对于fastJson结合Nutz.Mapl的进阶应用感兴趣的读者,本文将提供您所需要的所有信息,我们将详细讲解fastjsonmap,并且为您提供关于@JsonInclude注解,RestTempla
对于fastJson结合Nutz.Mapl的进阶应用感兴趣的读者,本文将提供您所需要的所有信息,我们将详细讲解fastjson map,并且为您提供关于@JsonInclude注解,RestTemplate传输值为null的属性,利用FastJson将属性中有空值null的对象转化成Json字符串、alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject:Map跟Json String转换、Android 使用fastjson找不到fastjson包问题的解决方法、com.alibaba.fastjson.support.spring.FastJsonJsonView的实例源码的宝贵知识。
本文目录一览:- fastJson结合Nutz.Mapl的进阶应用(fastjson map)
- @JsonInclude注解,RestTemplate传输值为null的属性,利用FastJson将属性中有空值null的对象转化成Json字符串
- alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject:Map跟Json String转换
- Android 使用fastjson找不到fastjson包问题的解决方法
- com.alibaba.fastjson.support.spring.FastJsonJsonView的实例源码

fastJson结合Nutz.Mapl的进阶应用(fastjson map)
今天要做一堆数据的序列化, 反序列化, 序列化没问题, 反序列化却遇到了点小意外, 这一堆数据不是一个类!!!!!!当然可以通过类内部的一个类型对象来判断, 但是fastJson并没有这个功能, 只能自己一个一个的遍历一个一个的手工填充. 很麻烦呀.
之前一直是使用NUTZ的, 只是JSON部分有些BUG导致不能序列化, 反序列化这次的需求. 不过, 她里面还有好多不错的东西, 比如Mapl包, 一个对MAP, LIST结构进行操作的工具包, 这也fastJson有什么关系呢?
JSON, 说白了, 就是MAP, LIST结构!!!NUTZ.Json, fastJson.JSON.parse在不传入类型的情况下, 生成的都是MAPLIST结构.
String json = "{..."type":{"id":4005}...}";
Object obj = JSON.parse(json);
System.out.println(Mapl.cell(obj, "[0].type.id"));
这样就可以得到类型, 然后使用Mapl.maplistToObj()方法就可以组装成对应对象了.

@JsonInclude注解,RestTemplate传输值为null的属性,利用FastJson将属性中有空值null的对象转化成Json字符串
一个pojo类:
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class Friend {
private String name;
private int age;
private String sex;
}
初始化一个Friend对象,该对象属性为"sex"对应的值设置为null:
public class FriendTest {
private Friend friend = new Friend();
@Before
public void init(){
friend.setAge(26);
friend.setName("xiaofang");
friend.setSex(null);
}
使用FastJson将该对象转化为Json字符串:
@Test
public void testObjectToJson(){
String jsonString = JSONObject.toJSONString(friend);
System.out.println(jsonString);
}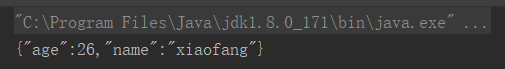
可以看到,"sex"字段由于为null,转化时该字段没了。
设置序列化类型
@Test
public void testJsonSerializer(){
String jsonString = JSONObject.toJSONString(friend, SerializerFeature.WriteMapNullValue);
System.out.println(jsonString);
}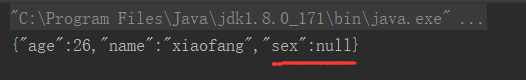
就有值为null的属性了。
RestTemplate传输值为null的属性
使用RestTemplate传输该Friend对象时,值为null的属性会被忽略掉,但是我们在某些情况下想要传输值为null的属性,我们可以在该字段上加上com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.@JsonInclude注解,通过RestTemplate传输,就不会忽略值为null的属性。
alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject:Map跟Json String转换
String test = "jdkalkjda|||djkdla|||djlak";
String str[] = test.split("\\|\\|\\|");
System.out.println(str.length);
HashMap<String,Object> t= new HashMap<String,Object>();
HashMap<String,Object> t1 = new HashMap<String,Object>();
t1.put("k","3");
Object s1 = JSONObject.toJSON(t1);
t.put("key",s1);
String s = JSONObject.toJSONString(t);
System.out.println(s);
String s2 = JSONObject.parSEObject(s).getJSONObject("key").toString();
System.out.println(JSONObject.parSEObject(s2).getDouble("k"));
System.out.println(JSONObject.parSEObject(s).getJSONObject("key").getDouble("k"));
Android 使用fastjson找不到fastjson包问题的解决方法
JSON解析库有很多,诸如Jackson,Json-lib,org.json,Gson和fastjson等,但是fastjson以其解析速度最快而脱颖而出。详细的测试地址如下:
https://github.com/eishay/jvm-serializers/wiki/Staging-Results
fastjson是国内alibaba公司的wenshao开发的,项目Git地址:
https://github.com/alibaba/fastjson
今天测试了下发现fastjson挺好用,比Android自带的org.json库要好用多了。当然我没有对fastjson的性能进行测试,只是因为Android自带的不太好。
