对于SpringBoot系列之@PropertySource和@Value注解感兴趣的读者,本文将提供您所需要的所有信息,我们将详细讲解二,并且为您提供关于3springboot:springboot
对于SpringBoot 系列之 @PropertySource 和 @Value 注解感兴趣的读者,本文将提供您所需要的所有信息,我们将详细讲解二,并且为您提供关于3springboot:springboot配置文件(配置文件、YAML、属性文件值注入<@Value、@ConfigurationProperties、@PropertySource,@...、java – Spring boot无法找到PropertySource:找不到标签、org.springframework.boot.bind.PropertySourcesPropertyValues的实例源码、PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer未在SpringBoot项目中向环境注册的宝贵知识。
本文目录一览:- SpringBoot 系列之 @PropertySource 和 @Value 注解(二)(springboot的@value注解)
- 3springboot:springboot配置文件(配置文件、YAML、属性文件值注入<@Value、@ConfigurationProperties、@PropertySource,@...
- java – Spring boot无法找到PropertySource:找不到标签
- org.springframework.boot.bind.PropertySourcesPropertyValues的实例源码
- PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer未在SpringBoot项目中向环境注册

SpringBoot 系列之 @PropertySource 和 @Value 注解(二)(springboot的@value注解)
前言
本文我们来看看在 Spring 中如何使用 @PropertySource 和 @Value 注解从属性文件读取值,同时呢我们也将讨论有关 Spring Environment 接口的信息以及相应的 XML 配置。@PropertySource 注解主要使用 Spring 的 Environment 接口从属性文件中读取,事实上,此注解位于 @Configuration 类上,而 Spring @Value 注解可用于在字段或方法上指定表达式,常见的例子是从.properties 文件中指定属性以及默认值,接下来我们一起来看看。
@PropertySource 和 @Value 注解
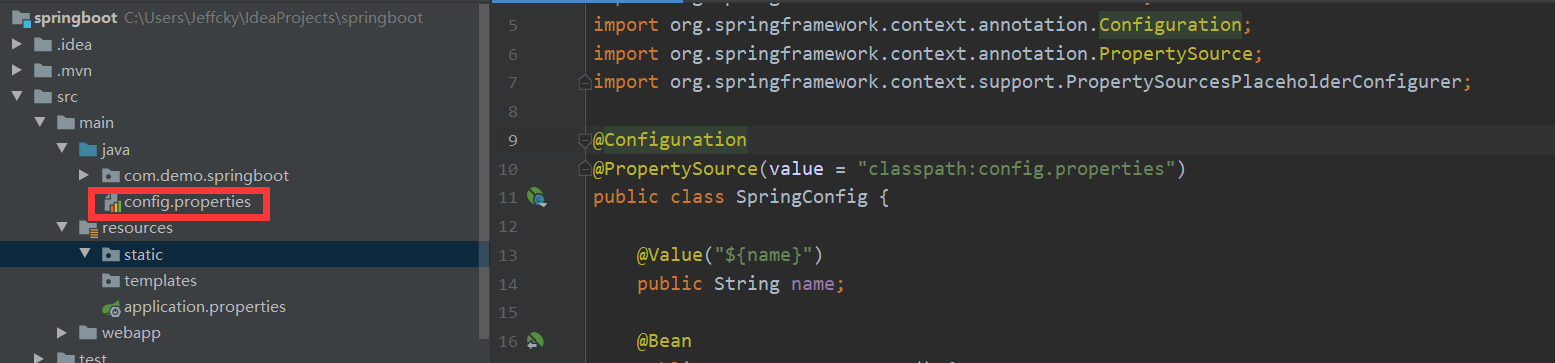
首先我们在 resources 文件夹下创建一个名为 config.properties 的文件,内容如下:
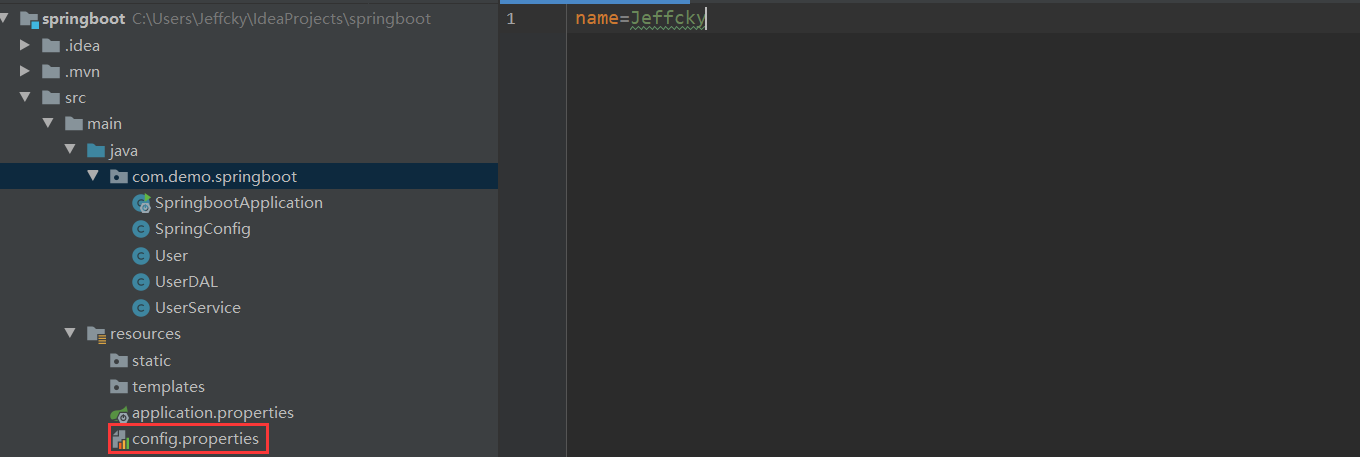
接下来我们在上一节所创建的 SpringConfig 配置文件中添加一个 name 字段,如下:
package com.demo.springboot;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
