以上就是给各位分享c–如何在boost图库中使用带有捆绑属性图的`randomize_property`?,其中也会对boost图形库进行解释,同时本文还将给你拓展2021-11-10:O(1)时间插
以上就是给各位分享c – 如何在boost图库中使用带有捆绑属性图的`randomize_property`?,其中也会对boost图形库进行解释,同时本文还将给你拓展2021-11-10:O(1) 时间插入、删除和获取随机元素。实现RandomizedSet 类:RandomizedSet() 初始化 RandomizedSet 对象。bool insert(in、Android coredomain 如何使用自定义的 property type?、Android 属性property_get/property_set、Android 属性之 build.prop,及 property_get/property_set等相关知识,如果能碰巧解决你现在面临的问题,别忘了关注本站,现在开始吧!
本文目录一览:- c – 如何在boost图库中使用带有捆绑属性图的`randomize_property`?(boost图形库)
- 2021-11-10:O(1) 时间插入、删除和获取随机元素。实现RandomizedSet 类:RandomizedSet() 初始化 RandomizedSet 对象。bool insert(in
- Android coredomain 如何使用自定义的 property type?
- Android 属性property_get/property_set
- Android 属性之 build.prop,及 property_get/property_set

c – 如何在boost图库中使用带有捆绑属性图的`randomize_property`?(boost图形库)
只有一个函数原型,我找不到一个有效的例子.
我尝试了几件事,但它无法编译.
这是一个简单的源代码:
#include <ctime>
#include <iostream>
#include <boost/graph/random.hpp>
#include <boost/graph/adjacency_list.hpp>
#include <boost/random/linear_congruential.hpp>
#include <boost/graph/erdos_renyi_generator.hpp>
#include <boost/graph/graphviz.hpp>
using namespace std;
using namespace boost;
struct EdgeProperty {
int cost;
};
typedef adjacency_list<
setS,// disallow parallel edge
vecS,undirectedS,no_property,EdgeProperty
> Graph;
typedef erdos_renyi_iterator<minstd_rand,Graph> ERGen;
int main(int argc,const char *argv[])
{
minstd_rand gen(time(0));
assert(argc >= 3);
int n = atoi(argv[1]);
double p = atof(argv[2]);
Graph g(ERGen(gen,n,p),ERGen(),n);
// randomize_property< [unkNown class] >(g,gen);
return 0;
}
更新:@phooji提供的代码有效.我为EdgeProperty添加了一个默认构造函数,我的代码也编译了:
struct EdgeProperty {
EdgeProperty(int x = 0) : cost(x) { }
int cost;
};
原始编译错误发布为gist here,我无法理解.希望有人告诉我这是如何工作的.
解决方法
#include <boost/graph/adjacency_list.hpp>
#include <boost/graph/random.hpp>
#include <boost/random/linear_congruential.hpp>
struct myedge {
myedge(int x) : testme(x) {
}
int testme;
};
typedef boost::adjacency_list<boost::setS,// disallow parallel edge
boost::vecS,boost::undirectedS,boost::no_property,myedge
> mygraph;
int main(int argc,char**argv) {
mygraph g;
// auto pmap = boost::get(&myedge::testme,g);
boost::minstd_rand gen(0);
boost::randomize_property<boost::edge_bundle_t>(g,gen);
return EXIT_SUCCESS; // :)
}
希望有所帮助 – 我没有时间对它进行实际测试,所以如果这不是你想要的,那么道歉.

