最近很多小伙伴都在问Python在列表中查找元素并返回true或false和python查找列表中的元素这两个问题,那么本篇文章就来给大家详细解答一下,同时本文还将给你拓展2022-09-30:以下g
最近很多小伙伴都在问Python 在列表中查找元素并返回 true 或 false和python查找列表中的元素这两个问题,那么本篇文章就来给大家详细解答一下,同时本文还将给你拓展2022-09-30:以下go语言代码输出什么?A: true true false true false; B: true false false true false; C: true true、2022-10-28:以下go语言代码输出什么?A:false false;B:true false;C:true true;D:false true。 package main import “f、2023-07-19:布尔表达式 是计算结果不是 true 就是 false 的表达式 有效的表达式需遵循以下约定: ‘t‘,运算结果为 true ‘f‘,运算结果为 false ‘!(subExpr、Apache下commons-lang工具包下BooleanUtils类的xor(true, true, true)结果为false,为什么?等相关知识,下面开始了哦!
本文目录一览:- Python 在列表中查找元素并返回 true 或 false(python查找列表中的元素)
- 2022-09-30:以下go语言代码输出什么?A: true true false true false; B: true false false true false; C: true true
- 2022-10-28:以下go语言代码输出什么?A:false false;B:true false;C:true true;D:false true。 package main import “f
- 2023-07-19:布尔表达式 是计算结果不是 true 就是 false 的表达式 有效的表达式需遵循以下约定: ‘t‘,运算结果为 true ‘f‘,运算结果为 false ‘!(subExpr
- Apache下commons-lang工具包下BooleanUtils类的xor(true, true, true)结果为false,为什么?

Python 在列表中查找元素并返回 true 或 false(python查找列表中的元素)
如何解决Python 在列表中查找元素并返回 true 或 false
我一直在研究字符串列表中的元素。 我拿了一个带有数字(字符串)的文本,并尝试找到诸如“+”或“-”之类的符号 我的代码:
Lista=np.array([s for s in text])y=np.where(Lista==''+'')if y==[]: /*so,if it''s void*/print("any elements")else:print("yes")
我尝试这样做,因为我想创建一个计算器,现在我只能做 + 操作(在我的代码的第二部分,我使用 split("+") 并将 string 转换为 int )。 所以我想用 if,else,elif 创建一个类似于 switch case 的结构。类似:if (''+'') -> 做这个操作,else if (''-'')-> 做这个操作,ecc。 显然,我想创建 4 y=np.where(lista=''+''/=''-''/=''''...) 并为每个人创建 if else。因此,如果在口渴的情况下我找不到“+”:pass。如果在第二种情况下我没有找到“-”:pass。如果在第三种情况下我发现 '''' :做 moltiplicato。我尝试用 y==[] 或 y!=[] 来做这些事情。当我打印 y=np.where(lista=''+'') 的结果时,我看到它返回 array[1] 或 array[],但是如果我尝试将其作为条件,则它不起作用.
示例。在我的计算器中,我写了 4+5。 4+5 它保存在一个名为 text 的 var 中。我在 Lista=np.array([s for s in text]) 中转换 var 文本。 在我尝试在 Lista 中搜索符号 ''+'' 后,y=np.where(Lista==''+'')。在控制台中,我看到它位于第一个位置,因此在数组 [1] 中。所以如果条件
if y==[]:print("the list it''s void")passelse: print("the elemnt it''s at firt position")Lista=np.array([s for s in text.split(''+'')])v=[int(v) for v in Lista]c=sum(v)print(c)
但是,当我写 4+5 时,在条件 y==[] 的情况下,它打印出列表是无效的,但它不是真的,因为在 arrayIndex 我看到在位置 y[1] 有一个 ''+ ''.