@Configuration
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:config.properties")
public class SpringConfig {
@Value("${name}")
public String name;
@Bean
public UserDAL getUserDAL() {
System.out.println(name);
return new UserDAL();
}
} 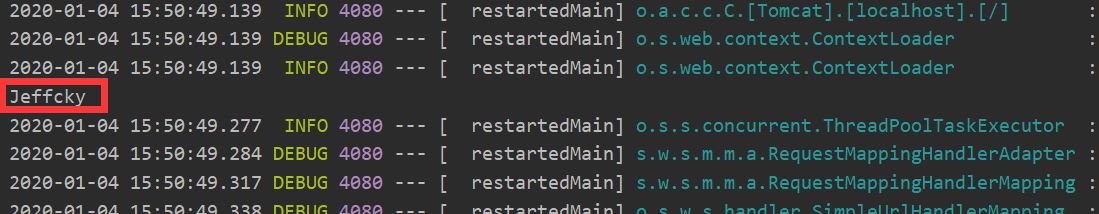
我们通过 @PropertySource 注解声明配置文件存放的地方,一般来讲如果是内部配置文件约定是放在 spring 默认为我们创建的 resources 文件夹下,当然我们也可以在此文件夹下创建目录,同时更改注解存放的地址即可。如果要读取的值存放到内部不同文件夹或者内部和外部,此时我们需要使用 @PropertySources,要是读取的多个配置文件中对应的键一样,此时会以最后读取的配置文件中的值进行覆盖,比如如下 b 配置文件中也存在 name,那么配置文件中的值将覆盖 a 配置文件中的值。
@PropertySources({@PropertySource("classpath:a.properties"),@PropertySource("classpath:b.properties")})我们通过注解 @Value 来读取找到的配置文件中的值,其中 $ 符号相信我们都不陌生,起到占位符的作用。此时我们不禁想,要是指定配置文件不存在或者找到的配置文件中的值和声明注解的占位符不匹配会怎样呢?下面我们将我们创建的配置文件中的 name 修改为如下名称,此时将抛出如下异常:
name11=Jeffcky
同理对于配置文件中未查找到,那更加值也将不存在也会抛出如上异常,由于映射值是交给 spring 内置在处理,我们可能完全捕捉不到这种异常,所以为了解决映射出现异常情况,我们需要给个默认值,对 name 字段进行如下修改:
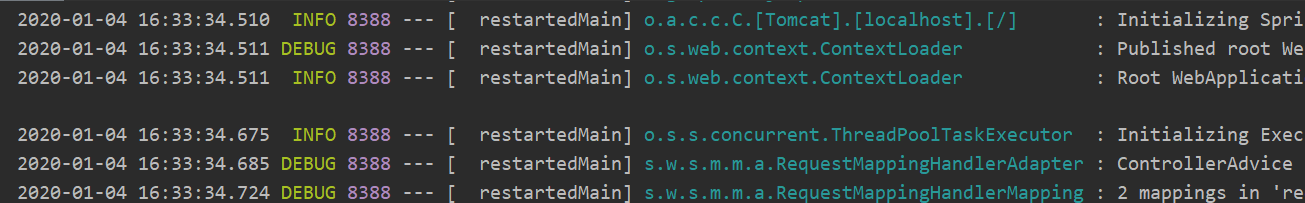
@Value("${name:}")
public String name;在占位符中通过冒号指定若映射值不存则使用上述默认空字符串,很完美的解决了这个问题,此时我们打印出如下空字符串
在开头我们讲解到注解 @PropertySource 是添加到了 Spring Environment 接口中,所以我们可以从 Spring IOC 容器中获取该接口,同样也可以获取上述 name 值,如下:
package com.demo.springboot;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
@Configuration
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:config.properties")
public class SpringConfig {
@Autowired
private Environment environment;
@Bean
public UserDAL getUserDAL() {
System.out.println(environment.getProperty("name"));