在普通的java项目下,只需要导入fastjson.jar就可以,无需依赖其他包,这一点相比json-lib要好多,json-lib依赖五六个包。但是将fastjson.jar导入Android工程后,在使用时会出现 java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError:can''t find com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON等错误消息。
初步认为是与Android自带的org.json冲突。于是Build Path->Configure Build Path->Order And Export下将fastjson.jar上调至Android xx.jar上(xx为android 版本号)。再运行工程,这个错误不再出现了,奇迹般的没问题了。
然后现在再调整fastjson.jar和Android.jar顺序也不会出现can''t not find com.alibaba.fastjson的错误,不知道为何,继续看。
文章Java虚拟机类加载顺序讲解了java 虚拟机加载class和jar包的顺序。
bootstrap classloader ->extension classloader->system classloader
其中bootstrap引导类加载器;
extension classloader扩展类加载器,它负责加载JRE的扩展目录(JAVA_HOME/jre/lib/ext或者由java.ext.dirs系统属性指定的)中JAR的类包;
system classloader系统(也称为应用)类加载器,它负责在JVM被启动时,加载来自在命令java中的-classpath或者java.class.path系统属性或者 CLASSPATH操作系统属性所指定的JAR类包和类路径.
该文中还有一句话是这么说的,应该能解决我们的疑惑:
“此外类加载还采用了cache机制,也就是如果 cache中保存了这个Class就直接返回它,如果没有才从文件中读取和转换成Class,并存入cache,这就是为什么我们修改了Class但是必须重新启动JVM才能生效的原因。”
我想应该是Android虚拟机中已经有了fastjson的cache了,所以导致如何更改项目的fastjson.jar和Android.jar顺序都不会有任何反应。我的理解是这样,不知道对不对,欢迎大侠指正。
解释到这里,也解决了我另外一个疑问,就是在Android的工程中新建一个java类,并生成main方法,然后Run->Java Application. 结果会出现如下的错误:
#
# A fatal error has been detected by the Java Runtime Environment:
#
# Internal Error (classFileParser.cpp:3494), pid=5940, tid=5632
# Error: ShouldNotReachHere()
这个问题的产生就是和bootstrap classloard 有关了,文件上右键Run As->Run Configuration选择Java Application下的这个Java类,然后选择右侧的Classpath标签页下有两个目录,分别是Bootstrap Entries 和 User Entries。
Android工程中Bootsrap下默认的是Android Classpath Container,而Java则应该是JRE System Library。所以按照该文Error: ShouldNotReachHere()的解决方法,更改就好了。

com.alibaba.fastjson.support.spring.FastJsonJsonView的实例源码
@Test
public void test_jsonp() throws Exception {
FastJsonjsonView view = new FastJsonjsonView();
Assert.assertNotNull(view.getFastJsonConfig());
view.setFastJsonConfig(new FastJsonConfig());
view.setExtractValueFromSingleKeyModel(true);
view.setdisableCaching(true);
MockHttpServletRequest request = new MockHttpServletRequest();
request.addParameter("callback","queryName");
MockHttpServletResponse response = new MockHttpServletResponse();
Assert.assertEquals(true,view.isExtractValueFromSingleKeyModel());
view.render(Collections.singletonMap("abc","cde中文"),request,response);
String contentAsstring = response.getContentAsstring();
int contentLength = response.getContentLength();
Assert.assertEquals(contentLength,contentAsstring.getBytes(view.getFastJsonConfig().getCharset().name()).length);
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/getProgress/{fileKey}",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public ModelAndView getProgress(@PathVariable("fileKey") String fileKey,Map<String,Object> model) {
if (PROCESS_MAP.containsKey(fileKey)) {
Tuple2Unit<Integer,Integer> progresstuple = PROCESS_MAP.get(fileKey);
model.put("status","processing");
model.put("precent",progresstuple.getP1() * 100 / progresstuple.getP2());
} else {
model.put("status","OK");
}
return new ModelAndView(new FastJsonjsonView());
}
@Override
public void configureViewResolvers(ViewResolverRegistry registry) {
FastJsonjsonView fastJsonjsonView = new FastJsonjsonView();
registry.enableContentNegotiation(fastJsonjsonView);
}
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
public void test_0() throws Exception {
FastJsonjsonView view = new FastJsonjsonView();
Assert.assertEquals(Charset.forName("UTF-8"),view.getCharset());
view.setCharset(Charset.forName("GBK"));
Assert.assertEquals(Charset.forName("GBK"),view.getCharset());
Assert.assertNull(view.getDateFormat());