Java 代码示例。我想在 Python 中也有同样的 公共类 Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {boolean findSymbol=true;char [] p = {31,28,31,30,''-''};for (char c : p) {if (c == ''+'') {findSymbol= true;System.out.println("let''s do something");} elsefindSymbol = false;System.out.println("nope");if (c == ''-'') {findSymbol=true;System.out.println("let''s do something");}elsefindSymbol = false;System.out.println("nope");}}}
解决方法
Python 3.10 有一个 match 语句,它是 switch 的 Python 版本。
无论如何,正如您所说,您可以使用 if ... elif ... else:
if s==''+'':##handle additionelif s==''-'':##handle subtractionelif s==''*'':##handle multiplication##etcelse:##did not match any previous check,raise exception or something

2022-09-30:以下go语言代码输出什么?A: true true false true false; B: true false false true false; C: true true
2022-09-30:以下go语言代码输出什么?A: true true false true false; B: true false false true false; C: true true true false false;D: true true false true true。
package main
func main() {
var (
a int = 0
b int64 = 0
c interface{} = int(0)
d interface{} = int64(0)
)
println(c == 0)
println(c == a)
println(c == b)
println(d == b)
println(d == 0)
}
答案选A。第3个为false,是因为c是int类型,b是int64类型。第5个为false,那是因为d是int64类型,0是int类型,这个0很容易被当成无类型,会误认为是true。从这里可以看出,做比较的时候,是没有无类型的概念的。

2022-10-28:以下go语言代码输出什么?A:false false;B:true false;C:true true;D:false true。 package main import “f
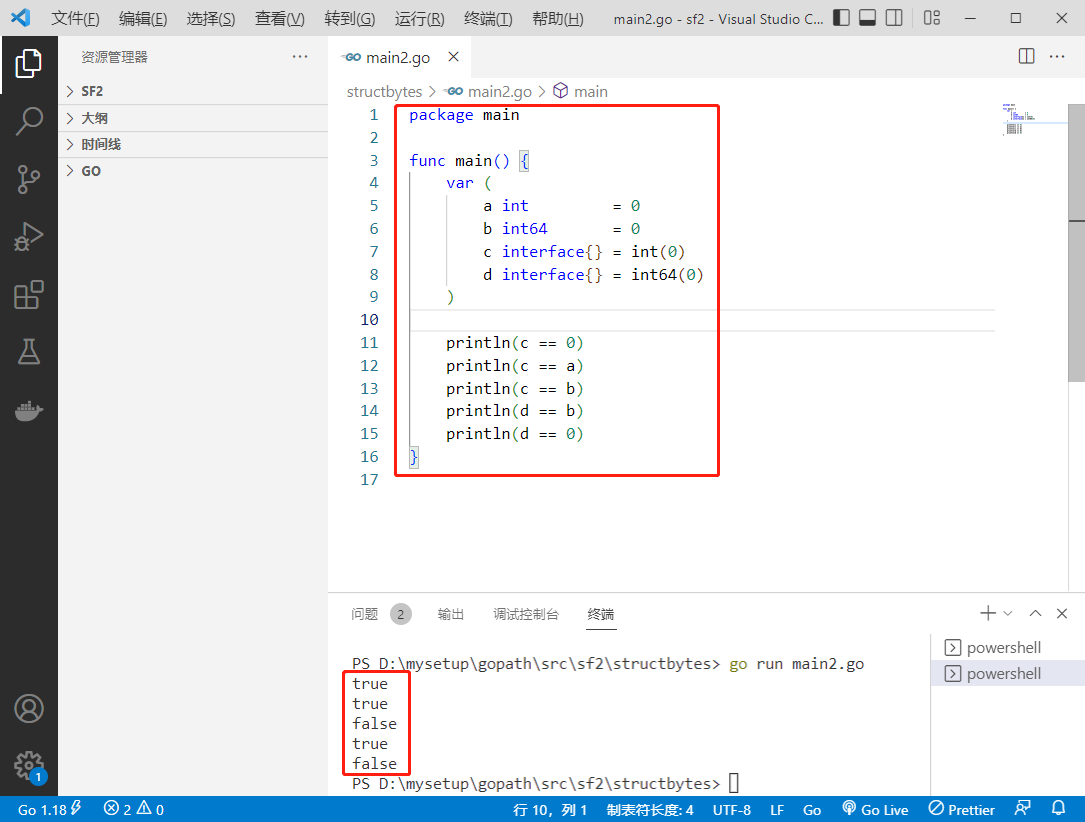
2022-10-28:以下go语言代码输出什么?A:false false;B:true false;C:true true;D:false true。
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
s := []string{"A", "B", "C"}
t := s[:1]
fmt.Println(&s[0] == &t[0])
u := append(s[:1], s[2:]...)
