对于如何确定实际使用的日志配置源Logback?感兴趣的读者,本文将提供您所需要的所有信息,我们将详细讲解日志的配置文件,并且为您提供关于0104代码方式动态刷新logback日志配置、0104代码方
对于如何确定实际使用的日志配置源Logback?感兴趣的读者,本文将提供您所需要的所有信息,我们将详细讲解日志的配置文件,并且为您提供关于0104 代码方式动态刷新 logback 日志配置、0104 代码方式动态刷新logback日志配置、Java 日志框架 - logback 配置文件多环境日志配置(开发、测试、生产)(原始解决方法)、Java日志配置 SLF4J + Logback的宝贵知识。
本文目录一览:- 如何确定实际使用的日志配置源Logback?(日志的配置文件)
- 0104 代码方式动态刷新 logback 日志配置
- 0104 代码方式动态刷新logback日志配置
- Java 日志框架 - logback 配置文件多环境日志配置(开发、测试、生产)(原始解决方法)
- Java日志配置 SLF4J + Logback

如何确定实际使用的日志配置源Logback?(日志的配置文件)
log4j具有属性,log4j.debug可以帮助用户指示实际使用哪个配置文件来配置日志记录系统。
我还没有找到与(否则更高级的)Logback日志记录框架等效的东西。有什么方法可以在运行时打印(用于诊断目的)Logback用来引导自身的配置文件?
[编辑]澄清一下,理想情况下,我想要一个不需要我修改配置文件本身的解决方案(例如,由于组装错误的第三方JAR可能会被错误地提取,并且在我的注销配置之前)
XML)。
答案1
小编典典您可以设置Java系统属性以输出Logback调试信息:
java -Dlogback.statusListenerClass=ch.qos.logback.core.status.OnConsoleStatusListener用于自动状态打印的Logback文档(最下面提到强制输出状态)和logback.statusListenerClass属性进一步解释了这一点:
在没有状态消息的情况下,很难追踪到流氓logback.xml配置文件,尤其是在生产中,其中应用程序源不容易被修改。为了帮助识别恶意配置文件的位置,可以通过“
logback.statusListenerClass”系统属性(定义如下)来设置StatusListener,以强制输出状态消息。系统属性“
logback.statusListenerClass”也可以用于使出现错误时自动生成的输出静音。

0104 代码方式动态刷新 logback 日志配置
0104 代码方式刷新 logback 日志配置
背景
日志是一个系统或者说一个产品技术架构中重要组成部分。 常见的日志框架如下:
| 日志框架 | 说明 | 跟 slf4j 集成所需依赖 |
|---|---|---|
| slf4j | 日志门面,具体实现由程序决定 | |
| jcl | commons-logging | <br />jcl-over-slf4j |
| jul | jdk-logging | slf4j-api<br />jul-to-slf4j<br />slf4j-jdk14 |
| log4j | log4j | slf4j-api<br />log4j-over-slf4j<br />slf4j-log4j12 |
| log4j2 | log4j-api,log4j-core | slf4j-api<br />log4j-slf4j-impl |
| logback | logback-core,logback-classic | slf4j-api |
slf4j-logback 的启动过程
一般使用 slf4j 来操作日志:
private static final Logger LOGGER =
LoggerFactory.getLogger(LogbackAppenderExample.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
LOGGER.trace("trace log");
LOGGER.debug("debug log");
LOGGER.info("info log");
LOGGER.warn("warn log");
LOGGER.error("error log");
LOGGER.error("error log xxx");
LOGGER.error("error log yyy");
LOGGER.error("error log zzz");
LOGGER.error("error log aaa");
}
通过这个来跟踪 Logger 的初始过程;
1 LoggerFactory.getLogger
代码如下:
public static Logger getLogger(Class<?> clazz) {
Logger logger = getLogger(clazz.getName());
if (DETECT_LOGGER_NAME_MISMATCH) {
Class<?> autoComputedCallingClass = Util.getCallingClass();
if (autoComputedCallingClass != null && nonMatchingClasses(clazz, autoComputedCallingClass)) {
Util.report(String.format("Detected logger name mismatch. Given name: \"%s\"; computed name: \"%s\".", logger.getName(),
autoComputedCallingClass.getName()));
Util.report("See " + LOGGER_NAME_MISMATCH_URL + " for an explanation");
}
}
return logger;
}
过程:
| 步骤 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 获取得到 Logger 对象 |
| 2 | 如果有设置系统属性 slf4j.detectLoggerNameMismatch=true<br /> 则找到调用 getLogger 方法的类名 <br /> 如果跟传入的类名不一致,则给出警告,给的类和调用方法的类不一致,并给出文档地址 |
| 3 | 返回 Logger 对象 |
2 getLogger(clazz.getName())
通过类名得到 Logger 代码如下:
public static Logger getLogger(String name) {
ILoggerFactory iLoggerFactory = getILoggerFactory();
return iLoggerFactory.getLogger(name);
}
核心步骤
| 序号 | 步骤 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 得到 ILggerFactory 对象 |
| 2 | 通过工厂,传入名字,得到 Logger 对象 |
3 getILoggerFactory()
得到日志工厂 代码如下:
public static ILoggerFactory getILoggerFactory() {
if (INITIALIZATION_STATE == UNINITIALIZED) {
synchronized (LoggerFactory.class) {
if (INITIALIZATION_STATE == UNINITIALIZED) {
INITIALIZATION_STATE = ONGOING_INITIALIZATION;
performInitialization();
}
}
}
switch (INITIALIZATION_STATE) {
case SUCCESSFUL_INITIALIZATION:
return StaticLoggerBinder.getSingleton().getLoggerFactory();
case NOP_FALLBACK_INITIALIZATION:
return NOP_FALLBACK_FACTORY;
case FAILED_INITIALIZATION:
throw new IllegalStateException(UNSUCCESSFUL_INIT_MSG);
case ONGOING_INITIALIZATION:
// support re-entrant behavior.