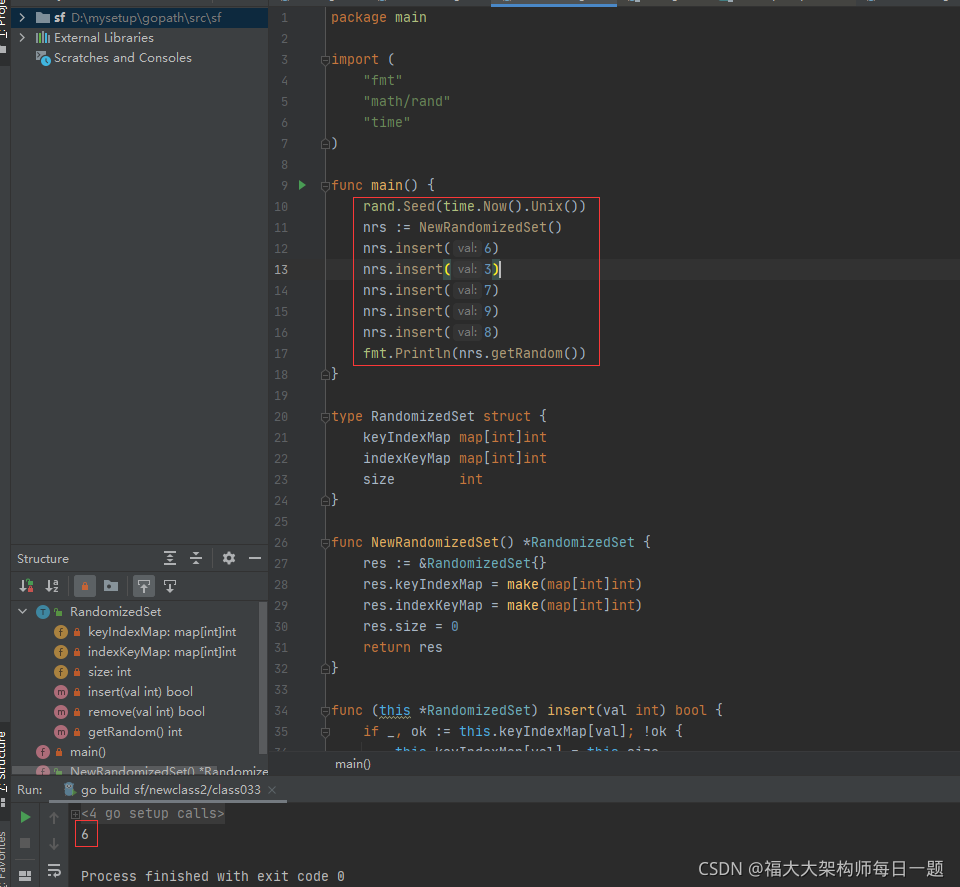
2021-11-10:O(1) 时间插入、删除和获取随机元素。实现RandomizedSet 类:RandomizedSet() 初始化 RandomizedSet 对象。bool insert(in
2021-11-10:O(1) 时间插入、删除和获取随机元素。实现RandomizedSet 类:RandomizedSet() 初始化 RandomizedSet 对象。bool insert(int val) 当元素 val 不存在时,向集合中插入该项,并返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。bool remove(int val) 当元素 val 存在时,从集合中移除该项,并返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。int getRandom() 随机返回现有集合中的一项(测试用例保证调用此方法时集合中至少存在一个元素)。每个元素应该有 相同的概率 被返回。你必须实现类的所有函数,并满足每个函数的 平均 时间复杂度为 O(1) 。力扣380。
答案2021-11-10:
两张哈希表。
v→index。
index→v。
index一定是连续的。
删除中间位置的元素,用最后一个元素顶替。这样index就连续了。
代码用golang编写。代码如下:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"math/rand"
"time"
)
func main() {
rand.Seed(time.Now().Unix())
nrs := NewRandomizedSet()
nrs.insert(6)
nrs.insert(3)
nrs.insert(7)
nrs.insert(9)
nrs.insert(8)
fmt.Println(nrs.getRandom())
}
type RandomizedSet struct {
keyIndexMap map[int]int
indexKeyMap map[int]int
size int
}
func NewRandomizedSet() *RandomizedSet {
res := &RandomizedSet{
}
res.keyIndexMap = make(map[int]int)
res.indexKeyMap = make(map[int]int)
res.size = 0
return res
}
func (this *RandomizedSet) insert(val int) bool {
if _, ok := this.keyIndexMap[val]; !ok {
this.keyIndexMap[val] = this.size
this.indexKeyMap[this.size] = val
this.size++
return true
}
return false
}
func (this *RandomizedSet) remove(val int) bool {
if _, ok := this.keyIndexMap[val]; ok {
deleteIndex := this.keyIndexMap[val]
this.size--
lastIndex := this.size
lastKey := this.indexKeyMap[lastIndex]
this.keyIndexMap[lastKey] = deleteIndex
this.indexKeyMap[deleteIndex] = lastKey
delete(this.keyIndexMap, val)
delete(this.indexKeyMap, lastIndex)
return true
}
return false
}
func (this *RandomizedSet) getRandom() int {
if this.size == 0 {
return -1
}
randomIndex := rand.Intn(this.size)
return this.indexKeyMap[randomIndex]
}执行结果如下:
左神java代码

Android coredomain 如何使用自定义的 property type?