fmt.Println(&s[0] == &u[0])
}
答案选C。这里的关键点是 append(s[:1], s[2:]...) 会不会导致扩容。s[:1] 相当于 s[:1:3],即容量是也是 3,因此 append 一个元素(s[2:]...)并不会导致扩容,因此第一个元素还是原来 s[0] 的元素。 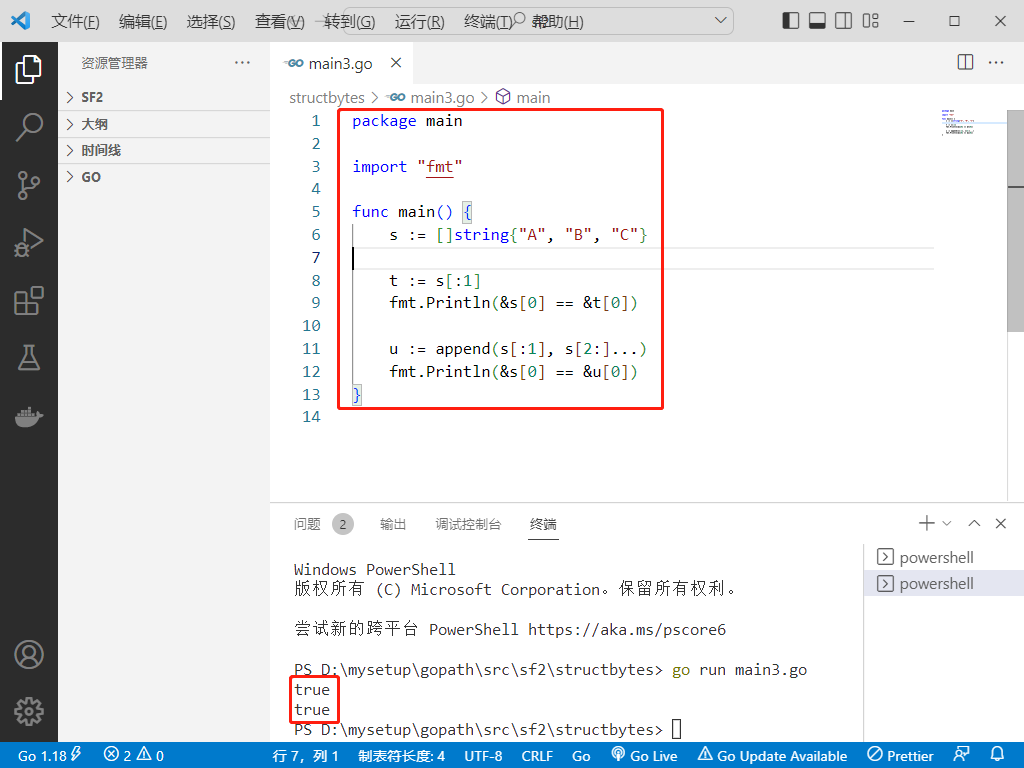

2023-07-19:布尔表达式 是计算结果不是 true 就是 false 的表达式 有效的表达式需遵循以下约定: ‘t‘,运算结果为 true ‘f‘,运算结果为 false ‘!(subExpr
2023-07-19:布尔表达式 是计算结果不是 true 就是 false 的表达式
有效的表达式需遵循以下约定:
''t'',运算结果为 true
''f'',运算结果为 false
''!(subExpr)'',运算过程为对内部表达式 subExpr 进行 逻辑非(NOT)运算
''&(subExpr1, subExpr2, ..., subExprn)''
运算过程为对 2 个或以上内部表达式
subExpr1, subExpr2, ..., subExprn 进行 逻辑与(AND)运算
''|(subExpr1, subExpr2, ..., subExprn)''
运算过程为对 2 个或以上内部表达式
subExpr1, subExpr2, ..., subExprn 进行 逻辑或(OR)运算
给你一个以字符串形式表述的 布尔表达式 expression,返回该式的运算结果。
题目测试用例所给出的表达式均为有效的布尔表达式,遵循上述约定。
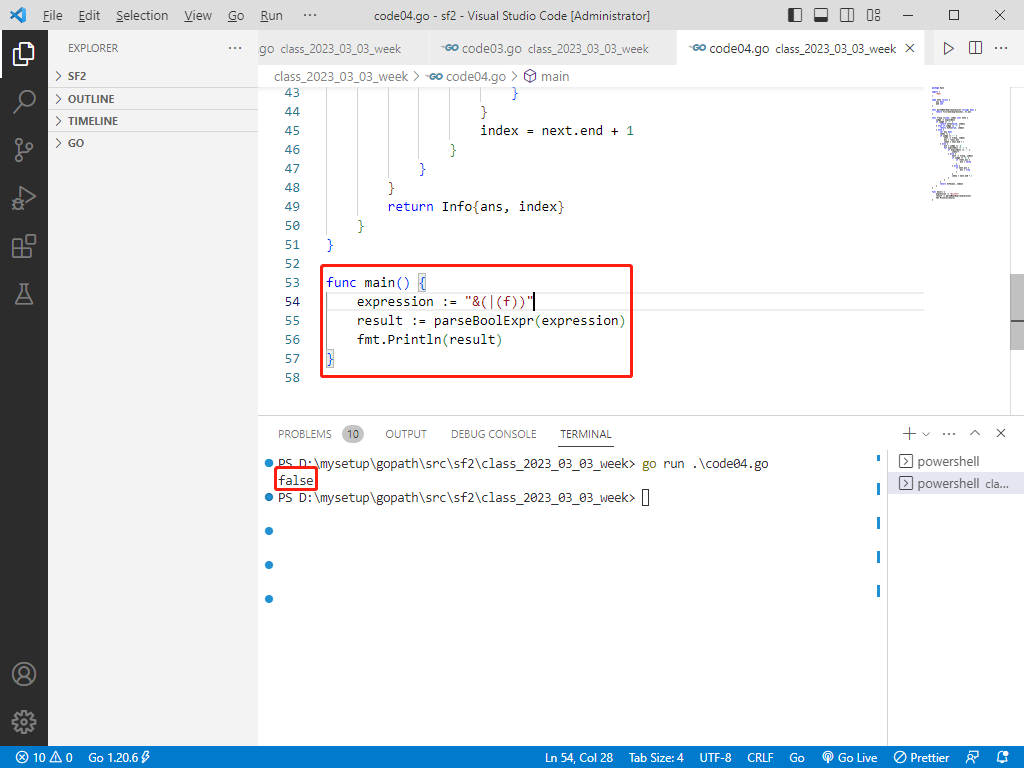
输入:expression = "&(|(f))"。
输出:false。
答案2023-07-19:
大体过程如下:
1.主函数main中定义了一个布尔表达式expression为"&(|(f))",该表达式需要计算结果。
2.调用parseBoolExpr函数,并将布尔表达式作为参数传递给它。
3.parseBoolExpr函数中定义了一个内部递归函数f,接收两个参数:表达式字符串exp和当前字符索引index。
4.函数f中首先获取当前索引处的字符judge,判断其类型。
5.如果judge为''t'',返回结果为true,索引保持不变。
6.如果judge为''f'',返回结果为false,索引保持不变。
7.如果judge为其他字符,进行进一步判断。
8.如果judge为''!'',则递归调用f函数,并将索引加1作为参数,获取递归调用的结果next,对该结果执行逻辑非运算,返回结果为!next.ans,索引更新为next.end + 1。
9.如果judge为''&''或''|'',则设置布尔变量ans为相应的值(true或false),并在循环中处理多个子表达式。