return new UserDAL();
}
}上述我们讲解了映射的占位符不匹配的问题,要是映射的占位符找到了,但是值的类型不匹配该咋办呢?比如如下,将抛出异常:
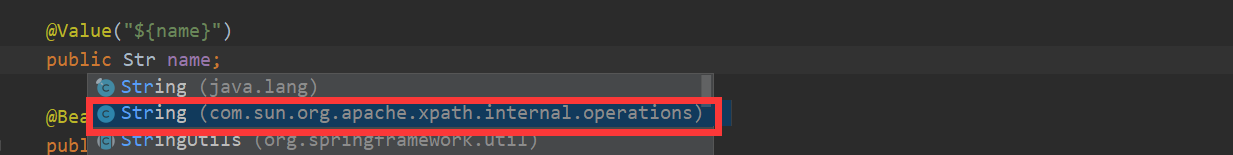
org.springframework.beans.factory.UnsatisfiedDependencyException: Cannot convert value of type ''java.lang.String'' to required type ''com.sun.org.apache.xpath.internal.operations.String''.....当然上述情况是及其不可能发生的,我是手贱搞了快捷方式看都没看,发现也是字符串怎么会抛出如上异常,搞了一会才发现导入的包搞错了。要是我们将配置文件中 name 修改为 1.0,同时我们将字段 name 类型修改为 int,此时会怎样呢?
Failed to convert value of type ''java.lang.String'' to required type ''int''; nested exception is java.lang.NumberFormatException: For input string: "1.0"此时将出现映射类型不匹配的情况,首先确认到底是映射类型是否为 int,若是将配置文件中类型修改 1,或者进行如下修改:
@Value("#{new Double(''${name}'')}")
public int name;或者
@Value("#{T(Double).parseDouble(''${name}'')}")
public int name;否则将字段类型修改为 double(当然包装类型也可)。如下:
@Value("${name}")
public double name;如上我们一直讨论的是将配置文件放在 spring resources 目录下,要是我们现在将上述配置文件放在其他目录(外部目录)呢,比如如下:
org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanDefinitionStoreException:...... class path resource [config.properties] cannot be opened because it does not exist对于内部目录即放在 resources 目录下,声明注解 @PropertySource 时参数使用 classpath,而对于外部目录声明注解 @PropertySource 时参数使用 file。如下:
@PropertySource(value = "file:../../config.properties")此时我们发现同样会抛出异常,只不过内容不一样而已。这是因为无论是将文件放在内外部,路径必须绝对路径而非相对路径,只不过将文件放在内部默认目录是 resources 而已。
org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanDefinitionStoreException: ....... nested exception is java.io.FileNotFoundException: ..\..\config.properties (系统找不到指定的文件。)针对 Windows 系统而言,我们可使用定义环境变量来解决,这里需要注意,定义完环境变量后,此时需要重启 idea 才能重新加载系统定义的环境变量,否则不生效,如下:
@PropertySource(value = "file:${Test}/config.properties")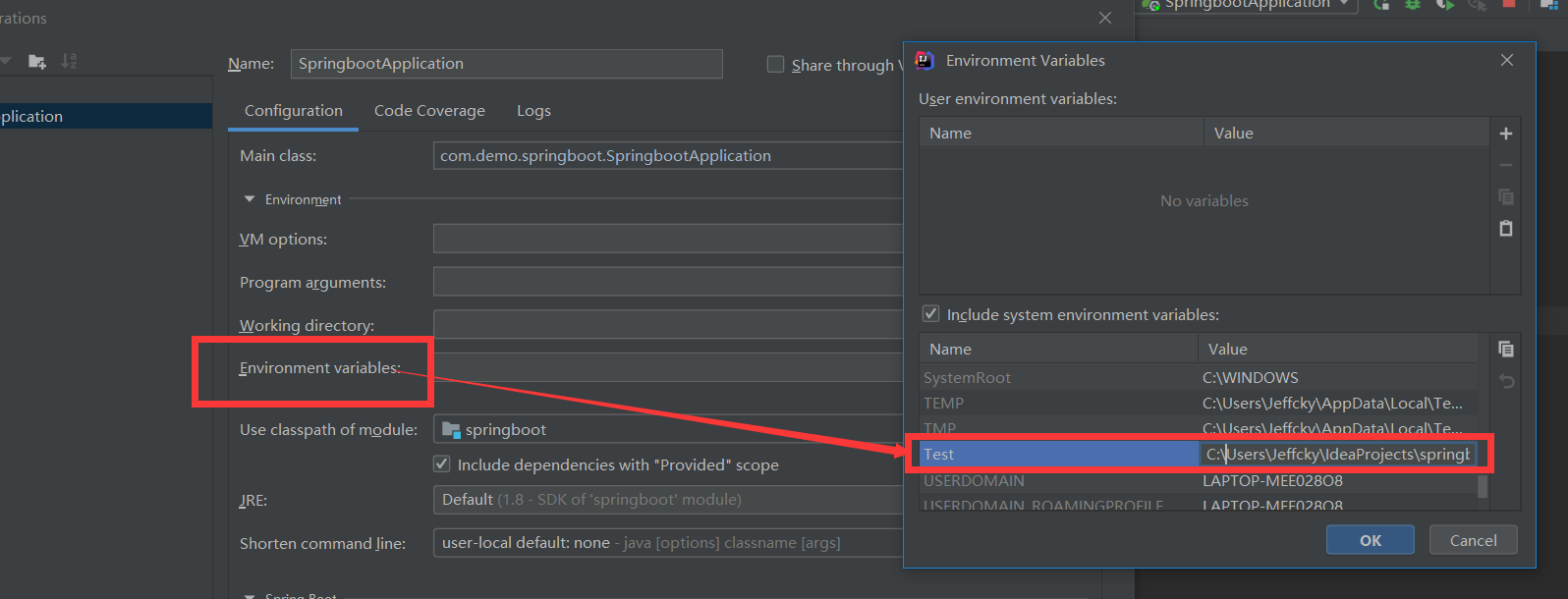
总结
本文我们详细讲解了 @PropertySource 和 @Value 注解,针对读取外部配置文件其实还有一些细节需要深入,这里并未过多深讨,等待哪天再次有了更多积累会进一步分析,好了,感谢阅读本文的您,我们下节见。

3springboot:springboot配置文件(配置文件、YAML、属性文件值注入<@Value、@ConfigurationProperties、@PropertySource,@...
1.配置文件:
配置文件有两种(开头均是application,主要是文件的后缀):
作用:修改springboot自动配置的默认值
位置:
配置文件放在src/main/resourcr目录或者 类路径/config 下
2.YAML:
YAML(YAML Ain''t Markup Language)
YAML A Markup Language:是一个标记语言
YAML isn''t Markup Language:不是一个标记语言;
标记语言:
以前的配置文件;大多都使用的是 xxxx.xml文件;
YAML:以数据为中心,比json、xml等更适合做配置文件;
参考:http://yaml.org/
该语法风格:
server:
port: 8088
使用语法:
k:(空格)v:表示一对键值对(空格必须有);
以空格的缩进来控制层级关系;只要是左对齐的一列数据,都是同一个层级的
值的写法:
字面量:普通的值(数字,字符串,布尔)
k: v:字面直接来写;
字符串默认不用加上单引号或者双引号;
" ":双引号;不会转义字符串里面的特殊字符;特殊字符会作为本身想表示的意思
name: "zhangsan \n lisi":输出;zhangsan 换行 lisi
'' '':单引号;会转义特殊字符,特殊字符最终只是一个普通的字符串数据
name: ‘zhangsan \n
1.对象、Map(属性和值)(键值对):
注意空格
Person:
name:xxxx
age:12行内写法:
Person: {name:xxx,age=12}2.数组(List、Set):
用-(空格) 值表示数组中的一个元素行内写法
gender: [gril,boy]
导入配置文件处理器,配置文件进行绑定就会有提示
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
3.代码测试

//将配置文件中的每一个属性的值映射到这个组件中
//告诉springboot将本类中的所有属性和配置文件中的相关配置进行绑定
//(prefix = "person")将配置文件中以person下的所有属性进行绑定
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private boolean boss;//布尔值
private Date bir;//时间