// See also http://jira.qos.ch/browse/SLF4J-97
return SUBST_FACTORY;
}
throw new IllegalStateException("Unreachable code");
}
核心步骤:
| 序号 | 步骤 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 如果初始化状态值为 未初始化 <br /> 同步加锁 synchronized (LoggerFactory.class)<br /> 再次判断 初始化状态值为 未初始化,如果是:<br /> 设置初始化状态值为 正在初始化 < br /> 然后 执行初始化 performInitialization() |
| 2 | 然后根据初始化状态的条件做不同的处理 <br /> 如果 初始化失败,抛出异常,并提示哪里失败了 < br /> 如果 正在初始化, 返回替代工厂 SubstituteLoggerFactory, 日志一般也是委托给 NOPLogger<br /> 如果 空回退初始化 返回空的工厂 NOPLoggerFactory,不输出日志的空实现 < br /> 如果 成功初始化,调用 StaticLoggerBinder.getLoggerFactory 返回工厂 < br /> 如果不在以上的状态,直接抛出异常,无法抵达的 code; |
4 performInitialization()
执行初始化 代码:
private final static void performInitialization() {
bind();
if (INITIALIZATION_STATE == SUCCESSFUL_INITIALIZATION) {
versionSanityCheck();
}
}
核心步骤
| 序号 | 步骤说明 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 绑定 |
| 2 | 如果初始化成功,则进行版本明智检查 |
5 bind()
绑定 代码:
private final static void bind() {
try {
Set<URL> staticLoggerBinderPathSet = findPossibleStaticLoggerBinderPathSet();
reportMultipleBindingAmbiguity(staticLoggerBinderPathSet);
// the next line does the binding
StaticLoggerBinder.getSingleton();
INITIALIZATION_STATE = SUCCESSFUL_INITIALIZATION;
reportActualBinding(staticLoggerBinderPathSet);
fixSubstitutedLoggers();
playRecordedEvents();
SUBST_FACTORY.clear();
} catch (NoClassDefFoundError ncde) {
String msg = ncde.getMessage();
if (messageContainsOrgSlf4jImplStaticLoggerBinder(msg)) {
INITIALIZATION_STATE = NOP_FALLBACK_INITIALIZATION;
Util.report("Failed to load class \"org.slf4j.impl.StaticLoggerBinder\".");
Util.report("Defaulting to no-operation (NOP) logger implementation");
Util.report("See " + NO_STATICLOGGERBINDER_URL + " for further details.");
} else {
failedBinding(ncde);
throw ncde;
}
} catch (java.lang.NoSuchMethodError nsme) {
String msg = nsme.getMessage();
if (msg != null && msg.contains("org.slf4j.impl.StaticLoggerBinder.getSingleton()")) {
INITIALIZATION_STATE = FAILED_INITIALIZATION;
Util.report("slf4j-api 1.6.x (or later) is incompatible with this binding.");
Util.report("Your binding is version 1.5.5 or earlier.");
Util.report("Upgrade your binding to version 1.6.x.");
}
throw nsme;
} catch (Exception e) {
failedBinding(e);
throw new IllegalStateException("Unexpected initialization failure", e);
}
}
关键步骤
| 序号 | 步骤 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 找到可能的静态日志绑定器的路径集合 findPossibleStaticLoggerBinderPathSet**()** |
| 2 | 如果日志有多个绑定器,打印到控制台 <br /> 如果是 android 平台,忽略 < br /> 依次打印出多个日志绑定器,并给出文档提示 |
| 3 | 获得唯一的静态日志绑定器 StaticLoggerBinder.getSingleton ()<br /> 绑定器内部持有 LoggerContext 和 ContextSelectorStaticBinder |
| 4 | 设置初始化状态为成功 |
| 5 | 打印出实际的日志绑定器 ContextSelectorStaticBinder |
| 6 | 设置 SubstitutedLogger 的委托为实际的 Logger; fixSubstitutedLoggers() |
| 7 | 播放记录的事件 playRecordedEvents**()** |
| 8 | 清空委托工厂 SubstituteLoggerFactory |
6 findPossibleStaticLoggerBinderPathSet**()**
找到可能的静态日志绑定器的路径
代码:<br />**
static Set<URL> findPossibleStaticLoggerBinderPathSet() {
// use Set instead of list in order to deal with bug #138
// LinkedHashSet appropriate here because it preserves insertion order during iteration
Set<URL> staticLoggerBinderPathSet = new LinkedHashSet<URL>();
try {
ClassLoader loggerFactoryClassLoader = LoggerFactory.class.getClassLoader();
Enumeration<URL> paths;
if (loggerFactoryClassLoader == null) {
paths = ClassLoader.getSystemResources(STATIC_LOGGER_BINDER_PATH);
} else {
paths = loggerFactoryClassLoader.getResources(STATIC_LOGGER_BINDER_PATH);
}
while (paths.hasMoreElements()) {
URL path = paths.nextElement();
staticLoggerBinderPathSet.add(path);
}
} catch (IOException ioe) {
Util.report("Error getting resources from path", ioe);
}
return staticLoggerBinderPathSet;
}
关键步骤:
| 序号 | 步骤 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 如果 LoggerFactory 的类加载器为空,系统类加载器得到 <br />org/slf4j/impl/StaticLoggerBinder.class 这个文件 <br /> 分布在不同的 jar 中,可能有多个; |
| 2 | 如果不为空,则通过 LoggerFactoryLoader 找到 <br />org/slf4j/impl/StaticLoggerBinder.class 这个文件 |
| 3 | 把这些 class 对应的 url 汇总到结合中返回 |
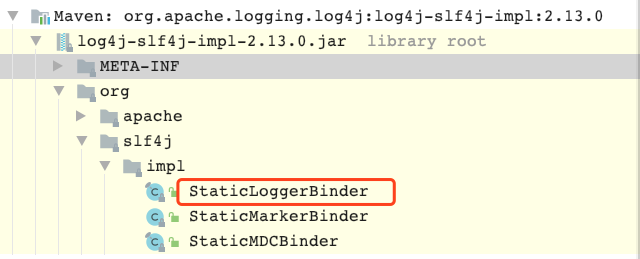
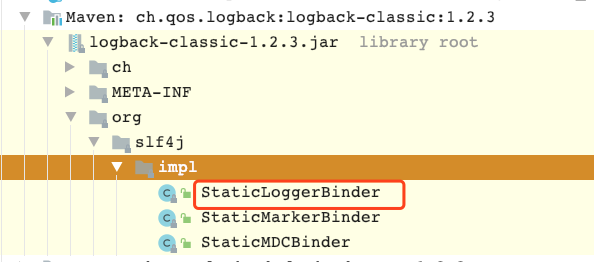
7 playRecordedEvents**()**
放映记录的事件
代码:
private static void playRecordedEvents() {
List<SubstituteLoggingEvent> events = SUBST_FACTORY.getEventList();
if (events.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < events.size(); i++) {
SubstituteLoggingEvent event = events.get(i);
SubstituteLogger substLogger = event.getLogger();
if( substLogger.isDelegateNOP()) {
break;
} else if (substLogger.isDelegateEventAware()) {
if (i == 0)
emitReplayWarning(events.size());
substLogger.log(event);
} else {
if(i == 0)
emitSubstitutionWarning();
Util.report(substLogger.getName());
}
}
}
关键步骤:
| 序号 | 步骤 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 得到委托日志工厂的事件,如果为空,则结束 |
| 2 | 如果事件不为空,取出来,<br /> 如果委托的日志有空日志,中断 < br /> 如果委托的日志是委托事件, 打印日志,并打印出播放的警告 < br /> 否则,警告委托的日志不可用,并打印出日志的名称 |
8 versionSanityCheck()
得到 StaticLoggerBinder 的版本,并进行判断是否合适。 LoggerFactory 放了允许使用的 StaticLoggerBinder 的版本,如果不合适,会答应出警告。 源码:
private final static void versionSanityCheck() {
try {
String requested = StaticLoggerBinder.REQUESTED_API_VERSION;
boolean match = false;
for (String aAPI_COMPATIBILITY_LIST : API_COMPATIBILITY_LIST) {
if (requested.startsWith(aAPI_COMPATIBILITY_LIST)) {
match = true;
}
}
if (!match) {
Util.report("The requested version " + requested + " by your slf4j binding is not compatible with "
+ Arrays.asList(API_COMPATIBILITY_LIST).toString());
Util.report("See " + VERSION_MISMATCH + " for further details.");
}
} catch (java.lang.NoSuchFieldError nsfe) {
// given our large user base and SLF4J''s commitment to backward
// compatibility, we cannot cry here. Only for implementations
// which willingly declare a REQUESTED_API_VERSION field do we
// emit compatibility warnings.
