[Swift]LeetCode679. 24点游戏 | 24 Game(24点游戏6779)
3
在这里,我们将给大家分享关于[Swift]LeetCode679.24点游戏|24Game的知识,让您更了解24点游戏6779的本质,同时也会涉及到如何更有效地2023-08-10:景区里有m个项目,
在这里,我们将给大家分享关于[Swift]LeetCode679. 24点游戏 | 24 Game 的知识,让您更了解24点游戏6779 的本质,同时也会涉及到如何更有效地2023-08-10:景区里有 m 个项目,也就是项目数组为 int [][] game,这是一个 m*2 的二维数组 景区的第 i 个项目有如下两个参数: game [i] = { Ki, Bi } Ki 一定是负数,、24点游戏、Acer Swift 3笔记本怎么样 Acer Swift 3笔记本上手图赏、Codeforces Round #426 (Div. 2) C. The Meaningless Game C. The Meaningless Game 的内容。
本文目录一览:
[Swift]LeetCode679. 24点游戏 | 24 Game(24点游戏6779)
You have 4 cards each containing a number from 1 to 9. You need to judge whether they Could operated through *, /, +, -, (, )to get the value of 24.
Example 1:
Input: [4,1,8,7]
Output: True
Explanation: (8-4) * (7-1) = 24
Example 2:
Input: [1,2,2]
Output: False
Note:
The division operator / represents real division,not integer division. For example,4 / (1 - 2/3) = 12.
Every operation done is between two numbers. In particular,we cannot use - as a unary operator. For example,with [1,1] as input,the expression -1 - 1 - 1 - 1 is not allowed.
You cannot concatenate numbers together. For example,if the input is [1,2],we cannot write this as 12 + 12.
你有 4 张写有 1 到 9 数字的牌。你需要判断是否能通过 *,/,+,-,(,) 的运算得到 24。
示例 1:
输入: [4,7]
输出: True
解释: (8-4) * (7-1) = 24
示例 2:
输入: [1,2]
输出: False
注意:
除法运算符 / 表示实数除法,而不是整数除法。例如 4 / (1 - 2/3) = 12 。
每个运算符对两个数进行运算。特别是我们不能用 - 作为一元运算符。例如,[1,1] 作为输入时,表达式 -1 - 1 - 1 - 1 是不允许的。
你不能将数字连接在一起。例如,输入为 [1,2] 时,不能写成 12 + 12 。
1 class Solution {
2 func oneOperation(_ nums: [Double],_ i: Int,_ j: Int, 3 _ op: (Double,Double)->Double?) -> [Double]? {
4 var arr = [Double]()
5 for k in 0 ..<nums.count {
6 if k != i && k != j {
7 arr.append(nums[k])
8 }
9 }
10 if let num = op(nums[i],nums[j]) {
11 arr.append(num)
12 return arr
13 } else {
14 return nil
15 }
16 }
17 func judgePoint24Internal(_ nums: [Double]) -> Bool {
18 if nums.count == 2 {
19 return nums[0 ]*nums[1 ] == 24 || nums[0 ]+nums[1 ] == 24
20 || nums[0 ] - nums[1 ] == 24 || nums[1 ] - nums[0 ] == 24
21 || (nums[0 ] != 0 && 24.0 -0.00001 < nums[1 ]/nums[0 ] && nums[1 ]/nums[0 ] < 24.0 + 0.0000001 )
22 || (nums[1 ] != 0 && fabs(nums[0 ]/nums[1 ]-24.0 ) < 0.00001 )
23 }
24
25 for i in 0 ..<nums.count-1 {
26 for j in i+1 ..<nums.count {
27 var arr = oneOperation(nums,i,j,{$0 +$1 })
28 if judgePoint24Internal(arr!) == true {
29 return true
30 }
31
32 arr = oneOperation(nums,{$0 *$1 })
33 if judgePoint24Internal(arr!) == true {
34 return true
35 }
36
37 arr = oneOperation(nums,{$0 -$1 })