背景
Android 8.1 中引入了 Project Treble 架构,用于将 vendor 下的驱动和 Android system 系统分开,Android system 可以单独升级。SELinux 同样分成了两部分,位于 /system/etc/selinux 下的 platform 部分和位于 /vendor/etc/selinux 下的 vendor 部分。本文分析 Android 大版本升级过程中对 property 增加的一些限制,以及如何绕过这些限制。
Coredomain
哪些是 coredomain?
Coredomain 是 attribute,属于 domain (针对进程) 或者 type (针对对象,如文件等) 的集合。coremain 可以理解为包含 system 下可执行文件和 apps 所运行的 domain 或者说包含所有属于 Android 的 domain。
如何查看?
代码中查看
有两种定义方式:
1. type XXX ..., coredomain ...;
2. typeattribute XXX coredomain;
上面两种方式都是将 XXX 放入到 coredomain 集合中,即 XXX 是属于 coredomain,对 coredomain 配置的权限也会同步给 XXX,同样对 coredomain 的限制也会限制 XXX。
工具查看
Android system/sepolicy 源码下有 sepolicy-analyze 工具,然后需要编译好的 sepolicy 文件,使用下面命令可以查看 coredomain 都包含那些 domain:
sepolicy-analyze 编译好的sepolicy attribute coredomain
{:.warning} 编译好的 policy,手机上可以从这两个地方取:1. /vendor (或者 odm)/etc/selinux/precompiled_sepolicy; 2. /sys/fs/selinux/policy
Android P
新增限制
升级 Android P 后发现 property 新增了一个 neverallow (neverallow 用于限制配置,明确指定不能干什么)。来看下该 neverallow:
#https://cs.android.com/android/platform/superproject/+/android-9.0.0_r11:system/sepolicy/public/property.te;l=314
compatible_property_only(`
# Neverallow coredomain to set vendor properties
neverallow {
coredomain
-init
-system_writes_vendor_properties_violators
} {
property_type
-apexd_prop
-audio_prop
-bluetooth_a2dp_offload_prop
-bluetooth_audio_hal_prop
-bluetooth_prop
-bootloader_boot_reason_prop
-boottime_prop
-bpf_progs_loaded_prop
-config_prop
-cppreopt_prop
-ctl_adbd_prop
-ctl_bootanim_prop
-ctl_bugreport_prop
-ctl_console_prop
-ctl_default_prop
-ctl_dumpstate_prop
-ctl_fuse_prop
-ctl_gsid_prop
-ctl_interface_restart_prop
-ctl_interface_start_prop
-ctl_interface_stop_prop
-ctl_mdnsd_prop
-ctl_restart_prop
-ctl_rildaemon_prop
-ctl_sigstop_prop
-ctl_start_prop
-ctl_stop_prop
-dalvik_prop
-debug_prop
-debuggerd_prop
-default_prop
-device_logging_prop
-dhcp_prop
-dumpstate_options_prop
-dumpstate_prop
-exported2_config_prop
-exported2_default_prop
-exported2_radio_prop
-exported2_system_prop
-exported2_vold_prop
-exported3_default_prop
-exported3_radio_prop
-exported3_system_prop
-exported_bluetooth_prop
-exported_config_prop
-exported_dalvik_prop
-exported_default_prop
-exported_dumpstate_prop
-exported_ffs_prop
-exported_fingerprint_prop
-exported_overlay_prop
-exported_pm_prop
-exported_radio_prop
-exported_secure_prop
-exported_system_prop
-exported_system_radio_prop
-exported_vold_prop
-exported_wifi_prop
-extended_core_property_type
-ffs_prop
-fingerprint_prop
-firstboot_prop
-device_config_activity_manager_native_boot_prop
-device_config_reset_performed_prop
-device_config_boot_count_prop
-device_config_input_native_boot_prop
-device_config_netd_native_prop
-device_config_runtime_native_boot_prop
-device_config_runtime_native_prop
-device_config_media_native_prop
-dynamic_system_prop
-gsid_prop
-heapprofd_enabled_prop
-heapprofd_prop
-hwservicemanager_prop
-last_boot_reason_prop
-system_lmk_prop
-log_prop
-log_tag_prop
-logd_prop
-logpersistd_logging_prop
-lowpan_prop
-lpdumpd_prop
-mmc_prop
-net_dns_prop
-net_radio_prop
-netd_stable_secret_prop
-nfc_prop
-overlay_prop
-pan_result_prop
-persist_debug_prop
-persistent_properties_ready_prop
-pm_prop
-powerctl_prop
-radio_prop
-restorecon_prop
-safemode_prop
-serialno_prop
-shell_prop
-system_boot_reason_prop
-system_prop
-system_radio_prop
-system_trace_prop
-test_boot_reason_prop
-test_harness_prop
-theme_prop
-time_prop
-traced_enabled_prop
-traced_lazy_prop
-vendor_default_prop
-vendor_security_patch_level_prop
-vold_prop
-wifi_log_prop
-wifi_prop
}:property_service set;
'')
可以看到限制的是除了 init 和 system_writes_vendor_properties_violators 的 coredomain, 这些 domains 不能设置上述白名单之外的 property type, 这些属于 AOSP 定义的 types,所以是限制 system domains 不能设置 vendor properties,符合 Prject Treble 设计思想。
如何绕过限制?