} catch (Throwable e) {
// we should never reach here
Util.report("Unexpected problem occured during version sanity check", e);
}
}
9 StaticLoggerBinder.init()
静态日志绑定器的初始化
代码:
void init() {
try {
try {
new ContextInitializer(defaultLoggerContext).autoConfig();
} catch (JoranException je) {
Util.report("Failed to auto configure default logger context", je);
}
// logback-292
if (!StatusUtil.contextHasStatusListener(defaultLoggerContext)) {
StatusPrinter.printInCaseOfErrorsOrWarnings(defaultLoggerContext);
}
contextSelectorBinder.init(defaultLoggerContext, KEY);
initialized = true;
} catch (Exception t) { // see LOGBACK-1159
Util.report("Failed to instantiate [" + LoggerContext.class.getName() + "]", t);
}
}
核心过程
| 序号 | 步骤 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 新建上下文初始化器,然后自动配置;<br />new ContextInitializer(defaultLoggerContext).autoConfig**()**; |
| 2 | 如果没有配置状态监听器,则打印出警告 |
| 3 | 上下文选择绑定器初始化 |
10 ContextInitializer.autoConfig**()**;
自动配置上下文
代码:
public void autoConfig() throws JoranException {
StatusListenerConfigHelper.installIfAsked(loggerContext);
URL url = findURLOfDefaultConfigurationFile(true);
if (url != null) {
configureByResource(url);
} else {
Configurator c = EnvUtil.loadFromServiceLoader(Configurator.class);
if (c != null) {
try {
c.setContext(loggerContext);
c.configure(loggerContext);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new LogbackException(String.format("Failed to initialize Configurator: %s using ServiceLoader", c != null ? c.getClass()
.getCanonicalName() : "null"), e);
}
} else {
BasicConfigurator basicConfigurator = new BasicConfigurator();
basicConfigurator.setContext(loggerContext);
basicConfigurator.configure(loggerContext);
}
}
}
核心步骤
| 序号 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 如果没有,安装状态监听器 |
| 2 | 找到默认的配置文件或者 URL, 一次按照系统属性 <br />logback.configurationFile 查找 <br /> 按照 logback-test.xml<br /> 按照 logback.groovy<br /> 按照 logback.xml<br /> 得到配置文件 |
| 3 | 如果找到了,configureByResource**(url)**; |
| 4 | 否则,按照 spi 的方式找到 Configurator 的实现类,设置上下文,进行配置 |
| 如果 spi 方式拿不到,则使用缺省的 BasicConfigurator(里面只配置了一个控制台)<br /> 设置上下文,进行配置 |
11 StaticLoggerBinder.getLoggerFactory
通过静态日志绑定器得到日志工厂,实现类是 LoggerContext;
源码:
public ILoggerFactory getLoggerFactory() {
if (!initialized) {
return defaultLoggerContext;
}
if (contextSelectorBinder.getContextSelector() == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("contextSelector cannot be null. See also " + NULL_CS_URL);
}
return contextSelectorBinder.getContextSelector().getLoggerContext();
}
核心流程:
| 序号 | 步骤 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 如果没有初始化,返回默认的 LoggerContext |
| 2 | 如果 ContextSelectBinder 不为空,得到 ContextSeleter |
| 3 | 通过 ContextSelector 得到 LoggerContext; |
12 iLoggerFactory.getLogger(name)
这是一个接口,直接得到一个 Logger 实例; 从上面的代码之后,这里的实例应该是一个 LoggerContext 对象 这个对象是核心,所有的日志动作都在里面;
logback-aliyun-appender
直接把日志接入到阿里云 对于初创企业来说,直接使用阿里云的日志服务非常方便,减少了自己搭建 ELK 的运维成本,直接按量付费,非常方便,我贴一下我的接入过程;
引入依赖:
<!--日志-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.aliyun.openservices</groupId>
<artifactId>aliyun-log-logback-appender</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--spring日志桥接,使用的commoon-logging-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>jcl-over-slf4j</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--log4j日志桥接,zk使用的log4j-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-over-slf4j</artifactId>
</dependency>
然后按照 代码刷新 logback 日志配置的方法,把日志配置放到 apollo, 启动的时候就可以接入到阿里云日志了。
贴一下配置:
<configuration>
<!--为了防止进程退出时,内存中的数据丢失,请加上此选项-->
<shutdownHook class="ch.qos.logback.core.hook.DelayingShutdownHook"/>
<appender name="loghubAppender" class="com.aliyun.openservices.log.logback.LoghubAppender">
<!--必选项-->
<!-- 账号及网络配置 -->
<endpoint>cn-xxx.log.aliyuncs.com</endpoint>
<accessKeyId>xxxxx</accessKeyId>
<accessKeySecret>xxxxx</accessKeySecret>
<!-- sls 项目配置 -->
<project>ts-app-xxx</project>
<logStore>ts-app-xxx</logStore>
<!--必选项 (end)-->
<!-- 可选项 -->
<topic>topic2</topic>
<source>source2</source>
<!-- 可选项 详见 ''参数说明''-->
<totalSizeInBytes>104857600</totalSizeInBytes>
<maxBlockMs>60</maxBlockMs>
<ioThreadCount>2</ioThreadCount>
<batchSizeThresholdInBytes>524288</batchSizeThresholdInBytes>
<batchCountThreshold>4096</batchCountThreshold>
<lingerMs>2000</lingerMs>
<retries>3</retries>
<baseRetryBackoffMs>100</baseRetryBackoffMs>
<maxRetryBackoffMs>100</maxRetryBackoffMs>
<!-- 可选项 通过配置 encoder 的 pattern 自定义 log 的格式 -->
<encoder>
<pattern>%d %-5level [%thread] %logger{0}: %msg</pattern>
</encoder>
<!-- 可选项 设置时间格式 -->
<timeFormat>yyyy-MM-dd''T''HH:mmZ</timeFormat>
<!-- 可选项 设置时区 -->
<timeZone>Asia/Shanghai</timeZone>
<filter class="ch.qos.logback.classic.filter.ThresholdFilter"><!-- 只打印INFO级别的日志 -->
<level>INFO</level>
<!-- <onMatch>ACCEPT</onMatch>-->
<!-- <onMismatch>DENY</onMismatch>-->
</filter>
<!-- <mdcFields>THREAD_ID,MDC_KEY</mdcFields>-->
</appender>
<appender name="STDOUT" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender">
<encoder>
<pattern>%d{HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%thread] %-5level %logger - %msg %X{THREAD_ID} %n</pattern>
</encoder>
</appender>
<!-- 可用来获取StatusManager中的状态 -->
<statusListener class="ch.qos.logback.core.status.OnConsoleStatusListener"/>
<!-- 解决debug模式下循环发送的问题 -->
<logger name="org.apache.http.impl.conn.Wire" level="WARN" />
<root>
<level value="DEBUG"/>
<appender-ref ref="loghubAppender"/>
<appender-ref ref="STDOUT"/>
</root>
</configuration>
代码刷新 logback 日志配置
主要是模仿 LogbackLister 的实现细节来模仿: 简单的贴一下我的实现代码:
package com.lifesense.opensource.spring;
import ch.qos.logback.classic.BasicConfigurator;
import ch.qos.logback.classic.LoggerContext;
import ch.qos.logback.classic.joran.JoranConfigurator;
import ch.qos.logback.core.joran.spi.JoranException;
import ch.qos.logback.core.util.StatusPrinter;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
import org.springframework.util.ClassUtils;