10.在循环中,当当前字符不是'')''时,执行以下操作:
- 如果当前字符是'','',则将索引加1,跳过逗号字符。
- 否则,递归调用`f`函数,并将当前索引作为参数获取递归结果`next`。
- 根据父表达式的运算符进行相应的逻辑运算,更新布尔变量`ans`的值。
- 更新索引为`next.end + 1`。
11.循环结束后,返回结果为Info{ans, index},其中ans为布尔表达式的计算结果,index为当前索引。
12.返回到parseBoolExpr函数,获取f函数的结果Info,返回Info.ans作为布尔表达式的最终计算结果。
13.输出最终结果。根据给定的表达式"&(|(f))",计算结果为false,打印结果false。
时间复杂度:假设表达式字符串的长度为n,递归过程涉及到遍历字符串中的每个字符,因此时间复杂度为O(n)。
空间复杂度:递归调用过程中会使用额外的栈空间来保存递归的状态,最坏情况下递归的深度可以达到n,因此空间复杂度为O(n)。
go完整代码如下:
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
type Info struct {
ans bool
end int
}
func parseBoolExpr(expression string) bool {
return f([]rune(expression), 0).ans
}
func f(exp []rune, index int) Info {
judge := exp[index]
if judge == ''f'' {
return Info{false, index}
} else if judge == ''t'' {
return Info{true, index}
} else {
var ans bool
index += 2
if judge == ''!'' {
next := f(exp, index)
ans = !next.ans
index = next.end + 1
} else {
ans = judge == ''&''
for exp[index] != '')'' {
if exp[index] == '','' {
index++
} else {
next := f(exp, index)
if judge == ''&'' {
if !next.ans {
ans = false
}
} else {
if next.ans {
ans = true
}
}
index = next.end + 1
}
}
}
return Info{ans, index}
}
}
func main() {
expression := "&(|(f))"
result := parseBoolExpr(expression)