由于厂商基本都会:
- 定义新的 property type,用于细粒度控制访问权限,如 platform_app 或者 system_app 设置新的 property,三方 app 可以读;
- coredomain 需要设置 vendor properties。
但现在增加了 neverallow 限制,这些规则在编译阶段就会报错,所以需要想办法绕过限制。
从上面可以看到限制会排除 init 和 system_writes_vendor_properties_violators,init 是 domain,不能满足要求,我们是需要 platform_app 或者 system_app 有权限。看下 system_writes_vendor_properties_violators 的定义:
# All system domains which violate the requirement of not writing vendor
# properties.
# TODO(b/78598545): Remove this once there are no violations
attribute system_writes_vendor_properties_violators;
首先是 attribute,不是具体的 type, 并且从注释上看到,表示 system domains 违反去写 vendor properties 的集合。这个也是 google 用于在升级中故意新增的,用于临时绕过 neverallow 限制。所以,我们可以需要违反 neverallow 的添加上该 attribute。
解决方案为: 为需要违反的 domain 添加 system_writes_vendor_properties_violators。
如要给 platform_app 添加,配置下面规则:
typeattribute platform_app system_writes_vendor_properties_violators;
Android Q
新增限制
google 在 GTS 中新增了一条测试 case:
com.google.android.security.gts.SELinuxHostTest#testNoExemptionsForCoreWritingVendorSysprops
SELinuxHostTest 是在 GTS GtsSecurityHostTestCases.jar 中,使用 JD-GUI 反编译找到 testNoExemptionsForCoreWritingVendorSysprops 方法:
public void testNoExemptionsForCoreWritingVendorSysprops() {
if (this.mFirstApiLevel < 29) { // 使用 firstApi 排除升级的老机型
return;
}
// 是获取有 attribute 是 system_writes_vendor_properties_violators 的 domain
Set<String> types = sepolicyAnalyzeGetTypesAssociatedWithAttribute("system_writes_vendor_properties_violators");
if (!types.isEmpty()) {
List<String> sortedTypes = new ArrayList<String>(types);
Collections.sort(sortedTypes);
fail("Policy exempts core domains from ban on writing vendor system properties: " + sortedTypes); // 不为空,则测试失败
}
}
}
从上面看到: 1)针对的是 Q 新机型; 2)若指定有 system_writes_vendor_properties_violators 的则失败,即不能为 domain 指定 system_writes_vendor_properties_violators。
所有针对 Q 新机型,不能采用 P 绕过方式。
如何绕过限制?
使用现有的 AOSP property type
Neverallow 不能从 domain 进行绕过,只能选择从 property type,即不能定义新的 property,只能使用现有的。这样有两个弊端:
- 不能对权限细粒度控制,只能在现有权限的基础上增加,而不能减少,这样修改的话势必导致权限扩大;
- type 名字选择都是有意义,但现在只能从权限和名字上找到平衡,可能权限满足,但名字意义差太远。
那有没有更好的方式?