import org.springframework.util.ReflectionUtils;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* @author carter
*/
public class LogbackLoader {
private static final String DEFAULT_LOG_BACK_XML = "<configuration>" +
"<shutdownHook class=\"ch.qos.logback.core.hook.DelayingShutdownHook\"/>" +
"<appender name=\"STDOUT\" class=\"ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender\">" +
"<encoder><pattern>%d{HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%thread] %-5level %logger - %msg %X{THREAD_ID} %n</pattern></encoder>" +
"</appender>" +
"<statusListener class=\"ch.qos.logback.core.status.OnConsoleStatusListener\"/>" +
"<logger name=\"org.apache.http.impl.conn.Wire\" level=\"WARN\" />" +
"<root><level value=\"DEBUG\"/><appender-ref ref=\"STDOUT\"/>" +
"</root></configuration>";
/**
* 初始化日志配置
*/
public static void initLogbackWithoutConfigFile(ServletContext servletContext) {
initLogbackConfigFromXmlString(servletContext, DEFAULT_LOG_BACK_XML);
}
public static void initLogbackConfigFromXmlString(ServletContext servletContext, String xmlStr) {
System.out.println("Initializing Logback from [\n" + xmlStr + "\n]");
LoggerContext loggerContext = (LoggerContext) LoggerFactory.getILoggerFactory();
Assert.notNull(loggerContext, "获取不到LoggerContext");
loggerContext.getStatusManager().clear();
loggerContext.reset();
//安装默认的日志配置
if (StringUtils.isBlank(xmlStr)) {
BasicConfigurator basicConfigurator = new BasicConfigurator();
basicConfigurator.setContext(loggerContext);
basicConfigurator.configure(loggerContext);
return;
}
//按照传入的配置文件来配置
JoranConfigurator configurator = new JoranConfigurator();
configurator.setContext(loggerContext);
InputStream in = new ByteArrayInputStream(xmlStr.getBytes());
try {
configurator.doConfigure(in);
} catch (JoranException e) {
System.out.println("初始化配置logback发生错误");
e.printStackTrace();
}
//If SLF4J''s java.util.logging bridge is available in the classpath, install it. This will direct any messages
//from the Java Logging framework into SLF4J. When logging is terminated, the bridge will need to be uninstalled
try {
Class<?> julBridge = ClassUtils.forName("org.slf4j.bridge.SLF4JBridgeHandler", ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());
Method removeHandlers = ReflectionUtils.findMethod(julBridge, "removeHandlersForRootLogger");
if (removeHandlers != null) {
servletContext.log("Removing all previous handlers for JUL to SLF4J bridge");
ReflectionUtils.invokeMethod(removeHandlers, null);
}
Method install = ReflectionUtils.findMethod(julBridge, "install");
if (install != null) {
servletContext.log("Installing JUL to SLF4J bridge");
ReflectionUtils.invokeMethod(install, null);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ignored) {
//Indicates the java.util.logging bridge is not in the classpath. This is not an indication of a problem.
servletContext.log("JUL to SLF4J bridge is not available on the classpath");
}
StatusPrinter.print(loggerContext);
}
}
在 springmvc 上下文启动的时候,可以使用代码的方式加载默认的日志配置; 启动完成之后,加上 apollo 的配置监听器,这样就可以在 apollo 中实时的修改日志的配置文件,代码实时生效。
package com.lifesense.opensource.spring;
import com.ctrip.framework.apollo.Config;
import com.ctrip.framework.apollo.ConfigService;
import com.ctrip.framework.apollo.model.ConfigChange;
import com.google.common.base.Strings;
import com.lifesense.opensource.commons.utils.WebResourceUtils;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.util.CollectionUtils;
import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.web.context.support.WebApplicationContextUtils;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletContextEvent;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* @author carter
*/
@Slf4j
public class ContextLoaderListener extends org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener {
private static final String APOLLO_LOG_BACK_CONFIG_KEY = "log4j2.xml";
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
final ServletContext servletContext = event.getServletContext();
final Config configFile = ConfigService.getAppConfig();
String xmlContent = configFile.getProperty(APOLLO_LOG_BACK_CONFIG_KEY, "");
if (!Strings.isNullOrEmpty(xmlContent)) {
LogbackLoader.initLogbackConfigFromXmlString(servletContext, xmlContent);
configFile.addChangeListener(configFileChangeEvent -> {
final Set<String> newValue = configFileChangeEvent.changedKeys();
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(newValue) && newValue.contains(APOLLO_LOG_BACK_CONFIG_KEY)) {
final ConfigChange change = configFileChangeEvent.getChange(APOLLO_LOG_BACK_CONFIG_KEY);
System.out.println(String.format("log4j2.ml changed:old:\n %s , new : \n %s ", change.getOldValue(), change.getNewValue()));
LogbackLoader.initLogbackConfigFromXmlString(servletContext, change.getNewValue());
}
});
}
}
}
小结
今天学会了:
- slf4j 的日志装配过程,分析了源码;
- 学会了使用代码的方式动态刷新 logback 的日志配置;
- 一种接入阿里云日志的实现方式。
- 常见的 slf4j 的日志组合方式的使用;
原创不易,转载请注明出处。

0104 代码方式动态刷新logback日志配置
背景
日志是一个系统或者说一个产品技术架构中重要组成部分。
常见的日志框架如下:
| 日志框架 | 说明 | 跟slf4j集成所需依赖 |
|---|---|---|
| slf4j | 日志门面,具体实现由程序决定 | |
| jcl | commons-logging |
jcl-over-slf4j |
| jul | jdk-logging | slf4j-api jul-to-slf4j slf4j-jdk14 |
| log4j | log4j | slf4j-api log4j-over-slf4j slf4j-log4j12 |
| log4j2 | log4j-api,log4j-core | slf4j-api log4j-slf4j-impl |
| logback | logback-core,logback-classic | slf4j-api |
slf4j-logback的启动过程
一般使用slf4j来操作日志:
private static final Logger LOGGER =
LoggerFactory.getLogger(LogbackAppenderExample.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
LOGGER.trace("trace log");
LOGGER.debug("debug log");
LOGGER.info("info log");
LOGGER.warn("warn log");
LOGGER.error("error log");
LOGGER.error("error log xxx");
LOGGER.error("error log yyy");
LOGGER.error("error log zzz");
LOGGER.error("error log aaa");
}通过这个来跟踪Logger的初始过程;
1 LoggerFactory.getLogger
代码如下:
public static Logger getLogger(Class<?> clazz) {
Logger logger = getLogger(clazz.getName());
