如果您对OracleFor循环,字符串拼接,查找和oraclefor循环查询语句感兴趣,那么这篇文章一定是您不可错过的。我们将详细讲解OracleFor循环,字符串拼接,查找的各种细节,并对oracl
如果您对Oracle For 循环,字符串拼接,查找和oracle for循环查询语句感兴趣,那么这篇文章一定是您不可错过的。我们将详细讲解Oracle For 循环,字符串拼接,查找的各种细节,并对oracle for循环查询语句进行深入的分析,此外还有关于1.Python学习笔记:[Print()格式;缩进;变量命名;注释;字符串拼接;表达式和运算符;变量赋值;输入;强制类型转换;IF语句]、c++字符串拼接, 整数和字符串的转换,string, const char*, char[]类型之间的转换、C语言——字符串拼接、ES6 字符串拼接的实用技巧。
本文目录一览:- Oracle For 循环,字符串拼接,查找(oracle for循环查询语句)
- 1.Python学习笔记:[Print()格式;缩进;变量命名;注释;字符串拼接;表达式和运算符;变量赋值;输入;强制类型转换;IF语句]
- c++字符串拼接, 整数和字符串的转换,string, const char*, char[]类型之间的转换
- C语言——字符串拼接
- ES6 字符串拼接

Oracle For 循环,字符串拼接,查找(oracle for循环查询语句)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------xqp 20180209
begin
--找出有关这个配送单的相关记录,遍历
--一个配送单号可能由多个看板组成,
for curr in (select t.kanban_id,
t.plant_id,
t.item_id,
t.station_id,
t.kanban_group_qty,
t.ref_kb_dis_kid,
t.kanban_qty
from fy_ps_report_data t
where instr(concat(CONCAT('','', t.ref_kb_dis_kid), '',''),
concat(CONCAT('','', to_char(p_kid)), '','')) > 0) loop
if curr.ref_kb_dis_kid = to_char(p_kid) then
--当看板的配送单ID号跟P_kid相等时,直接改状态
ln_message_id := fy_ps_pck.update_ps_report_data(p_kanban_id => curr.kanban_id,
p_kanban_status => ''D'');
IF ln_message_id <> hcm_public_pck.g_success THEN
-- RETURN ln_message_id;
dbms_output.put_line(''-------error1--------'');
END IF;
else
--当不相等时,看板生成多个配送单号,取这个物料生成的配送数量
begin
select t.apply_dis_qty
into ln_ps_qty
from fy_ps_line t
where t.kid = p_kid
and t.item_id = curr.item_id
and t.plant_id = curr.plant_id;
exception
when others then
ln_ps_qty := 0;
end;
ln_message_id := fy_ps_pck.update_ps_report_data(p_kanban_id => curr.kanban_id,
p_kanban_qty => curr.kanban_qty -
ln_ps_qty);
IF ln_message_id <> hcm_public_pck.g_success THEN
-- RETURN ln_message_id;
dbms_output.put_line(''----error2--------'');
END IF;
end if;
end loop;
end;
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
![1.Python学习笔记:[Print()格式;缩进;变量命名;注释;字符串拼接;表达式和运算符;变量赋值;输入;强制类型转换;IF语句] 1.Python学习笔记:[Print()格式;缩进;变量命名;注释;字符串拼接;表达式和运算符;变量赋值;输入;强制类型转换;IF语句]](http://www.gvkun.com/zb_users/upload/2025/04/76e9449f-3bb6-4b05-b5c5-4ccf177e2f5f1745466549705.jpg)
1.Python学习笔记:[Print()格式;缩进;变量命名;注释;字符串拼接;表达式和运算符;变量赋值;输入;强制类型转换;IF语句]
一、Print()格式:
print() #等价于print(end="\n")print(''hello word'') 或 print("hello word")
print(''hello word\n''*8)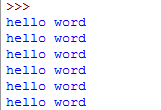
print(''hello word'')
print(''hello word'')
print(''hello word'')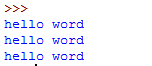
print(''hello word'',end=" ") #输出在同一行
print(''hello word'',end=" ")
print(''hello word'',end=" ")结果: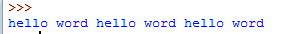
二、缩进:
- Tab不等于四个空格
- 缩进级别一致(官方建议四个空格)
三、变量命名:
- 具有描述性:Student_number(良好习惯)
- 支持中文命名,但不推荐
- 不能以数字开头
- 变量名只能数字字母组成,不可一是空格或特殊字符(#?<,./$%^#等)
- 保留字符不用做变量:print=5(不可)
- Python不分常量,变量。全部大写默认常量(STUDENT_NUMBER)
- Python区分大小写
四、注释:
单行注释:
#print()多行注释:(三引号。单引,或双引)
''''''print()
print()
print()''''''解释:
print() #打印多行打印:
msg=''''''hello word
hello word
hello word''''''
print(msg)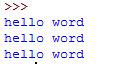
五、字符串类型(string):
字符串拼接:
print("good"+"well")
结果: 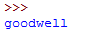
a=''123''
b=''abc''
c=''789''
d2=''---''.join([a,b,c])
print(d2) #123---abc---789 用---拼接(建议用这拼接)print(''helloworld''[2:]) #lloworld 这里和列表的切片操作是相同的print(''el'' in ''hello'') #True 成员运算符 - 如果字符串中包含给定的字符返回 True六、表达式和运算符:
算术运算符 : + - * / //(取整除,3//2=1) %(取余) **(次方)
赋值运算符: = 、+= -= *= /= %= //= **=
>>> num = 2
>>> num += 1 # 等价于 num = num + 1
>>> num -= 1 # 等价于 num = num - 1
>>> num *= 1 # 等价于 num = num * 1
>>> num /= 1 # 等价于 num = num / 1
>>> num //= 1 # 等价于 num = num // 1
>>> num %= 1 # 等价于 num = num % 1
>>> num **= 2 # 等价于 num = num ** 2比较运算符:>、 <、 >=、 <=、 ==、!=
逻辑运算符: not 、and、 or
>>> a > b and a < b # 如果两个操作数都是True,那么结果为True,否则结果为False。
False
>>> a > b or a < b # 如果有两个操作数至少有一个为True, 那么条件变为True,否则为False。
True
>>> not a > b # 反转操作的状态,操作数为True,则结果为False,反之则为True
False成员运算符: not in 、in (判断某个单词里是不是有某个字母)
>>> "h" in "hello" # 这里的意思是 “h” 在“Hello” 中,判断后结果为True
True
>>> "h" not in "hello" # 这里的意思是 “h” 不在“Hello” 中,判断后结果为False
False身份运算符: is、is not(讲数据类型时讲解,一般用来判断变量的数据类型)
>>> a=123
>>> b=123
>>> a is b
True
>>> a is not b
Falseprint(''3*4='',3*4)
x=3
y=4
print(''x*y='',x*y)
x=3
y=4
z=x*y
print(z)优先级用(): >>> (((2+3)*2+3)/2)*5
七、变量赋值:
name="梁志伟"
name2="小李"
print(name,name2)结果: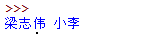
八、输入:
age=input(''你的年龄:'') #默认输入的是字符串
change=int(age)九、强制类型转换
>>> a=3
>>> int(a)
3
>>> str(a)
''3''
>>> float(3)
3.0十、IF语句:
if (3>2) and (4>2) : #and orif a<b<c : #在python可以if 1<=z<=5 :
print('''')
else :
print('''')
if score>90 :
print(''优秀'')
elif score>80 :
print(''良好'')
elif score>60 :
print(''及格'')
else :
print(''滚'')
#score=91 结果为:优秀![c++字符串拼接, 整数和字符串的转换,string, const char*, char[]类型之间的转换 c++字符串拼接, 整数和字符串的转换,string, const char*, char[]类型之间的转换](http://www.gvkun.com/zb_users/upload/2025/04/b279ea59-d253-4148-8e1d-8f86154a32c01745466550148.jpg)
c++字符串拼接, 整数和字符串的转换,string, const char*, char[]类型之间的转换
1. string字符串拼接
a. 拼接char指针(C - String)类型的字符串, 可以指定长度
如果没有指定长度,拼接C - String的起始位置到''\0''的位置
char a[] = { ''a'', ''b'', ''c'', ''d'', ''\0''};
const char *b = "wangjing";
s.append(a);
s.append(b);
s.append(a, 3);b. 拼接string类型的字符串
string c = "helloworld";
s.append(c);c. 拼接字符类型:第一个参数用于指定拼接该字符的个数
char ch = ''m'';
s.append(2, ch);2. 整数类型和字符串类型之间的转换
a. 整数类型转字符串类型