fmt.Println(result)
}
rust代码如下:
fn main() {
let expression = "&(|(f))";
let result = parse_bool_expr(expression.to_string());
println!("{}", result);
}
fn parse_bool_expr(expression: String) -> bool {
let exp: Vec<char> = expression.chars().collect();
let info = f(&exp, 0);
info.ans
}
struct Info {
ans: bool,
end: usize,
}
fn f(exp: &[char], index: usize) -> Info {
let judge = exp[index];
if judge == ''f'' {
return Info {
ans: false,
end: index,
};
} else if judge == ''t'' {
return Info {
ans: true,
end: index,
};
} else {
let mut ans: bool;
let mut index = index + 2;
if judge == ''!'' {
let next = f(exp, index);
ans = !next.ans;
index = next.end + 1;
} else {
ans = judge == ''&'';
while exp[index] != '')'' {
if exp[index] == '','' {
index += 1;
} else {
let next = f(exp, index);
if judge == ''&'' {
if !next.ans {
ans = false;
}
} else {
if next.ans {
ans = true;
}
}
index = next.end + 1;
}
}
}
Info { ans, end: index }
}
}

c++完整代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct Info {
bool ans;
// 结束下标!
int end;
Info(bool a, int e) {
ans = a;
end = e;
}
};
Info f(const string& exp, int index) {
char judge = exp[index];
if (judge == ''f'') {
return Info(false, index);
}
else if (judge == ''t'') {
return Info(true, index);
}
else {
// !