private Map<String,Object> map;//Map
private List<String> lists;//List
private Dog dog;//对象
}public class Dog {
private String name;
private Integer age;
}
在yml配置文件中
person:
name: Mr
age: 14
boss: true
bir: 2018/12/21
map: {m1: v1,m2: v2}
lists:
- mc
- mt
dog:
name: dogdog
age: 10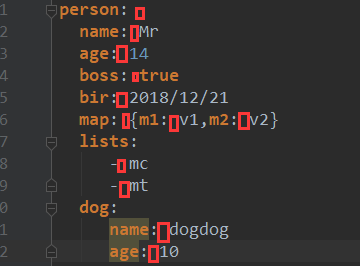
测试:
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class Springboot01ApplicationTests {
@Autowired
Person person;
@Test
public void contextLoads() {
System.out.println(person);
}
}Person{name=''Mr'', age=14, boss=true, bir=Fri Dec 21 00:00:00 CST 2018, map={m1=v1, m2=v2},
lists=[mc, mt], dog=Dog{name=''dogdog'', age=10}}
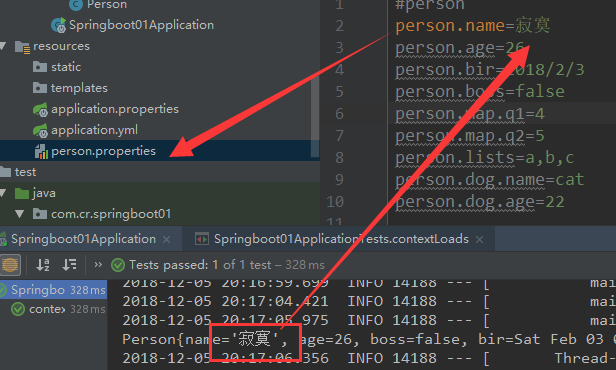
使用properties后缀的:
person.name=mr
person.age=22
person.bir=2018/12/11
person.boss=true
person.map.q1=1
person.map.q2=2
person.lists=a,b,c
person.dog.name=cat
person.dog.age=22 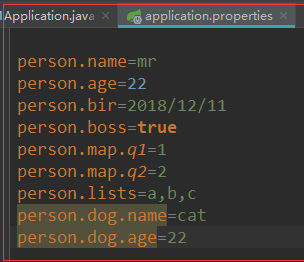
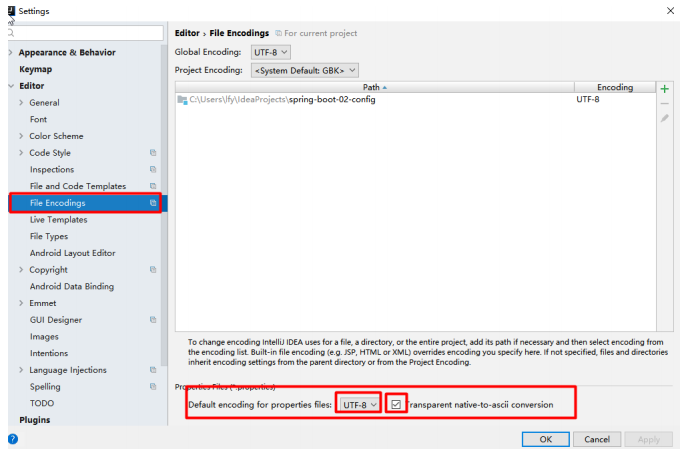
关于乱码的问题:
properties配置文件在idea中默认utf-8可能会乱码
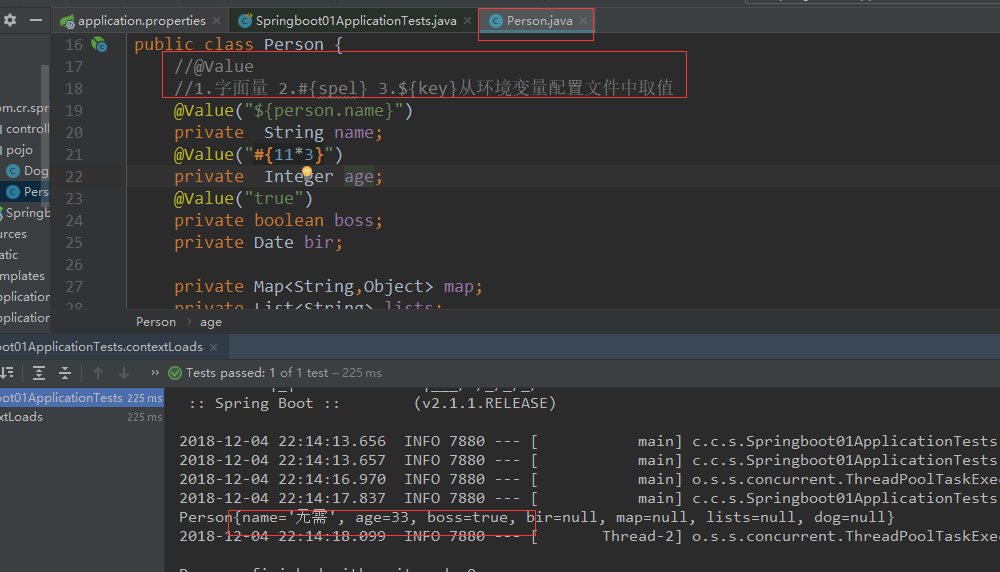
4.配置文件值注入@Value
@Value:1.字面量 2.#{spel} 3.${key}从环境变量配置文件中取值
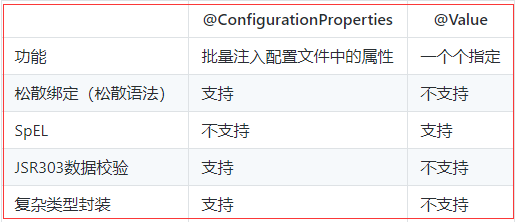
@Value获取值和@ConfigurationProperties获取值比较
松散语法绑定:last_name = last-name = lastName 他们取的值都是相同的
配置文件yml还是properties他们都能获取到值;
如果说,我们只是在某个业务逻辑中需要获取一下配置文件中的某项值,使用@Value;
如果说,我们专门编写了一个javaBean来和配置文件进行映射,我们就直接使用@ConfigurationProperties;
数据校验:
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
@Validated
public class Person {
@Email
private String name;
...