if (DETECT_LOGGER_NAME_MISMATCH) {
Class<?> autoComputedCallingClass = Util.getCallingClass();
if (autoComputedCallingClass != null && nonMatchingClasses(clazz, autoComputedCallingClass)) {
Util.report(String.format("Detected logger name mismatch. Given name: \"%s\"; computed name: \"%s\".", logger.getName(),
autoComputedCallingClass.getName()));
Util.report("See " + LOGGER_NAME_MISMATCH_URL + " for an explanation");
}
}
return logger;
}过程:
| 步骤 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 获取得到Logger对象 |
| 2 | 如果有设置系统属性 slf4j.detectLoggerNameMismatch=true 则找到调用getLogger方法的类名 如果跟传入的类名不一致,则给出警告,给的类和调用方法的类不一致,并给出文档地址 |
| 3 | 返回Logger对象 |
2 getLogger(clazz.getName())
通过类名得到Logger
代码如下:
public static Logger getLogger(String name) {
ILoggerFactory iLoggerFactory = getILoggerFactory();
return iLoggerFactory.getLogger(name);
}核心步骤
| 序号 | 步骤 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 得到ILggerFactory对象 |
| 2 | 通过工厂,传入名字,得到Logger对象 |
3 getILoggerFactory()
得到日志工厂
代码如下:
public static ILoggerFactory getILoggerFactory() {
if (INITIALIZATION_STATE == UNINITIALIZED) {
synchronized (LoggerFactory.class) {
if (INITIALIZATION_STATE == UNINITIALIZED) {
INITIALIZATION_STATE = ONGOING_INITIALIZATION;
performInitialization();
}
}
}
switch (INITIALIZATION_STATE) {
case SUCCESSFUL_INITIALIZATION:
return StaticLoggerBinder.getSingleton().getLoggerFactory();
case NOP_FALLBACK_INITIALIZATION:
return NOP_FALLBACK_FACTORY;
case FAILED_INITIALIZATION:
throw new IllegalStateException(UNSUCCESSFUL_INIT_MSG);
case ONGOING_INITIALIZATION:
// support re-entrant behavior.
// See also http://jira.qos.ch/browse/SLF4J-97
return SUBST_FACTORY;
}
throw new IllegalStateException("Unreachable code");
}核心步骤:
| 序号 | 步骤 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 如果初始化状态值为 未初始化 同步加锁 synchronized(LoggerFactory.class) 再次判断 初始化状态值为 未初始化,如果是: 设置初始化状态值为 正在初始化 然后 执行初始化 _performInitialization_() |
| 2 | 然后根据初始化状态的条件做不同的处理 如果 初始化失败,抛出异常,并提示哪里失败了 如果 正在初始化, 返回替代工厂SubstituteLoggerFactory,日志一般也是委托给NOPLogger 如果 空回退初始化 返回空的工厂 NOPLoggerFactory,不输出日志的空实现 如果 成功初始化,调用StaticLoggerBinder.getLoggerFactory返回工厂 如果不在以上的状态,直接抛出异常,无法抵达的code; |
4 _performInitialization_()
执行初始化
代码:
private final static void performInitialization() {
bind();
if (INITIALIZATION_STATE == SUCCESSFUL_INITIALIZATION) {
versionSanityCheck();
}
}核心步骤
| 序号 | 步骤说明 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 绑定 |
| 2 | 如果初始化成功,则进行版本明智检查 |
5 bind()
绑定
代码:
private final static void bind() {
try {
Set<URL> staticLoggerBinderPathSet = findPossibleStaticLoggerBinderPathSet();
reportMultipleBindingAmbiguity(staticLoggerBinderPathSet);
// the next line does the binding
StaticLoggerBinder.getSingleton();
INITIALIZATION_STATE = SUCCESSFUL_INITIALIZATION;
reportActualBinding(staticLoggerBinderPathSet);
fixSubstitutedLoggers();
playRecordedEvents();
SUBST_FACTORY.clear();
} catch (NoClassDefFoundError ncde) {
String msg = ncde.getMessage();
if (messageContainsOrgSlf4jImplStaticLoggerBinder(msg)) {
INITIALIZATION_STATE = NOP_FALLBACK_INITIALIZATION;
Util.report("Failed to load class \"org.slf4j.impl.StaticLoggerBinder\".");
Util.report("Defaulting to no-operation (NOP) logger implementation");
Util.report("See " + NO_STATICLOGGERBINDER_URL + " for further details.");
} else {
failedBinding(ncde);
throw ncde;
}
} catch (java.lang.NoSuchMethodError nsme) {
String msg = nsme.getMessage();
if (msg != null && msg.contains("org.slf4j.impl.StaticLoggerBinder.getSingleton()")) {
INITIALIZATION_STATE = FAILED_INITIALIZATION;
Util.report("slf4j-api 1.6.x (or later) is incompatible with this binding.");
Util.report("Your binding is version 1.5.5 or earlier.");
Util.report("Upgrade your binding to version 1.6.x.");
}
throw nsme;
} catch (Exception e) {
failedBinding(e);
throw new IllegalStateException("Unexpected initialization failure", e);
}
}关键步骤
| 序号 | 步骤 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 找到可能的静态日志绑定器的路径集合findPossibleStaticLoggerBinderPathSet() |
| 2 | 如果日志有多个绑定器,打印到控制台 如果是android平台,忽略 依次打印出多个日志绑定器,并给出文档提示 |
| 3 | 获得唯一的静态日志绑定器StaticLoggerBinder.getSingleton() 绑定器内部持有LoggerContext和ContextSelectorStaticBinder |
| 4 | 设置初始化状态为成功 |
| 5 | 打印出实际的日志绑定器 ContextSelectorStaticBinder |
| 6 | 设置SubstitutedLogger的委托为实际的Logger; _fixSubstitutedLoggers_() |
| 7 | 播放记录的事件 playRecordedEvents() |
| 8 | 清空委托工厂 SubstituteLoggerFactory |
6 findPossibleStaticLoggerBinderPathSet()
找到可能的静态日志绑定器的路径
代码:
**
static Set<URL> findPossibleStaticLoggerBinderPathSet() {
// use Set instead of list in order to deal with bug #138
// LinkedHashSet appropriate here because it preserves insertion order during iteration
Set<URL> staticLoggerBinderPathSet = new LinkedHashSet<URL>();
try {
ClassLoader loggerFactoryClassLoader = LoggerFactory.class.getClassLoader();
Enumeration<URL> paths;
if (loggerFactoryClassLoader == null) {
paths = ClassLoader.getSystemResources(STATIC_LOGGER_BINDER_PATH);
} else {
paths = loggerFactoryClassLoader.getResources(STATIC_LOGGER_BINDER_PATH);
}
while (paths.hasMoreElements()) {
URL path = paths.nextElement();
staticLoggerBinderPathSet.add(path);
}
} catch (IOException ioe) {
Util.report("Error getting resources from path", ioe);
}
return staticLoggerBinderPathSet;
}关键步骤:
| 序号 | 步骤 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 如果LoggerFactory的类加载器为空,系统类加载器得到 org/slf4j/impl/StaticLoggerBinder.class 这个文件 分布在不同的jar中,可能有多个; |
| 2 | 如果不为空,则通过LoggerFactoryLoader找到 org/slf4j/impl/StaticLoggerBinder.class 这个文件 |
| 3 | 把这些class对应的url汇总到结合中返回 |
7 playRecordedEvents()
放映记录的事件
代码:
private static void playRecordedEvents() {
List<SubstituteLoggingEvent> events = SUBST_FACTORY.getEventList();
if (events.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < events.size(); i++) {
SubstituteLoggingEvent event = events.get(i);
SubstituteLogger substLogger = event.getLogger();
if( substLogger.isDelegateNOP()) {
break;
} else if (substLogger.isDelegateEventAware()) {
