
<span class="prev"></span>
<span class="next"></span>
</div>
</div>
3. 水平垂直居中
3.1 行内元素水平居中显示
1. 第一种方式:line-height+text-align
p {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background: #666;
color: #fff;
line-height: 200px;
text-align: center;
}
2. 第二种方式:给父元素设置 display:table-cell;, 并且设置 vertical-align:middle
.box{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
border: 1px solid #000;
display: table-cell;
vertical-align: middle;
text-align: center;
}
3.2 块级元素水平垂直居中
1. 方法一:position+margin
<style>
.father{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: red;
position: relative;
}
.child{
position: absolute;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: green;
margin: auto;
left: 0;
right: 0;
top: 0;
bottom: 0;
}
</style>
<div class="father">
<div class="child">我是个居中的盒子</div>
</div>
2. 方法二:display:table-cell
<style type="text/css">
.father{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: red;
display: table-cell;
vertical-align: middle;
text-align: center;
}
.child{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: green;
display: inline-block;
vertical-align: middle;
}
</style>
<div class="father">
<div class="child">我是个居中的盒子</div>
</div>
3. 第三种:纯 position
<style>
.father{
width: 500px;
height: 300px;
background-color: red;
position: relative;
}
.child{
/*如何让一个绝对定位的垂直居中: top设置50%,margin-top设置当前盒子的一半,并且是负*/
position: absolute;
width: 100px;
height: 140px;
background-color: green;
left: 50%;
margin-left: -50px;
top: 50%;
margin-top: -70px;
}
</style>
<div class="father">
<div class="child">我是个居中的盒子</div>
</div>

CSS 介绍、什么是 CSS、为什么我们使用 CSS 以及 CSS 如何描述 HTML 元素

CSS是什么?
CSS 代表层叠样式表
CSS 描述了 HTML 元素如何在屏幕、纸张或其他媒体上显示
CSS 节省了大量工作。它可以同时控制多个网页的布局
外部样式表存储在 CSS 文件中
为什么我们使用CSS?
CSS 用于定义网页的样式,包括设计、布局以及针对不同设备和屏幕尺寸的显示变化。
示例
身体{
背景颜色:浅蓝色;
}
h1 {
白颜色;
文本对齐:居中;
}
p {
字体系列:verdana;
字体大小:20px;
}
CSS解决了一个大问题
HTML 从来没有打算包含用于格式化网页的标签!
HTML 的创建是为了描述网页的内容,例如:
这是一个标题
这是一个段落。
CSS 节省了大量工作!
样式定义通常保存在外部.
CSS 语法
CSS 规则由选择器和声明块组成。
h1 {颜色:蓝色;字体大小:12px;}
选择器指向您想要设置样式的 HTML 元素。
声明块包含一个或多个以分号分隔的声明。
每个声明都包含一个 CSS 属性名称和一个值,以冒号分隔。
示例
p {
红色;
文本对齐:居中;
}
示例解释
p 是 CSS 中的选择器(它指向您想要设置样式的 HTML 元素:
)。
颜色是一个属性,红色是属性值
text-align 是一个属性,center 是属性值
CSS 选择器
CSS 选择器用于“查找”(或选择)您想要设置样式的 HTML 元素。
我们可以将 CSS 选择器分为五类:
简单选择器(根据名称、id、类选择元素)
组合选择器(根据元素之间的特定关系选择元素)
伪元素选择器(选择元素的一部分并为其设置样式)
CSS 元素选择器
元素选择器根据元素名称选择 HTML 元素。
示例
p {
文本对齐:居中;
红色;
}
以上就是CSS 介绍、什么是 CSS、为什么我们使用 CSS 以及 CSS 如何描述 HTML 元素的详细内容,更多请关注php中文网其它相关文章!
今天关于CSS:布局 - 水平垂直居中和css水平垂直居中的几种方法的分享就到这里,希望大家有所收获,若想了解更多关于-水平居中、垂直居中、水平垂直居中、ccs 之经典布局(一)(水平垂直居中)、css — 定位、背景图、水平垂直居中、CSS 介绍、什么是 CSS、为什么我们使用 CSS 以及 CSS 如何描述 HTML 元素等相关知识,可以在本站进行查询。
本文标签:



![[转帖]Ubuntu 安装 Wine方法(ubuntu如何安装wine)](https://www.gvkun.com/zb_users/cache/thumbs/4c83df0e2303284d68480d1b1378581d-180-120-1.jpg)

