对于想了解AndroidSQLiteselect*fromtablewherenamelike%key%usingpreparedstatements的读者,本文将是一篇不可错过的文章,并且为您提供关
对于想了解Android SQLite select * from table where name like%key%using prepared statements的读者,本文将是一篇不可错过的文章,并且为您提供关于A2-03-13.DDL-How To Rename Table Using MySQL RENAME TABLE Statement、android – SQLiteDatabase.openDatabase vs SQLiteOpenHelper.getReadableDatabase、android.database.sqlite.SQLiteException:near“SELECT”:语法错误(代码1):,同时编译:SELECT * FROM Table_Name、androidx.sqlite.db.framework.FrameworkSQLiteDatabase.inTransaction上的NullPointerException-Android Room的有价值信息。
本文目录一览:- Android SQLite select * from table where name like%key%using prepared statements
- A2-03-13.DDL-How To Rename Table Using MySQL RENAME TABLE Statement
- android – SQLiteDatabase.openDatabase vs SQLiteOpenHelper.getReadableDatabase
- android.database.sqlite.SQLiteException:near“SELECT”:语法错误(代码1):,同时编译:SELECT * FROM Table_Name
- androidx.sqlite.db.framework.FrameworkSQLiteDatabase.inTransaction上的NullPointerException-Android Room

Android SQLite select * from table where name like%key%using prepared statements
我想使用预备的语句来防止在sql sql数据库上的sql注入.但是,当查询包含Like并且与Where name =?一起工作时,rawquery会崩溃?
有没有办法在Android sqlite数据库中使用类似和准备好的语句?
这是查询:
sqlQuery = "SELECT * FROM " + TABLE_CALLS + " where " + CALLER_NAME + " like ? COLLATE NOCASE or " + CALLER_NBR + " like ? or " + CALLER_EXT + " like ?" + " or " + IS_OUTGOING + " like ? COLLATE NOCASE or " + TYPE + " like ? COLLATE NOCASE";
Cursor cursor = database.rawQuery(sqlQuery,new String[]{"%" + criterion + "%","%" + criterion + "%","%" + criterion + "%"});
它会使绑定或列索引超出范围
谢谢.
解决方法
if (name.length() != 0) {
name = "%" + name + "%";
}
if (email.length() != 0) {
email = "%" + email + "%";
}
if (Phone.length() != 0) {
Phone = "%" + Phone + "%";
}
String selectQuery = " select * from tbl_Customer where Customer_Name like '"
+ name
+ "' or Customer_Email like '"
+ email
+ "' or Customer_Phone like '"
+ Phone
+ "' ORDER BY Customer_Id DESC";
Cursor cursor = mDb.rawQuery(selectQuery,null);`

A2-03-13.DDL-How To Rename Table Using MySQL RENAME TABLE Statement
转载自:http://www.mysqltutorial.org/mysql-rename-table/
How To Rename Table Using MySQL RENAME TABLE Statement
Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to rename tables using MySQL RENAME TABLE statement and ALTER TABLE statement.
Introduction to MySQL RENAME TABLE statement
Because business requirements change, we need to rename the current table to a new one to better reflect the new situation. MySQL provides us with a very useful statement that changes the name of one or more tables.
To change one or more tables, we use the RENAME TABLE statement as follows:
|
1
|
RENAME TABLE old_table_name TO new_table_name;
|
The old table ( old_table_name) must exist, and the new table ( new_table_name) must not. If the new table new_table_name does exist, the statement will fail.
In addition to the tables, we can use the RENAME TABLE statement to rename views.
Before we execute the RENAME TABLE statement, we must ensure that there is no active transactions or locked tables.
Note that you cannot use the RENAME TABLE statement to rename a temporary table, but you can use the ALTER TABLE statement to rename a temporary table.
In terms of security, any existing privileges that we granted to the old table must be manually migrated to the new table.
Before renaming a table, you should evaluate the impact thoroughly. For example, you should investigate which applications are using the table. If the name of the table changes, so the application code that refers to the table name needs to be changed as well. In addition, you must manually adjust other database objects such as views, stored procedures, triggers, foreign key constraints, etc., that reference to the table. We will discuss this in more detail in the following examples.