// &
// |
// 再说!
bool ans;
// ! ( ?
// i i+1 i+2
// & ( ?
// i i+1 i+2
// | ( ?
// i i+1 i+2
index += 2;
if (judge == ''!'') {
// ! ( ?...... )
// i i+1 i+2
Info next = f(exp, index);
ans = !next.ans;
index = next.end + 1;
}
else {
// &
// i
// judge == ''&'' 或者 judge == ''|''
ans = judge == ''&'';
while (exp[index] != '')'') {
if (exp[index] == '','') {
index++;
}
else {
Info next = f(exp, index);
if (judge == ''&'') {
if (!next.ans) {
ans = false;
}
}
else {
if (next.ans) {
ans = true;
}
}
index = next.end + 1;
}
}
}
return Info(ans, index);
}
}
bool parseBoolExpr(const string& expression) {
return f(expression, 0).ans;
}
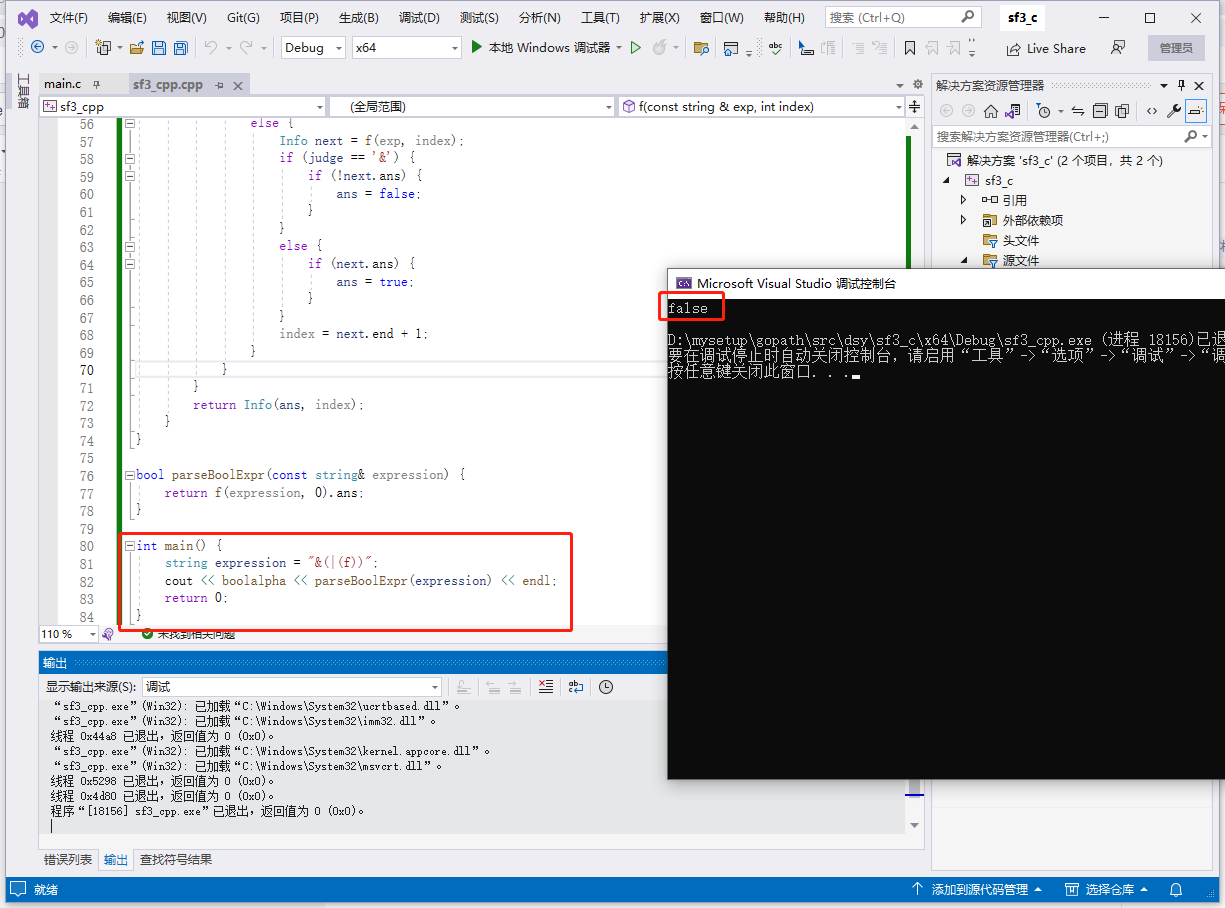
int main() {
string expression = "&(|(f))";
cout << boolalpha << parseBoolExpr(expression) << endl;
return 0;
}
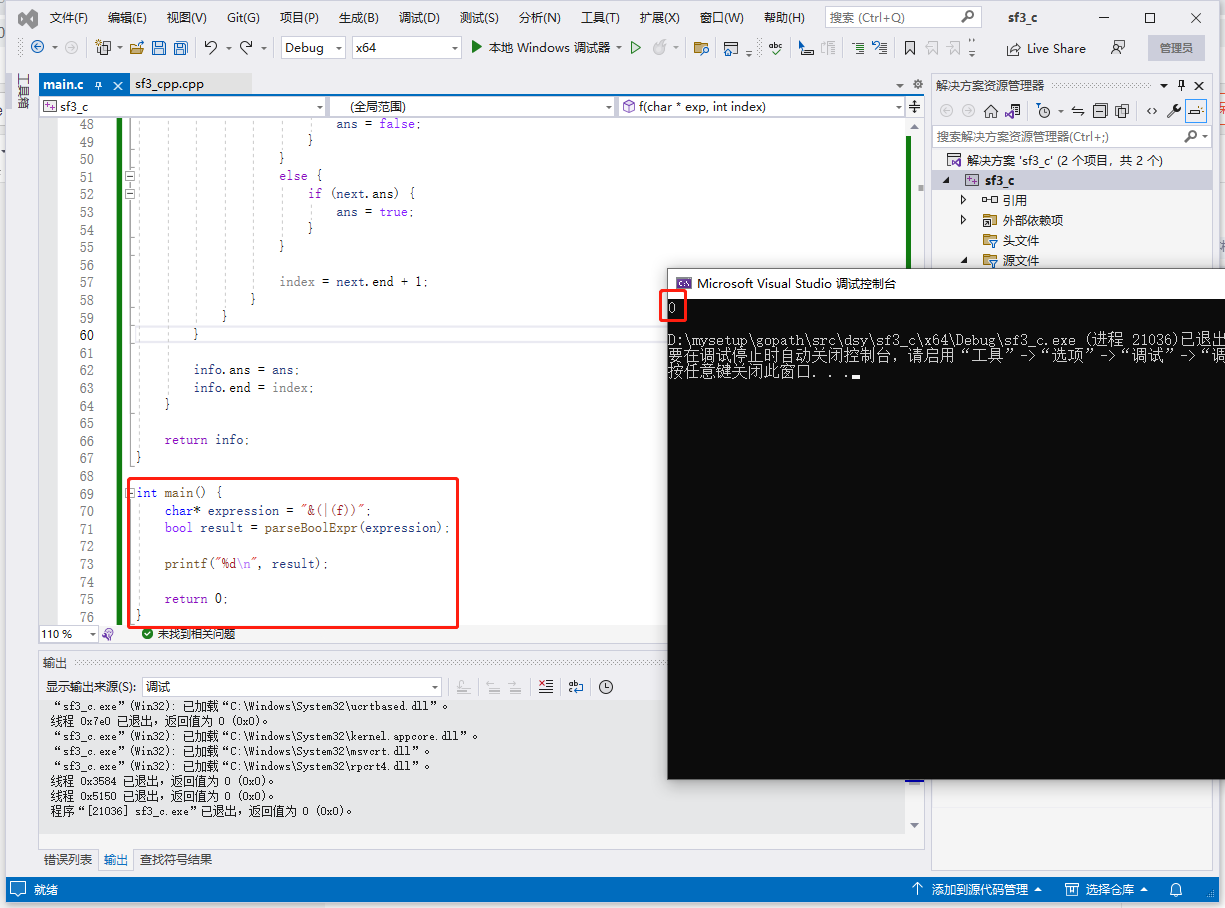
c完整代码如下:
#include <stdbool.h>
#include<stdio.h>
typedef struct Info {
bool ans;
int end;
} Info;
Info f(char* exp, int index);
bool parseBoolExpr(char* expression) {
return f(expression, 0).ans;
}