}
获取配置文件中的某个值:
@ResponseBody
@Controller
public class Helloword {
@Value("${person.name}")
private String name;
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
return "Hello tow!" + name;
}
}
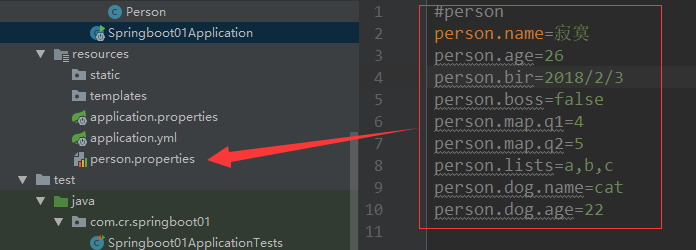
5@PropertySource,@ImportResource
@PropertySource(value = {"classpath:/person.properties"})
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private boolean boss;
private Date bir;
...
}
@ImportResource
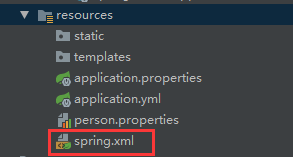
@ImportResource:导入Spring的配置文件,让配置文件里面的内容生效;
Spring Boot里面没有Spring的配置文件,我们自己编写的配置文件,也不能自动识别;
想让Spring的配置文件生效,加载进来;@ImportResource标注在一个配置类上
@ImportResource(locations = {"classpath:spring.xml"})
@SpringBootApplication
public class Springboot01Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Springboot01Application.class, args);
}
}public class helloword {
public void hello(){
System.out.println("hello");
}
} 
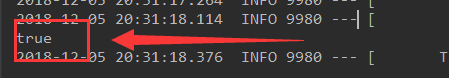
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="hello" class="com.cr.springboot01.ImportSoource.helloword"></bean>
</beans>@Autowired
ApplicationContext app;
@Test
public void testImportSourcr(){
boolean h = app.containsBean("hello");
System.out.println(h);
} 
@Bean
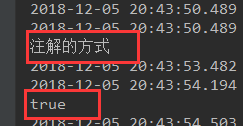
全注解方式:
新建一个配置类
//配置类,指明当前类使配置类,代替xml配置文件
@Configuration
public class MyConfig {
//将方法的返回值添加到容器中,容器中这个组件默认的id就是方法名
@Bean
public Helloword hello(){
System.out.println("注解的方式");
return new Helloword();
}
}@Autowired
ApplicationContext app;
@Test
public void testImportSourcr(){
boolean h = app.containsBean("hello");
System.out.println(h);
} 

java – Spring boot无法找到PropertySource:找不到标签
我正在尝试设置Spring Cloud Config Server,但是服务配置服务器,它运行在端口8888上是正确的,另一个服务应该在端口18060上运行,但是因为我启动的原因,它为我分配端口8080和返回警告“无法找到PropertySource:标签未找到”,我该怎么办?谢谢 !!!
首先在您的应用程序中启用调试模式.(在您的属性文件中:logging.level.= DEBUG.这只是为了确保问题与我的相同或者您可能有任何线索可能出错.)
然后启动应用程序并查看日志.日志显示配置的服务器URI以及获取所有属性资源的URL.
比较两个URL – 日志中的URL和配置服务器URI.
问题是错误地定义了属性文件的URL最后可能有空格. (当你从某个地方复制过去时会发生这种情况)示例:
spring.cloud.config.uri = http:localhost:<的值端口><另外的空白空间>
如果是这种情况,客户端的日志显示localhost:/ 20%/<应用名称> /<个人资料>
只需删除帖子空白空间.那它应该工作!