if (i == 0)
emitReplayWarning(events.size());
substLogger.log(event);
} else {
if(i == 0)
emitSubstitutionWarning();
Util.report(substLogger.getName());
}
}
}关键步骤:
| 序号 | 步骤 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 得到委托日志工厂的事件,如果为空,则结束 |
| 2 | 如果事件不为空,取出来, 如果委托的日志有空日志,中断 如果委托的日志是委托事件, 打印日志,并打印出播放的警告 否则,警告委托的日志不可用,并打印出日志的名称 |
8 versionSanityCheck()
得到StaticLoggerBinder的版本,并进行判断是否合适。
LoggerFactory放了允许使用的StaticLoggerBinder的版本,如果不合适,会答应出警告。
源码:
private final static void versionSanityCheck() {
try {
String requested = StaticLoggerBinder.REQUESTED_API_VERSION;
boolean match = false;
for (String aAPI_COMPATIBILITY_LIST : API_COMPATIBILITY_LIST) {
if (requested.startsWith(aAPI_COMPATIBILITY_LIST)) {
match = true;
}
}
if (!match) {
Util.report("The requested version " + requested + " by your slf4j binding is not compatible with "
+ Arrays.asList(API_COMPATIBILITY_LIST).toString());
Util.report("See " + VERSION_MISMATCH + " for further details.");
}
} catch (java.lang.NoSuchFieldError nsfe) {
// given our large user base and SLF4J''s commitment to backward
// compatibility, we cannot cry here. Only for implementations
// which willingly declare a REQUESTED_API_VERSION field do we
// emit compatibility warnings.
} catch (Throwable e) {
// we should never reach here
Util.report("Unexpected problem occured during version sanity check", e);
}
}9 StaticLoggerBinder.init()
静态日志绑定器的初始化
代码:
void init() {
try {
try {
new ContextInitializer(defaultLoggerContext).autoConfig();
} catch (JoranException je) {
Util.report("Failed to auto configure default logger context", je);
}
// logback-292
if (!StatusUtil.contextHasStatusListener(defaultLoggerContext)) {
StatusPrinter.printInCaseOfErrorsOrWarnings(defaultLoggerContext);
}
contextSelectorBinder.init(defaultLoggerContext, KEY);
initialized = true;
} catch (Exception t) { // see LOGBACK-1159
Util.report("Failed to instantiate [" + LoggerContext.class.getName() + "]", t);
}
}核心过程
| 序号 | 步骤 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 新建上下文初始化器,然后自动配置; new ContextInitializer(defaultLoggerContext).autoConfig(); |
| 2 | 如果没有配置状态监听器,则打印出警告 |
| 3 | 上下文选择绑定器初始化 |
10 ContextInitializer.autoConfig();
自动配置上下文
代码:
public void autoConfig() throws JoranException {
StatusListenerConfigHelper.installIfAsked(loggerContext);
URL url = findURLOfDefaultConfigurationFile(true);
if (url != null) {
configureByResource(url);
} else {
Configurator c = EnvUtil.loadFromServiceLoader(Configurator.class);
if (c != null) {
try {
c.setContext(loggerContext);
c.configure(loggerContext);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new LogbackException(String.format("Failed to initialize Configurator: %s using ServiceLoader", c != null ? c.getClass()
.getCanonicalName() : "null"), e);
}
} else {
BasicConfigurator basicConfigurator = new BasicConfigurator();
basicConfigurator.setContext(loggerContext);
basicConfigurator.configure(loggerContext);
}
}
}核心步骤
| 序号 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 如果没有,安装状态监听器 |
| 2 | 找到默认的配置文件或者URL,一次按照系统属性 logback.configurationFile查找 按照logback-test.xml 按照logback.groovy 按照logback.xml 得到配置文件 |
| 3 | 如果找到了,configureByResource(url); |
| 4 | 否则,按照spi的方式找到Configurator的实现类,设置上下文,进行配置 |
| 如果spi方式拿不到,则使用缺省的BasicConfigurator(里面只配置了一个控制台) 设置上下文,进行配置 |
11 StaticLoggerBinder.getLoggerFactory
通过静态日志绑定器得到日志工厂,实现类是 LoggerContext;
源码:
public ILoggerFactory getLoggerFactory() {
if (!initialized) {
return defaultLoggerContext;
}
if (contextSelectorBinder.getContextSelector() == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("contextSelector cannot be null. See also " + NULL_CS_URL);
}
return contextSelectorBinder.getContextSelector().getLoggerContext();
}核心流程:
| 序号 | 步骤 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 如果没有初始化,返回默认的LoggerContext |
| 2 | 如果ContextSelectBinder不为空,得到ContextSeleter |
| 3 | 通过ContextSelector得到LoggerContext; |
12 iLoggerFactory.getLogger(name)
这是一个接口,直接得到一个Logger实例;
从上面的代码之后,这里的实例应该是一个LoggerContext对象
这个对象是核心,所有的日志动作都在里面;
logback-aliyun-appender
直接把日志接入到阿里云
对于初创企业来说,直接使用阿里云的日志服务非常方便,减少了自己搭建ELK的运维成本,直接按量付费,非常方便,我贴一下我的接入过程;
引入依赖:
<!--日志-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.aliyun.openservices</groupId>
<artifactId>aliyun-log-logback-appender</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--spring日志桥接,使用的commoon-logging-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>jcl-over-slf4j</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--log4j日志桥接,zk使用的log4j-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-over-slf4j</artifactId>
</dependency>然后按照 代码刷新logback日志配置的方法,把日志配置放到apollo,启动的时候就可以接入到阿里云日志了。
贴一下配置:
<configuration>
<!--为了防止进程退出时,内存中的数据丢失,请加上此选项-->
<shutdownHook/>
<appender name="loghubAppender">
<!--必选项-->
<!-- 账号及网络配置 -->
<endpoint>cn-xxx.log.aliyuncs.com</endpoint>
<accessKeyId>xxxxx</accessKeyId>
<accessKeySecret>xxxxx</accessKeySecret>
<!-- sls 项目配置 -->
<project>ts-app-xxx</project>
<logStore>ts-app-xxx</logStore>
<!--必选项 (end)-->
<!-- 可选项 -->
<topic>topic2</topic>
<source>source2</source>
<!-- 可选项 详见 ''参数说明''-->
<totalSizeInBytes>104857600</totalSizeInBytes>
<maxBlockMs>60</maxBlockMs>
<ioThreadCount>2</ioThreadCount>
<batchSizeThresholdInBytes>524288</batchSizeThresholdInBytes>
<batchCountThreshold>4096</batchCountThreshold>
<lingerMs>2000</lingerMs>
<retries>3</retries>
<baseRetryBackoffMs>100</baseRetryBackoffMs>
<maxRetryBackoffMs>100</maxRetryBackoffMs>
<!-- 可选项 通过配置 encoder 的 pattern 自定义 log 的格式 -->
<encoder>
<pattern>%d %-5level [%thread] %logger{0}: %msg</pattern>
</encoder>
<!-- 可选项 设置时间格式 -->
<timeFormat>yyyy-MM-dd''T''HH:mmZ</timeFormat>
<!-- 可选项 设置时区 -->
<timeZone>Asia/Shanghai</timeZone>
<filter><!-- 只打印INFO级别的日志 -->
<level>INFO</level>
<!-- <onMatch>ACCEPT</onMatch>-->
<!-- <onMismatch>DENY</onMismatch>-->
</filter>
<!-- <mdcFields>THREAD_ID,MDC_KEY</mdcFields>-->
</appender>
<appender name="STDOUT">
<encoder>