MySQL RENAME TABLE examples
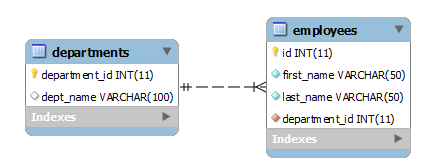
First, we create a new database named hr that consists of two tables: employees and departments for the demonstration.
|
1
|
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS hr;
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
CREATE TABLE departments (
department_id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
dept_name VARCHAR(100)
);
CREATE TABLE employees (
id int AUTO_INCREMENT primary key,
first_name varchar(50) not null,
last_name varchar(50) not null,
department_id int not null,
FOREIGN KEY (department_id)
REFERENCES departments (department_id)
);
|
Second, we insert sample data into both employees and departments tables:
|
1
2
|
INSERT INTO departments(dept_name)
VALUES(''Sales''),(''Markting''),(''Finance''),(''Accounting''),(''Warehouses''),(''Production'');
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
INSERT INTO employees(first_name,last_name,department_id)
VALUES(''John'',''Doe'',1),
(''Bush'',''Lily'',2),
(''David'',''Dave'',3),
(''Mary'',''Jane'',4),
(''Jonatha'',''Josh'',5),
(''Mateo'',''More'',1);
|
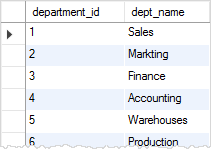
Third, we review our data in the departments and employees tables:
|
1
2
3
4
|
SELECT
department_id, dept_name
FROM
departments;
|
|
1
2
3
4
|
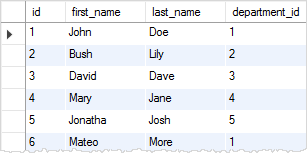
SELECT
id, first_name, last_name, department_id
FROM
employees;
|
Renaming a table referenced by a view
If the table that you are going to rename is referenced by a view, the view will become invalid if you rename the table, and you have to adjust the view manually.
For example, we create a view named v_employee_info based on the employees and departments tables as follows:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
CREATE VIEW v_employee_info as
SELECT
id, first_name, last_name, dept_name
from
employees
inner join
departments USING (department_id);
|
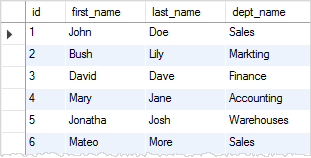
The views use the inner join clause to join departments and employees tables.
The following SELECT statement returns all data from the v_employee_info view.
|
1
2
3
4
|
SELECT
*
FROM
v_employee_info;
|
Now we rename the employees to people table and query data from the v_employee_info view again.
|
1
|
RENAME TABLE employees TO people;
|
|
1
2
3
4
|
SELECT
*
FROM
v_employee_info;
|
MySQL returns the following error message:
|
1
2
|
Error
Code: 1356. View ''hr.v_employee_info'' references invalid table(s) or
column(s) or function(s) or definer/invoker of view lack rights to use them
|
We can use the CHECK TABLE statement to check the status of the v_employee_info view as follows:
|
1
|
CHECK TABLE v_employee_info;
|
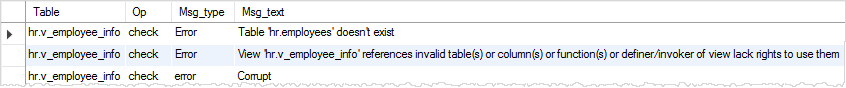
We need to manually change the v_employee_info view so that it refers to the people table instead of the employees table.
Renaming a table that referenced by a stored procedure
In case the table that you are going to rename is referenced by a stored procedure, you have to manually adjust it like you did with the view.
First, rename the people table back to the employees table.
|
1
|
RENAME TABLE people TO employees;
|
Then, create a new stored procedure named get_employee that refers to the employees table.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
DELIMITER $$
CREATE PROCEDURE get_employee(IN p_id INT)
BEGIN
SELECT first_name
,last_name
,dept_name
FROM employees
INNER JOIN departments using (department_id)
WHERE id = p_id;
END $$
DELIMITER;
|
Next, we execute the get_employee table to get the data of the employee with id 1 as follows:
|
1
|
CALL get_employee(1);
|
![]()
After that, we rename the employees to the people table again.
|
1
|
RENAME TABLE employees TO people;
|
Finally, we call the get_employee stored procedure to get the information of employee with id 2:
|
1
|
CALL get_employee(2);
|
MySQL returns the following error message:
|
1
|
Error
Code: 1146. Table ''hr.employees'' doesn''t exist
|
To fix this, we must manually change the employees table in the stored procedure to people table.