定义新的 property type
通过对 neverallow 中的每个 type 分析,发现 extended_core_property_type 是 attribute,而不是具体的 type:
# All properties that are not specific to device but are added from
# outside of AOSP. (e.g. OEM-specific properties)
# These properties are not accessible from device-specific domains
attribute extended_core_property_type;
从注释可以看到,这个 attribute 是 google 专门给厂商保留的,太好了。 但是 “These properties are not accessible from device-specific domains” 表示 device-specific domains 不能访问,来看下是怎么限制的:
# Prevent properties from being read
neverallow {
domain
-coredomain
-appdomain
-vendor_init
} {
core_property_type
extended_core_property_type # it
exported_dalvik_prop
exported_ffs_prop
exported_system_radio_prop
exported2_config_prop
exported2_system_prop
exported2_vold_prop
exported3_default_prop
exported3_system_prop
-debug_prop
-logd_prop
-nfc_prop
-powerctl_prop
-radio_prop
}:file no_rw_file_perms;
可以看到除了 coredomain, appdomain, vendor_init 外都不能访问,那这种方式定义的 property 只能由 coredomain, appdomain 和 vendor_init 来访问。虽然有限制,但是已经能满足大部分需求,如上面提到的规则: platform_app 或者 system_app 设置,三方 apps 去读。
解决方案:为新定义的 property type 指定 extended_core_property_type。
{:.warning} 这种方式 vendor domain 没有权限去读写。
思考
如果有需求是需要 coredomain 和 vendor domain 同时有读写权限,那怎么办?
目前来看,新建 property type 不能满足需求,现有 AOSP 存在的 property type 如果没有限制,也尽量不要使用,防止以后有变动,建议:
1. 业务逻辑上重新设计,尽量避免这种情况出现;
2. 使用 init 或者 vendor_init 代替设置,init 和 vendor_init 权限较高,并且限制较少,如对 init script 中配置自动 setprop 规则。
end
关注公众号,了解更多信息! 

Android 属性property_get/property_set
每个属性都有一个名称和值,他们都是字符串格式。属性被大量使用在Android系统中,用来记录系统设置或进程之间的信息交换。属性是在整个系统中全局可见的。每个进程可以get/set属性。
在系统初始化时,Android将分配一个共享内存区来存储的属性。这些是由“init”守护进程完成的,其源代码位于:device/system/init。“init”守护进程将启动一个属性服务。
属性服务在“init”守护进程中运行。每一个客户端想要设置属性时,必须连接属性服务,再向其发送信息。属性服务将会在共享内存区中修改和创建属性。任何客户端想获得属性信息,可以从共享内存直接读取。这提高了读取性能。客户端应用程序可以调用libcutils中的API函数以GET/SET属性信息。libcutils的源代码位于:device/libs/cutils。API函数是:
int property_get(const char *key, char *value, const char *default_value);
int property_set(const char *key, const char *value);
而libcutils又调用libc中的 __system_property_xxx 函数获得共享内存中的属性。libc的源代码位于:device/system/bionic。
属性服务调用libc中的__system_property_init函数来初始化属性系统的共享内存。当启动属性服务时,将从以下文件中加载默认属性:
/default.prop
/system/build.prop
/system/default.prop
/data/local.prop
属性将会以上述顺序加载。后加载的属性将覆盖原先的值。这些属性加载之后,最后加载的属性会被保持在/data/property中。
特别属性如果属性名称以“ro.”开头,那么这个属性被视为只读属性。一旦设置,属性值不能改变。
如果属性名称以“persist.”开头,当设置这个属性时,其值也将写入/data/property。
如果属性名称以“net.”开头,当设置这个属性时,“net.change”属性将会自动设置,以加入到最后修改的属性名。(这是很巧妙的。 netresolve模块的使用这个属性来追踪在net.*属性上的任何变化。)
属性“ ctl.start ”和“ ctl.stop ”是用来启动和停止服务。
每一项服务必须在/init.rc中定义.系统启动时,与init守护进程将解析init.rc和启动属性服务。一旦收到设置“ ctl.start ”属性的请求,属性服务将使用该属性值作为服务名找到该服务,启动该服务。这项服务的启动结果将会放入“ init.svc.<服务名>“属性中 。客户端应用程序可以轮询那个属性值,以确定结果
可以用命令 setprop ctl.start 服务名 来启动服务
比如
setprop ctl.start wpa_supplicant
setprop ctl.start bootanim
setprop ctl.stop bootanim

Android 属性之 build.prop,及 property_get/property_set
简要分析一下 build.prop 是如何生成的。Android 的 build.prop 文件是在 Android 编译时收集的各种 property(LCD density / 语言 / 编译时间,etc.),编译完成之后,文件生成在 out/target/product/<board>/system/ 目录下。在 Android 运行时可以通过 property_get ()[c/c++ 域] / SystemProperties_get*()[Java 域] 读取这些属性值。
(1)build.prop 的生成是由 make 系统解析 build/core/Makefile 完成。Makefile 中首先定义各种变量,这在下一步执行时会用到。比如:
[cpp] view plaincopy- ...