<pattern>%d{HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%thread] %-5level %logger - %msg %X{THREAD_ID} %n</pattern>
</encoder>
</appender>
<!-- 可用来获取StatusManager中的状态 -->
<statusListener/>
<!-- 解决debug模式下循环发送的问题 -->
<logger name="org.apache.http.impl.conn.Wire" level="WARN" />
<root>
<level value="DEBUG"/>
<appender-ref ref="loghubAppender"/>
<appender-ref ref="STDOUT"/>
</root>
</configuration>
代码刷新logback日志配置
主要是模仿LogbackLister的实现细节来模仿:
简单的贴一下我的实现代码:
package com.lifesense.opensource.spring;
import ch.qos.logback.classic.BasicConfigurator;
import ch.qos.logback.classic.LoggerContext;
import ch.qos.logback.classic.joran.JoranConfigurator;
import ch.qos.logback.core.joran.spi.JoranException;
import ch.qos.logback.core.util.StatusPrinter;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
import org.springframework.util.ClassUtils;
import org.springframework.util.ReflectionUtils;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* @author carter
*/
public class LogbackLoader {
private static final String DEFAULT_LOG_BACK_XML = "<configuration>" +
"<shutdownHook class=\"ch.qos.logback.core.hook.DelayingShutdownHook\"/>" +
"<appender name=\"STDOUT\" class=\"ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender\">" +
"<encoder><pattern>%d{HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%thread] %-5level %logger - %msg %X{THREAD_ID} %n</pattern></encoder>" +
"</appender>" +
"<statusListener class=\"ch.qos.logback.core.status.OnConsoleStatusListener\"/>" +
"<logger name=\"org.apache.http.impl.conn.Wire\" level=\"WARN\" />" +
"<root><level value=\"DEBUG\"/><appender-ref ref=\"STDOUT\"/>" +
"</root></configuration>";
/**
* 初始化日志配置
*/
public static void initLogbackWithoutConfigFile(ServletContext servletContext) {
initLogbackConfigFromXmlString(servletContext, DEFAULT_LOG_BACK_XML);
}
public static void initLogbackConfigFromXmlString(ServletContext servletContext, String xmlStr) {
System.out.println("Initializing Logback from [\n" + xmlStr + "\n]");
LoggerContext loggerContext = (LoggerContext) LoggerFactory.getILoggerFactory();
Assert.notNull(loggerContext, "获取不到LoggerContext");
loggerContext.getStatusManager().clear();
loggerContext.reset();
//安装默认的日志配置
if (StringUtils.isBlank(xmlStr)) {
BasicConfigurator basicConfigurator = new BasicConfigurator();
basicConfigurator.setContext(loggerContext);
basicConfigurator.configure(loggerContext);
return;
}
//按照传入的配置文件来配置
JoranConfigurator configurator = new JoranConfigurator();
configurator.setContext(loggerContext);
InputStream in = new ByteArrayInputStream(xmlStr.getBytes());
try {
configurator.doConfigure(in);
} catch (JoranException e) {
System.out.println("初始化配置logback发生错误");
e.printStackTrace();
}
//If SLF4J''s java.util.logging bridge is available in the classpath, install it. This will direct any messages
//from the Java Logging framework into SLF4J. When logging is terminated, the bridge will need to be uninstalled
try {
Class<?> julBridge = ClassUtils.forName("org.slf4j.bridge.SLF4JBridgeHandler", ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());
Method removeHandlers = ReflectionUtils.findMethod(julBridge, "removeHandlersForRootLogger");
if (removeHandlers != null) {
servletContext.log("Removing all previous handlers for JUL to SLF4J bridge");
ReflectionUtils.invokeMethod(removeHandlers, null);
}
Method install = ReflectionUtils.findMethod(julBridge, "install");
if (install != null) {
servletContext.log("Installing JUL to SLF4J bridge");
ReflectionUtils.invokeMethod(install, null);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ignored) {
//Indicates the java.util.logging bridge is not in the classpath. This is not an indication of a problem.
servletContext.log("JUL to SLF4J bridge is not available on the classpath");
}
StatusPrinter.print(loggerContext);
}
}
在springmvc上下文启动的时候,可以使用代码的方式加载默认的日志配置;
启动完成之后,加上apollo的配置监听器,这样就可以在apollo中实时的修改日志的配置文件,代码实时生效。
package com.lifesense.opensource.spring;
import com.ctrip.framework.apollo.Config;
import com.ctrip.framework.apollo.ConfigService;
import com.ctrip.framework.apollo.model.ConfigChange;
import com.google.common.base.Strings;
import com.lifesense.opensource.commons.utils.WebResourceUtils;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.util.CollectionUtils;
import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.web.context.support.WebApplicationContextUtils;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletContextEvent;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* @author carter
*/
@Slf4j
public class ContextLoaderListener extends org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener {
private static final String APOLLO_LOG_BACK_CONFIG_KEY = "log4j2.xml";
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
final ServletContext servletContext = event.getServletContext();
final Config configFile = ConfigService.getAppConfig();
String xmlContent = configFile.getProperty(APOLLO_LOG_BACK_CONFIG_KEY, "");
if (!Strings.isNullOrEmpty(xmlContent)) {
LogbackLoader.initLogbackConfigFromXmlString(servletContext, xmlContent);
configFile.addChangeListener(configFileChangeEvent -> {
final Set<String> newValue = configFileChangeEvent.changedKeys();
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(newValue) && newValue.contains(APOLLO_LOG_BACK_CONFIG_KEY)) {
final ConfigChange change = configFileChangeEvent.getChange(APOLLO_LOG_BACK_CONFIG_KEY);
System.out.println(String.format("log4j2.ml changed:old:\n %s , new : \n %s ", change.getOldValue(), change.getNewValue()));
LogbackLoader.initLogbackConfigFromXmlString(servletContext, change.getNewValue());
}
});
}
}
}
小结
今天学会了:
- slf4j的日志装配过程,分析了源码;
- 学会了使用代码的方式动态刷新logback的日志配置;
- 一种接入阿里云日志的实现方式。
- 常见的slf4j的日志组合方式的使用;
原创不易,转载请注明出处,欢迎沟通交流。

Java 日志框架 - logback 配置文件多环境日志配置(开发、测试、生产)(原始解决方法)
说明:这种方式应该算是最通用的,原理是通过判断标签实现。
<!-- if-then form -->
<if condition="some conditional expression">
<then>
...