Renaming a table that has foreign keys referenced to
The departments table links to the employees table using the department_id column. The department_id column in the employees table is the foreign key that references to the departments table.
If we rename the departments table, all the foreign keys that point to the departments table will not be automatically updated. In such cases, we must drop and recreate the foreign keys manually.
|
1
|
RENAME TABLE departments TO depts;
|
We delete a department with id 1, because of the foreign key constraint, all rows in the people table should be also deleted. However, we renamed the departments table to the depts table without updating the foreign key manually, MySQL returns an error as illustrated below:
|
1
2
3
|
DELETE FROM depts
WHERE
department_id = 1;
|
|
1
|
Error
Code: 1451. Cannot delete or update a parent row: a foreign key constraint fails (`hr`.`people`, CONSTRAINT `people_ibfk_1` FOREIGN KEY (`department_id`) REFERENCES `depts` (`department_id`))
|
Renaming multiple tables
We can also use the RENAME TABLE statement to rename multiple tables at a time. See the following statement:
|
1
2
|
RENAME TABLE old_table_name_1 TO new_table_name_2,
old_table_name_2 TO new_table_name_2,...
|
The following statement renames the people and depts tables to employees and departments tables:
|
1
2
|
RENAME TABLE depts TO departments,
people TO employees;
|
Note the RENAME TABLE statement is not atomic. It means that if any errors occurred, MySQL does a rollback all renamed tables to their old names.
Renaming tables using ALTER TABLE statement
We can rename a table using the ALTER TABLE statement as follows:
|
1
2
|
ALTER TABLE old_table_name
RENAME TO new_table_name;
|
The ALTER TABLE statement can rename a temporary table while the RENAME TABLE statement cannot.
Renaming temporary table example
First, we create a temporary table that contains all unique last names which come from the last_namecolumn of the employees table:
|
1
2
|
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE lastnames
SELECT DISTINCT last_name from employees;
|
Second, we use the RENAME TABLE to rename the lastnames table:
|
1
|
RENAME TABLE lastnames TO unique_lastnames;
|
MySQL returns the following error message:
|
1
|
Error
Code: 1017. Can''t find file: ''.\hr\lastnames.frm'' (errno: 2 - No such file or directory)
|
Third, we use the ALTER TABLE statement to rename the lastnames table.
|
1
2
|
ALTER TABLE lastnames
RENAME TO unique_lastnames;
|
Fourth, we query data from the unique_lastnames temporary table:
|
1
2
3
4
|
SELECT
last_name
FROM
unique_lastnames;
|
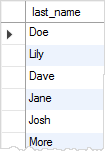
In this tutorial, we have shown you how to rename tables using MySQL RENAME TABLE and ALTER TABLE statements.
Related Tutorials
- MySQL DROP COLUMN
- How to Add Columns to a Table Using MySQL ADD COLUMN Statement

android – SQLiteDatabase.openDatabase vs SQLiteOpenHelper.getReadableDatabase
我应该使用哪种方法?基于我见过的示例代码,我首先使用sqliteOpenHelper创建数据库,但在需要使用数据库时调用sqliteDatabase.openDatabase.