Info f(char* exp, int index) {
char judge = exp[index];
Info info;
if (judge == ''f'') {
info.ans = false;
info.end = index;
}
else if (judge == ''t'') {
info.ans = true;
info.end = index;
}
else {
bool ans;
index += 2;
if (judge == ''!'') {
Info next = f(exp, index);
ans = !next.ans;
index = next.end + 1;
}
else {
ans = judge == ''&'';
while (exp[index] != '')'') {
if (exp[index] == '','') {
index++;
}
else {
Info next = f(exp, index);
if (judge == ''&'') {
if (!next.ans) {
ans = false;
}
}
else {
if (next.ans) {
ans = true;
}
}
index = next.end + 1;
}
}
}
info.ans = ans;
info.end = index;
}
return info;
}
int main() {
char* expression = "&(|(f))";
bool result = parseBoolExpr(expression);
printf("%d\n", result);
return 0;
}

Apache下commons-lang工具包下BooleanUtils类的xor(true, true, true)结果为false,为什么?
如何解决Apache下commons-lang工具包下BooleanUtils类的xor(true, true, true)结果为false,为什么??
Apache下commons-lang工具包下BooleanUtils类的xor(true,true,true)结果为false,但是System.out.println(true ^ true ^ true) 的结果是true。为什么?