org.springframework.boot.bind.PropertySourcesPropertyValues的实例源码
@Override
public ConditionOutcome getMatchOutcome(ConditionContext context,AnnotatedTypeMetadata Metadata) {
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = (ConfigurableEnvironment) context
.getEnvironment();
ResourceProperties properties = new ResourceProperties();
RelaxedDataBinder binder = new RelaxedDataBinder(properties,"spring.resources");
binder.bind(new PropertySourcesPropertyValues(environment.getPropertySources()));
Boolean match = properties.getChain().getEnabled();
if (match == null) {
boolean webJarsLocatorPresent = ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBJAR_ASSERT_LOCATOR,getClass().getClassLoader());
return new ConditionOutcome(webJarsLocatorPresent,"Webjars locator (" + WEBJAR_ASSERT_LOCATOR + ") is "
+ (webJarsLocatorPresent ? "present" : "absent"));
}
return new ConditionOutcome(match,"Resource chain is " + (match ? "enabled" : "disabled"));
}
@Override public ConditionOutcome getMatchOutcome(ConditionContext context,"Resource chain is " + (match ? "enabled" : "disabled")); }
private List<String> getExcludeAutoConfigurationsproperty() {
if (getEnvironment() instanceof ConfigurableEnvironment) {
Excludes excludes = new Excludes();
RelaxedDataBinder binder = new RelaxedDataBinder(excludes,"spring.autoconfigure.");
binder.bind(new PropertySourcesPropertyValues(
((ConfigurableEnvironment) getEnvironment()).getPropertySources()));
return excludes.getExclude();
}
RelaxedPropertyResolver resolver = new RelaxedPropertyResolver(getEnvironment(),"spring.autoconfigure.");
String[] exclude = resolver.getProperty("exclude",String[].class);
return (Arrays.asList(exclude == null ? new String[0] : exclude));
}
@Override
public void setEnvironment(Environment environment) {
this.environment = (ConfigurableEnvironment) environment;
this.target = new HashMap<String,Object>();
new RelaxedDataBinder(this.target).bind(
new PropertySourcesPropertyValues(this.environment.getPropertySources()));
this.propertyResolver = new RelaxedPropertyResolver(environment);
}
private List<String> getExcludeAutoConfigurationsproperty() {
if (getEnvironment() instanceof ConfigurableEnvironment) {
Excludes excludes = new Excludes();
RelaxedDataBinder binder = new RelaxedDataBinder(excludes,String[].class);
return (Arrays.asList(exclude == null ? new String[0] : exclude));
}
@Override
public void setEnvironment(Environment environment) {
this.environment = (ConfigurableEnvironment) environment;
this.target = new HashMap<String,Object>();
new RelaxedDataBinder(this.target).bind(
new PropertySourcesPropertyValues(this.environment.getPropertySources()));
this.propertyResolver = new RelaxedPropertyResolver(environment);
}
@Override
public ConditionOutcome getMatchOutcome(ConditionContext context,"spring.resources");
binder.bind(new PropertySourcesPropertyValues(environment.getPropertySources()));
Boolean match = properties.getChain().getEnabled();
return new ConditionOutcome(match,"Resource chain is " + (match ? "enabled" : "disabled"));
}
@Override
public void setEnvironment(Environment environment) {
this.environment = (ConfigurableEnvironment) environment;
this.target = new HashMap<String,Object>();
new RelaxedDataBinder(this.target).bind(
new PropertySourcesPropertyValues(this.environment.getPropertySources()));
this.propertyResolver = new RelaxedPropertyResolver(environment);
}
@Override
public void initialize(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) {
if (!isHasCloudConfigLocator(this.propertySourceLocators)) {
logger.info("未启用Config Server管理配置");
return;
}
logger.info("检查Config Service配置资源");
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = applicationContext.getEnvironment();
MutablePropertySources propertySources = environment.getPropertySources();
logger.info("加载PropertySources源:" + propertySources.size() + "个");
CloudConfigSupportProperties configSupportProperties = new CloudConfigSupportProperties();
new RelaxedDataBinder(configSupportProperties,CloudConfigSupportProperties.CONfig_PREFIX)
.bind(new PropertySourcesPropertyValues(propertySources));
if (!configSupportProperties.isEnable()) {
logger.warn("未启用配置备份功能,可使用{}.enable打开",CloudConfigSupportProperties.CONfig_PREFIX);
return;
}
if (isCloudConfigLoaded(propertySources)) {
PropertySource cloudConfigSource = getLoadedCloudPropertySource(propertySources);
logger.info("成功获取ConfigService配置资源");
//备份
Map<String,Object> backupPropertyMap = makeBackupPropertyMap(cloudConfigSource);
dobackup(backupPropertyMap,configSupportProperties.getFile());
} else {
logger.error("获取ConfigService配置资源失败");
Properties backupProperty = loadBackupProperty(configSupportProperties.getFile());
if (backupProperty != null) {
HashMap backupsourceMap = new HashMap<>(backupProperty);
PropertySource backupsource = new MapPropertySource("backupsource",backupsourceMap);
propertySources.addFirst(backupsource);
logger.warn("使用备份的配置启动:{}",configSupportProperties.getFile());
}
}
}
public Restifyapiclient client(RestifyableType type) {
Restifyapiclient restifyapiclient = new Restifyapiclient();
RelaxedDataBinder dataBinder = new RelaxedDataBinder(restifyapiclient,"restify." + type.name());
ConfigurableEnvironment configurableEnvironment = (ConfigurableEnvironment) environment;
dataBinder.bind(new PropertySourcesPropertyValues(configurableEnvironment.getPropertySources()));
return restifyapiclient;
}

PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer未在SpringBoot项目中向环境注册
如何解决PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer未在SpringBoot项目中向环境注册?