解决方法
android.database.sqlite.SQLiteException:near“SELECT”:语法错误(代码1):,同时编译:SELECT * FROM Table_Name
我有以下课程
用户类为
public class User {
private int univ_id;
private String univ_name,univ_abbr;
public User(int univ_id,String univ_name,String univ_abbr) {
this.univ_id = univ_id;
this.univ_name = univ_name;
this.univ_abbr = univ_abbr;
}
public User(String univ_name,String univ_abbr) {
this.univ_name = univ_name;
this.univ_abbr = univ_abbr;
}
public User() {
// Todo Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public int getUniv_id() {
return univ_id;
}
public void setUniv_id(int univ_id) {
this.univ_id = univ_id;
}
public String getUniv_name() {
return univ_name;
}
public void setUniv_name(String univ_name) {
this.univ_name = univ_name;
}
public String getUniv_abbr() {
return univ_abbr;
}
public void setUniv_abbr(String univ_abbr) {
this.univ_abbr = univ_abbr;
}
}
DBStorageFirst Class as
public class DBStorageFirst extends sqliteOpenHelper {
public static final String DATABASE_NAME = "STUPIDSID_OFFLINE_DB";
public static final String TABLE_NAME_UNIVERSITIES = "universities";
public static final String COLUMN_UNIV_ID = "univ_id";
public static final String COLUMN_UNIV_NAME = "univ_name";
public static final String COLUMN_UNIV_ABBR = "univ_abbr";
public DBStorageFirst(Context context) {
super(context,DATABASE_NAME,null,1);
}
@Override
public void onCreate(sqliteDatabase db) {
// Todo Auto-generated method stub
db.execsql("create table " + TABLE_NAME_UNIVERSITIES
+ "(" + COLUMN_UNIV_ID + " integer RIMARY KEY," + COLUMN_UNIV_NAME
+ " text," + COLUMN_UNIV_ABBR + " text )");
Log.e("Success","Universities Table Created");
}
@Override
public void onUpgrade(sqliteDatabase db,int oldVersion,int newVersion) {
// Todo Auto-generated method stub
db.execsql("DROP TABLE IF EXISTS " + TABLE_NAME_UNIVERSITIES);
onCreate(db);
}
public void addUniversities(int univ_id,String univ_abbr) {
sqliteDatabase db = this.getWritableDatabase();
String sql1 = "insert into " + DBStorageFirst.TABLE_NAME_UNIVERSITIES
+ " (" + DBStorageFirst.COLUMN_UNIV_ID + ","
+ DBStorageFirst.COLUMN_UNIV_NAME + ","
+ DBStorageFirst.COLUMN_UNIV_ABBR + ")" + " values(" + univ_id
+ ",''" + univ_name + " '',''" + univ_abbr + "'')";
db.execsql(sql1);
// database.execsql(sql2);
Log.e("Success","Data inserted Successfully into Universities Table");
}
public List<User> getAllContacts() {
List<User> contactList = new ArrayList<User>();
String selectQuery = "SELECT * FROM "+TABLE_NAME_UNIVERSITIES;
sqliteDatabase db1 = this.getWritableDatabase();
Cursor cursor = db1.rawQuery(selectQuery,null);
if (cursor.movetoFirst()) {
do {
User contact = new User();
contact.setUniv_id(Integer.parseInt(cursor.getString(0)));
contact.setUniv_name(cursor.getString(1));
contact.setUniv_abbr(cursor.getString(2));
contactList.add(contact);
} while (cursor.movetoNext());
}
return contactList;
}
}
和MainActivity一样
DBStorageFirst db = new DBStorageFirst(this);
// Inserting Contacts
Log.d("Insert: ","Inserting ..");
db.addUniversities(25,"ABC","UA");
db.addUniversities(26,"DEF","UB");
List<User> list = new ArrayList<User>();
list = db.getAllContacts();
for (User cn : list) {
String log = "Id: " + cn.getUniv_id() + ",Name: "
+ cn.getUniv_name() + ",Abbr: " + cn.getUniv_abbr();
// Writing Contacts to log
Log.d("Name: ",log);
}
解决方法

androidx.sqlite.db.framework.FrameworkSQLiteDatabase.inTransaction上的NullPointerException-Android Room
如何解决androidx.sqlite.db.framework.FrameworkSQLiteDatabase.inTransaction上的NullPointerException-Android Room?