方法一:使用_itoa_s(int integer, const char* target, int scale)
第一个参数:需要转换成整形的数;第二个参数:转换后存储的地址;第三个参数:采用的进制
会自动在char* 后面加上''\0'',所以可以直接输出结果
int main() {
char numtochar[20];
_itoa_s(234, numtochar, 10);
cout << numtochar;
}方法二:采用sprintf_s(const char* target, ''%d'', int integer)字符串格式化函数
第一个参数,存储的目的地址,第二个参数:转换为整形,第三个参数:需要转换成整形的数
int main() {
char numtochar[20];
sprintf_s(numtochar, "%d", 234);
cout << numtochar;
}b. 字符串类型转整数
atio(const char* charnumber)
int main() {
char numtochar[20] = { ''1'', ''3'', ''5'', ''7''};
cout << atoi(numtochar);
}3. const char *,string,char[]类型之间的转换
注:对于string中第k个字符,可以使用string[k]和string.at[k]来访问
a. string 转 const char*
方法一:使用data()函数
int main() {
string m = "2342";
const char* p = m.data();
int k = 0;
while (p[k] != NULL) {
cout << p[k] << ",";
k++;
}
}方法二:使用c_str()函数
int main() {
string m = "2342";
const char* p = m.c_str();
int k = 0;
while (p[k] != NULL) {
cout << p[k] << ",";
k++;
}
// 直接使用cout << p更加简单方便
}b. string转char[](string 转char *,不需要指定const char类型)
调用string的copy函数:第一个参数为数组对象,第二个参数为长度,第三个参数为起始位置。
int main() {
string m = "2342";
char p[50] = { 0 };
m.copy(p, 4, 0);
int k = 0;
while (p[k] != NULL) {
cout << p[k] << ",";
k++;
}
// 直接使用cout << p更加简单方便
}初始化一个数组时,char类型,默认为''\0'',但是需要至少指定第一个,否则认为没有初始化。int类型默认为0
增强版:采用动态内存分配可以减小程序需要的内存空间
int main() {
string m = "2342";
int len = m.length() + 1;
char *p = new char[len];
m.copy(p, 4, 0);
p[len - 1] = ''\0'';
cout << p;
delete[] p;
// 直接使用cout << p更加简单方便
}c char[]和char *转string
直接赋值即可。
int main() {
const char *p = "wang";
const char q[] = "helloworld";
string a = p;
string b = q;
cout << a;
cout << b;
}
C语言——字符串拼接
字符串拼接:
char *value = malloc(strlen(basePath) + strlen(resourceDirectory) + strlen(PATH_SEPARATOR) + 1);
if (value == NULL) {
exit(1);
}
strcpy(value, basePath);
strcat(value, resourceDirectory);
strcat(value, PATH_SEPARATOR);
ES6 字符串拼接
ES6 引入模板字符串来简化了字符串的拼接
传统字符串拼接代码如下
var firstname="张"
var lastname="三"
var Splicing="我的姓"+firstname+"名字叫"+lastname
console.log(Splicing) //我的姓张名字叫三
使用模板字符串拼接
var newSplicing=`我姓${firstname}名${lastname}`
console.log(newSplicing) //我姓张名三
模板字符串还支持表达式和函数
function add (x,y){
return x+y;
}
var x=5;
var y=3;
var result=`5+3=${x+y}`;
console.log(result) //5+3=8
var result2=`5+3=${add(x,y)}`
console.log(result) //5+3=8
我们今天的关于Oracle For 循环,字符串拼接,查找和oracle for循环查询语句的分享已经告一段落,感谢您的关注,如果您想了解更多关于1.Python学习笔记:[Print()格式;缩进;变量命名;注释;字符串拼接;表达式和运算符;变量赋值;输入;强制类型转换;IF语句]、c++字符串拼接, 整数和字符串的转换,string, const char*, char[]类型之间的转换、C语言——字符串拼接、ES6 字符串拼接的相关信息,请在本站查询。
本文标签:



![[转帖]Ubuntu 安装 Wine方法(ubuntu如何安装wine)](https://www.gvkun.com/zb_users/cache/thumbs/4c83df0e2303284d68480d1b1378581d-180-120-1.jpg)