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(org.apache.commons.lang.BooleanUtils.xor(new boolean[]{true,true}));
System.out.println(org.apache.commons.lang3.BooleanUtils.xor(new boolean[]{true,true}));
System.out.println(true ^ true ^ true);
}
}
/*
result:
false
false
true
*/
解决方法
您看到此行为的最可能原因是您使用的是旧版本的 commons-lang (
较新版本的行为 the same as Java(即从左到右一次计算一个异或)。
然而,旧版本使用 different approach:只有当整个数组中恰好有一个真值时,它们才返回真值。
此行为被认为不正确(请参阅 LANG-921)并已修复。
今天关于Python 在列表中查找元素并返回 true 或 false和python查找列表中的元素的讲解已经结束,谢谢您的阅读,如果想了解更多关于2022-09-30:以下go语言代码输出什么?A: true true false true false; B: true false false true false; C: true true、2022-10-28:以下go语言代码输出什么?A:false false;B:true false;C:true true;D:false true。 package main import “f、2023-07-19:布尔表达式 是计算结果不是 true 就是 false 的表达式 有效的表达式需遵循以下约定: ‘t‘,运算结果为 true ‘f‘,运算结果为 false ‘!(subExpr、Apache下commons-lang工具包下BooleanUtils类的xor(true, true, true)结果为false,为什么?的相关知识,请在本站搜索。
本文标签:



![[转帖]Ubuntu 安装 Wine方法(ubuntu如何安装wine)](https://www.gvkun.com/zb_users/cache/thumbs/4c83df0e2303284d68480d1b1378581d-180-120-1.jpg)