view.setDateFormat("yyyyMMdd");
Assert.assertNotNull(view.getFeatures());
Assert.assertEquals(1,view.getFeatures().length);
view.setSerializerFeature(SerializerFeature.browserCompatible);
Assert.assertEquals(1,view.getFeatures().length);
Assert.assertEquals(SerializerFeature.browserCompatible,view.getFeatures()[0]);
view.setFeatures(SerializerFeature.disableCheckSpecialChar,SerializerFeature.sortField);
Assert.assertEquals(2,view.getFeatures().length);
Assert.assertEquals(SerializerFeature.disableCheckSpecialChar,view.getFeatures()[0]);
Assert.assertEquals(SerializerFeature.sortField,view.getFeatures()[1]);
view.setFilters(serializefilter);
Assert.assertEquals(1,view.getFilters().length);
Assert.assertEquals(serializefilter,view.getFilters()[0]);
Map<String,Object> model = new HashMap<String,Object>();
MockHttpServletRequest request = new MockHttpServletRequest();
MockHttpServletResponse response = new MockHttpServletResponse();
view.render(model,response);
view.setRenderedAttributes(null);
view.setCharset(Charset.forName("UTF-8"));
view.render(model,response);
view.setUpdateContentLength(true);
view.setFeatures(SerializerFeature.browserCompatible);
view.render(model,response);
view.setCharset(Charset.forName("GBK"));
view.render(Collections.singletonMap("abc","cde"),response);
view.setdisableCaching(false);
view.setUpdateContentLength(false);
view.render(model,response);
view.setRenderedAttributes(new HashSet<String>(Collections.singletonList("abc")));
view.render(Collections.singletonMap("abc",response);
}
public void test_1() throws Exception {
FastJsonjsonView view = new FastJsonjsonView();
Assert.assertNotNull(view.getFastJsonConfig());
view.setFastJsonConfig(new FastJsonConfig());
Map<String,Object>();
MockHttpServletRequest request = new MockHttpServletRequest();
MockHttpServletResponse response = new MockHttpServletResponse();
view.render(model,response);
view.setRenderedAttributes(null);
view.render(model,response);
view.setUpdateContentLength(true);
view.render(model,response);
view.setExtractValueFromSingleKeyModel(true);
Assert.assertEquals(true,view.isExtractValueFromSingleKeyModel());
view.setdisableCaching(true);
view.render(Collections.singletonMap("abc",response);
}
@Test
public void test_jsonp_invalidparam() throws Exception {
FastJsonjsonView view = new FastJsonjsonView();
Assert.assertNotNull(view.getFastJsonConfig());
view.setFastJsonConfig(new FastJsonConfig());
view.setExtractValueFromSingleKeyModel(true);
view.setdisableCaching(true);
MockHttpServletRequest request = new MockHttpServletRequest();
request.addParameter("callback","-methodName");
MockHttpServletResponse response = new MockHttpServletResponse();
Assert.assertEquals(true,view.isExtractValueFromSingleKeyModel());
view.render(Collections.singletonMap("doesn't matter",Collections.singletonMap("abc","cde中文")),response);
String contentAsstring = response.getContentAsstring();
Assert.assertTrue(contentAsstring.startsWith("{\"abc\":\"cde中文\"}"));
}
今天的关于fastJson结合Nutz.Mapl的进阶应用和fastjson map的分享已经结束,谢谢您的关注,如果想了解更多关于@JsonInclude注解,RestTemplate传输值为null的属性,利用FastJson将属性中有空值null的对象转化成Json字符串、alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject:Map跟Json String转换、Android 使用fastjson找不到fastjson包问题的解决方法、com.alibaba.fastjson.support.spring.FastJsonJsonView的实例源码的相关知识,请在本站进行查询。
本文标签:



![[转帖]Ubuntu 安装 Wine方法(ubuntu如何安装wine)](https://www.gvkun.com/zb_users/cache/thumbs/4c83df0e2303284d68480d1b1378581d-180-120-1.jpg)