- PRODUCT_DEFAULT_LANGUAGE="$(calldefault-locale-language,$(PRODUCT_LOCALES))" \
- PRODUCT_DEFAULT_REGION="$(calldefault-locale-region,$(PRODUCT_LOCALES))" \
- ...
(2)Makefile 中调用 build/tools/buildinfo.sh 执行脚本,并输出到 build.prop。Buildinfo.sh 很简单,只是 echo 一些属性,比如:
[cpp] view plaincopy- ...
- echo"ro.product.locale.language=$PRODUCT_DEFAULT_LANGUAGE"
- echo"ro.product.locale.region=$PRODUCT_DEFAULT_REGION"
- ...
ro.product.locale.language/ro.product.locale.region 就是些属性,等号后面是值。
(3)Makefile 中直接把 $(TARGET_DEVICE_DIR)/system.prop 的内容追加到 build.prop 中,还会收集 ADDITIONAL_BUILD_PROPERTIES 中的属性,追加到 build.prop 中。
ADDITIONAL_BUILD_PROPERTIES 又会收集 PRODUCT_PROPERTY_OVERRIDES 中定义的属性,如下:
[cpp] view plaincopy- ADDITIONAL_BUILD_PROPERTIES:= \
- $(ADDITIONAL_BUILD_PROPERTIES)\
- $(PRODUCT_PROPERTY_OVERRIDES)
通过 build.prop 生成过程的分析,可知哪里可以修改原有的属性或加入自己定义属性,那就是 2) buildinfo.sh; 3) system.prop; 4) ADDITIONAL_BUILD_PROPERTIES 或 PRODUCT_PROPERTY_OVERRIDES。
(4)属性(property)都有一个名称和值,他们都是字符串格式,用来记录系统设置或进程之间的信息交换。属性是在整个系统中全局可见的。
在系统初始化时,Android 将分配一个共享内存区来存储的属性。这些是由 “init” 守护进程完成的,“init” 守护进程将启动一个属性服务。任何客户端想获得属性信息,可以从共享内存直接读取。客户端应用程序可以调用 libcutils 中的 API 函数以 GET/SET 属性信息:
int property_get(const char *key, char *value, const char *default_value);
int property_set(const char *key, const char *value);
当启动属性服务时,将从以下文件中加载默认属性:
/default.prop
/system/build.prop
/system/default.prop
/data/local.prop
属性将会以上述顺序加载,后加载的属性将覆盖原先的值。特别属性如果属性名称以 “ro.” 开头,那么这个属性被视为只读属性,比如 ro.mediatek.version.release=ALPS.ICS2.MP.V1 就是指示版本号,应用中用 property_get ("ro.mediatek.version.release", val, "unknown"); 即可用来获得版本信息;属性 “ ctrl.start ” 和 “ ctrl.stop ” 是用来启动和停止服务。每一项服务必须在 /init.rc 中定义,系统启动时 init 守护进程将解析 init.rc 和启动属性服务。一旦收到设置 “ ctrl.start ” 属性的请求,属性服务将使用该属性值作为服务名找到该服务,启动该服务。客户端应用程序可以轮询那个属性值,以确定结果。
关于c – 如何在boost图库中使用带有捆绑属性图的`randomize_property`?和boost图形库的问题我们已经讲解完毕,感谢您的阅读,如果还想了解更多关于2021-11-10:O(1) 时间插入、删除和获取随机元素。实现RandomizedSet 类:RandomizedSet() 初始化 RandomizedSet 对象。bool insert(in、Android coredomain 如何使用自定义的 property type?、Android 属性property_get/property_set、Android 属性之 build.prop,及 property_get/property_set等相关内容,可以在本站寻找。
本文标签:



![[转帖]Ubuntu 安装 Wine方法(ubuntu如何安装wine)](https://www.gvkun.com/zb_users/cache/thumbs/4c83df0e2303284d68480d1b1378581d-180-120-1.jpg)