在单元测试测试项目中,我试图查询实体EndPoint,但出现此错误:
java.lang.NullPointerException
at androidx.sqlite.db.framework.FrameworksqliteDatabase.inTransaction(FrameworksqliteDatabase.java:100)
at androidx.room.InvalidationTracker.syncTriggers(InvalidationTracker.java:480)
at androidx.room.RoomDatabase.beginTransaction(RoomDatabase.java:353)
at com.mypackged.data.dao.ConfigurationDao_Impl.setUpdateEndPointConfig(ConfigurationDao_Impl.java:120)
at com.mypackged.business.server.ServicioGeneralTests.test_just_run_please(ServicioGeneralTests.java:46)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:62)
at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:43)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:498)
at org.junit.runners.model.FrameworkMethod$1.runReflectiveCall(FrameworkMethod.java:50)
at org.junit.internal.runners.model.ReflectiveCallable.run(ReflectiveCallable.java:12)
at org.junit.runners.model.FrameworkMethod.invokeExplosively(FrameworkMethod.java:47)
at org.junit.internal.runners.statements.InvokeMethod.evaluate(InvokeMethod.java:17)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner.runLeaf(ParentRunner.java:325)
at org.junit.runners.BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.runchild(BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.java:78)
at org.junit.runners.BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.runchild(BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.java:57)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner$3.run(ParentRunner.java:290)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner$1.schedule(ParentRunner.java:71)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner.runchildren(ParentRunner.java:288)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner.access$000(ParentRunner.java:58)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner$2.evaluate(ParentRunner.java:268)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner.run(ParentRunner.java:363)
at org.mockito.internal.runners.JUnit45AndHigherRunnerImpl.run(JUnit45AndHigherRunnerImpl.java:37)
at org.mockito.runners.MockitoJUnitRunner.run(MockitoJUnitRunner.java:62)
at org.junit.runner.JUnitCore.run(JUnitCore.java:137)
at com.intellij.junit4.JUnit4IdeaTestRunner.startRunnerWithArgs(JUnit4IdeaTestRunner.java:68)
at com.intellij.rt.junit.IdeaTestRunner$Repeater.startRunnerWithArgs(IdeaTestRunner.java:33)
at com.intellij.rt.junit.JUnitStarter.prepareStreamsAndStart(JUnitStarter.java:230)
at com.intellij.rt.junit.JUnitStarter.main(JUnitStarter.java:58)
这是我正在尝试使用MockitoJUnitRunner测试的代码:
@Test
public void test_just_run_please() throws InterruptedException {
assertNotNull(context);
CIDatabase db = Room.databaseBuilder(context,CIDatabase.class,CIDatabase.DB_NAME)
.allowMainThreadQueries()
.build();
assertNotNull(db);
ConfigurationDao configdao = db.getConfiguracionDao();
assertNotNull(configdao);
EndPointConfig endPointConfig1 = new EndPointConfig();
endPointConfig1.setUrl("url");
configdao.setUpdateEndPointConfig(endPointConfig1); // <--- NullPointerException here
EndPointConfig endPointConfig = configdao.getEndpointConfig();
assertNull(endPointConfig);
}
这是实体:
@Entity(tableName = "endpoint_config")
public class EndPointConfig {
@PrimaryKey(autoGenerate = true)
@ColumnInfo(name = "id")
private int id;
@ColumnInfo(name = "url")
private String url;
public String getUrl() {
return url;
}
public void setUrl(String url) {
this.url = url;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
}
道:
@Dao
public interface ConfigurationDao {
@Insert(entity = EndPointConfig.class,onConflict = OnConflictStrategy.ABORT)
void setUpdateEndPointConfig(EndPointConfig endPointConfig);
// .. more methods
}
数据库:
@Database(entities = {TitularCuenta.class,Familiar.class,Parentesco.class,AppConfiguration.class,EndPointConfig.class},version = 2)
public abstract class CIDatabase extends RoomDatabase {
public static final String DB_NAME = "please_work_database";
public abstract ConfigurationDao getConfiguracionDao();
// more dao methods...
}
这里是gradle依赖项:
implementation "android.arch.persistence.room:runtime:2.2.4"
implementation "android.arch.persistence.room:compiler:2.2.4"
implementation "androidx.room:room-runtime:$room_version"
kapt "android.arch.persistence.room:compiler:1.0.0"
如果我导航到androidx.sqlite.db.framework.FrameworksqliteDatabase.inTransaction方法,则这里是引发错误的行:
@Override
public boolean inTransaction() {
return mDelegate.inTransaction();
}
解决方法
暂无找到可以解决该程序问题的有效方法,小编努力寻找整理中!
如果你已经找到好的解决方法,欢迎将解决方案带上本链接一起发送给小编。
小编邮箱:dio#foxmail.com (将#修改为@)
关于Android SQLite select * from table where name like%key%using prepared statements的介绍已经告一段落,感谢您的耐心阅读,如果想了解更多关于A2-03-13.DDL-How To Rename Table Using MySQL RENAME TABLE Statement、android – SQLiteDatabase.openDatabase vs SQLiteOpenHelper.getReadableDatabase、android.database.sqlite.SQLiteException:near“SELECT”:语法错误(代码1):,同时编译:SELECT * FROM Table_Name、androidx.sqlite.db.framework.FrameworkSQLiteDatabase.inTransaction上的NullPointerException-Android Room的相关信息,请在本站寻找。
本文标签:



![[转帖]Ubuntu 安装 Wine方法(ubuntu如何安装wine)](https://www.gvkun.com/zb_users/cache/thumbs/4c83df0e2303284d68480d1b1378581d-180-120-1.jpg)