这里的问题是区分PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer和StandardServletEnvironment,或Environment为简单起见。
的Environment是,备份整个对象ApplicationContext,并且可以解决一束性质(所述Environment接口延伸PropertyResolver)。AConfigurableEnvironment有一个MutablePropertySources您可以通过检索的对象getPropertySources()。它MutablePropertySources包含要检查LinkedList的PropertySource对象,以解析请求的属性。
PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer是具有自己状态的单独对象。它拥有自己的MutablePropertySources用于解析属性占位符的对象。PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer实现,EnvironmentAware以便在ApplicationContext获取它时为其提供Environment对象。在PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer添加此Environment的MutablePropertySources它自己的。然后,它还将添加Resource您指定的各种对象setLocation()作为附加属性。
因此,您无法直接将加载PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer到的属性Environment。你可以做的,而不是直接添加到Environment的MutablePropertySouces。一种方法是
@postconstruct
public void setup() throws IOException {
Resource resource = new FileSystemResource("spring.properties"); // your file
Properties result = new Properties();
PropertiesLoaderUtils.fillProperties(result, resource);
env.getPropertySources().addLast(new PropertiesPropertySource("custom", result));
}
或干脆(感谢@ M.Deinum)
@postconstruct
public void setup() throws IOException {
env.getPropertySources().addLast(new ResourcePropertySource("custom", "file:spring.properties")); // the name ''custom'' can come from anywhere
}
注意,添加a @PropertySource具有相同的效果,即。直接添加到中Environment,但您是在静态而不是动态地进行操作。
解决方法
我正在从使用SpringBoot命令行参数移动工作项目到从文件读取属性。这是@Configuration课程涉及的部分:
@Configuration
class RemoteCommunication {
@Inject
StandardServletEnvironment env
@Bean
static PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer placeholderConfigurer () {
// VERIFIED this is executing...
PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer target = new PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer()
// VERIFIED this files exists,is readable,is a valid properties file
target.setLocation (new FileSystemResource (''/Users/me/Desktop/mess.properties''))
// A Debugger does NOT show this property source in the inject Environment
target
}
@Bean // There are many of these for different services,only one shown here.
MedicalSorIdService medicalSorIdService () {
serviceInstantiator (MedicalSorIdService_EpicSoap,''uri.sor.id.lookup.internal'')
}
// HELPER METHODS...
private <T> T serviceInstantiator (final Class<T> classToInstantiate,final String propertyKeyPrimary) {
def value = retrieveSpringPropertyFromConfigurationParameter (propertyKeyPrimary)
classToInstantiate.newInstance (value)
}
private def retrieveSpringPropertyFromConfigurationParameter (String propertyKeyPrimary) {
// PROBLEM: the property is not found in the Environment
def value = env.getProperty (propertyKeyPrimary,'''')
if (value.isEmpty ()) throw new IllegalStateException (''Missing configuration parameter: '' + "\"$propertyKeyPrimary\"")
value
}
使用@Value注入属性 确实
可以,但是Environment如果可能的话,我宁愿直接使用属性。如果设置不在中,Environment则我不确定@Value从何处拉出它们…
env.getProperty() 当我通过命令行参数指定属性时,它仍然可以正常工作。
欢迎任何建议!
我们今天的关于SpringBoot 系列之 @PropertySource 和 @Value 注解和二的分享已经告一段落,感谢您的关注,如果您想了解更多关于3springboot:springboot配置文件(配置文件、YAML、属性文件值注入<@Value、@ConfigurationProperties、@PropertySource,@...、java – Spring boot无法找到PropertySource:找不到标签、org.springframework.boot.bind.PropertySourcesPropertyValues的实例源码、PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer未在SpringBoot项目中向环境注册的相关信息,请在本站查询。
本文标签:



![[转帖]Ubuntu 安装 Wine方法(ubuntu如何安装wine)](https://www.gvkun.com/zb_users/cache/thumbs/4c83df0e2303284d68480d1b1378581d-180-120-1.jpg)