</then>
</if>
<!-- if-then-else form -->
<if condition="some conditional expression">
<then>
...
</then>
<else>
...
</else>
</if>不过判断条件需要依赖 Janino library
<configuration debug="true"> <if condition=''property("HOSTNAME").contains("torino")''> <then> <appender name="CON" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender"> <encoder> <pattern>%d %-5level %logger{35} - %msg %n</pattern> </encoder> </appender> <root> <appender-ref ref="CON" /> </root> </then> </if> <appender name="FILE" class="ch.qos.logback.core.FileAppender"> <file>${randomOutputDir}/conditional.log</file> <encoder> <pattern>%d %-5level %logger{35} - %msg %n</pattern> </encoder> </appender> <root level="ERROR"> <appender-ref ref="FILE" /> </root> </configuration>
参考:
https://logback.qos.ch/manual/configuration.html#conditional(官方参考文档)

Java日志配置 SLF4J + Logback
这是个大标题
log4j 的日志用起来不是很爽,因为没有 "{}" 占位符功能所以被我弃用了。
项目中还有log4j,参考 slf4j + log4j 的配置及引用
新项目可用 slf4j + logback ,因为听说 logback 很牛皮 =_=
slf4j + log4j 依赖
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.slf4j/slf4j-api -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId>
<version>1.7.28</version>
</dependency>
<!-- slf4j 与 log4j 的兼容插件,这样项目中就可以写 log4j的写法和 slf4j的写法 -->
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.slf4j/slf4j-log4j12 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId>
<version>1.7.28</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/log4j/log4j -->
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.17</version>
</dependency>
slf4j + log4j 的配置文件
详细可参考:https://www.jianshu.com/p/ccafda45bcea
#log4j.properties 文件放在src目录下自动加载
log4j.rootLogger=INFO, console, file
# 控制台(console)
log4j.appender.console=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.console.Threshold=DEBUG
log4j.appender.console.ImmediateFlush=true
log4j.appender.console.Target=System.err
log4j.appender.console.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.console.layout.ConversionPattern=[%-5p] %d(%r) ~~> [%t] %l: %m %x %n
#滚动日志文件
log4j.appender.file=org.apache.log4j.DailyRollingFileAppender
log4j.appender.file.Append=true
log4j.appender.file.DatePattern=''_'' yyyy-MM-dd-HH ''.log''
log4j.appender.file.File=./log/yuwan.log
log4j.appender.file.Threshold=INFO
log4j.appender.file.Encoding=UTF-8
log4j.appender.file.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.file.layout.ConversionPattern=[%-5p] %d(%r) ~~> [%t] %l: %m %x %n
使用方式
//引用
import org.apache.log4j.Logger;
//使用
static Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(AppMainOfServer.class);
slf4j + logback 依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
<version>1.2.3</version>
<!--<scope>test</scope>-->
</dependency>引用后的明细:

(自动引用了 slf4j-api 和 logback-core)
logback XML配置
把文件 logback.xml (logback-test.xml)放在src目录下(resources目录下)即可自动装载
详细配置可参考:https://blog.csdn.net/sinat_25076521/article/details/80513543
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<configuration scan="true" scanPeriod="60 seconds" debug="false">
<property name="logbackPath" value="./logs/track-server/" />
<property name="logFileName" value="track-server" />
<contextName>${logFileName}</contextName>
<!--输出到控制台-->
<appender name="console">
<encoder>
<pattern>%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} %contextName [%thread] %-5level %logger{8} ~> %msg%n</pattern>
</encoder>
</appender>
<!--输出到文件-->
<appender name="file">
<rollingPolicy>
<fileNamePattern>${logbackPath}${logFileName}.%d{yyyy-MM-dd}.log</fileNamePattern>
<maxHistory>30</maxHistory><!-- 只保留30天的日志 -->
<totalSizeCap>5GB</totalSizeCap><!-- 日志文件超过5G自动删除旧文件 -->
</rollingPolicy>
<encoder>
<pattern>%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%thread] %-5level %logger{8} ~> %msg%n</pattern>
</encoder>
</appender>
<root level="INFO">
<appender-ref ref="console"/>
<appender-ref ref="file"/>
</root>
<!-- JdbcTemplate SQL语句 DEBUG-->
<!--<logger name="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate" level="DEBUG"/>-->
<!-- JdbcTemplate SQL 参数值 TRACE-->
<!--<logger name="org.springframework.jdbc.core.StatementCreatorUtils" level="TRACE"/>-->
<!-- mybatis -->
<!--<logger name="com.btcgame.web.dao" level="@the.mybatis.log.level@"/>-->
<!-- druid配置 -->
<!--<logger name="druid.sql" level="@the.logback.level@"/>-->
<!--<logger name="druid.sql.DataSource" level="@the.logback.level@"/>-->
<!--<logger name="druid.sql.Statement" level="@the.logback.level@"/>-->
<!--<logger name="druid.sql.ResultSet" level="@the.logback.level@"/>-->
</configuration>
slf4j 使用方式
package com.*.tserver;
import com.*.*.exception.MessageException;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
/**
* @Author wenqiang [2019-09-09]
* @Date September, 09, Monday
* @Comment ...
*/
public class AppMainOfServer {
static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AppMainOfServer.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
//PropertyConfigurator.configure("classpath:log-config.properties");
System.err.println("~~~> hello!!");
try {
logger.info("hello word");
throw new MessageException("hello ME");
} catch (MessageException e) {
logger.error("error: {}", "MessageException", e);
}
//打印 Logback 内部状态
//LoggerContext lc = (LoggerContext) LoggerFactory.getILoggerFactory();
//StatusPrinter.print(lc);
}
}
今天的关于如何确定实际使用的日志配置源Logback?和日志的配置文件的分享已经结束,谢谢您的关注,如果想了解更多关于0104 代码方式动态刷新 logback 日志配置、0104 代码方式动态刷新logback日志配置、Java 日志框架 - logback 配置文件多环境日志配置(开发、测试、生产)(原始解决方法)、Java日志配置 SLF4J + Logback的相关知识,请在本站进行查询。
本文标签:





![[转帖]Ubuntu 安装 Wine方法(ubuntu如何安装wine)](https://www.gvkun.com/zb_users/cache/thumbs/4c83df0e2303284d68480d1b1378581d-180-120-1.jpg)