38 if judgePoint24Internal(arr!) == true {
39 return true
40 }
41
42 arr = oneOperation(nums,{$1 != 0 ? $0 /$1 : nil})
43 if let arr = arr,judgePoint24Internal(arr) == true {
44 return true
45 }
46 arr = oneOperation(nums,{$1 -$0 })
47 if judgePoint24Internal(arr!) == true {
48 return true
49 }
50
51 arr = oneOperation(nums,{$0 != 0 ? $1 /$0 : nil})
52 if let arr = arr,judgePoint24Internal(arr) == true {
53 return true
54 }
55 }
56 }
57 return false
58 }
59
60 func judgePoint24(_ nums: [Int]) -> Bool {
61 return judgePoint24Internal(nums.map{Double($0 )})
62 }
63 }
40ms
1 class Solution {
2 func judgePoint24(_ nums: [Int]) -> Bool {
3 return solve(nums.map { Double($0 ) })
4 }
5
6 private func solve(_ nums: [Double]) -> Bool {
7 guard nums.count > 1 else {
8 return abs(nums[0 ] - 24.0 ) < 1e-6
9 }
10
11 for i in 0 ..<nums.count {
12 for j in 0 ..<nums.count {
13 guard i != j else {
14 continue
15 }
16
17 var newNums = [Double]()
18 for k in 0 ..<nums.count where k != i && k != j {
19 newNums.append(nums[k])
20 }
21
22 for k in 0 ..<4 {
23 switch k {
24 case 0 :
25 newNums.append(nums[i] + nums[j])
26 case 1 :
27 newNums.append(nums[i] - nums[j])
28 case 2 :
29 newNums.append(nums[i] * nums[j])
30 case 3 :
31 if nums[j] != 0.0 {
32 newNums.append(nums[i] / nums[j])
33 } else {
34 continue
35 }
36 default :
37 continue
38 }
39 if solve(newNums) {
40 return true
41 }
42 newNums.removeLast()
43 }
44 }
45 }
46 return false
47 }
48 }
44ms
1 class Solution {
2 private let esp: Double = 0.001
3
4 func judgePoint24(_ nums: [Int]) -> Bool {
5 var nums = nums.map { return Double($0 ) }
6 return dfs(nums)
7 }
8
9 private func dfs(_ nums: [Double]) -> Bool {
10 if nums.count == 1 {
11 if abs(nums.first! - 24 ) <= esp {
12 return true
13 } else {
14 return false
15 }
16 }
17
18 for i in 0 ..< nums.count {
19 for j in i + 1 ..< nums.count {
20 var next: [Double] = []
21
22 for k in 0 ..< nums.count {
23 if k != i && k != j {
24 next.append(nums[k])
25 }
26 }
27
28 let p1 = nums[i]
29 let p2 = nums[j]
30 let combines = [p1 + p2,p1 - p2,p2 - p1,p1 * p2,p1 / p2,p2 / p1]
31
32 for c in combines {
33 next.append(c)
34 if dfs(next) {
35 return true
36 }
37 next.removeLast()
38 }
39 }
40 }
41 return false
42 }
43 }
2023-08-10:景区里有 m 个项目,也就是项目数组为 int [][] game,这是一个 m*2 的二维数组 景区的第 i 个项目有如下两个参数: game [i] = { Ki, Bi } Ki 一定是负数, 2023-08-10:景区里有 m 个项目,也就是项目数组为 int [][] game,这是一个 m*2 的二维数组
景区的第 i 个项目有如下两个参数:
game[i] = { Ki, Bi }
Ki 一定是负数,Bi 一定是正数
举个例子 :
Ki = -2, Bi = 10
如果只有 1 个人买票,单张门票的价格为 : Ki * 1 + Bi = 8
所以这 1 个人游玩该项目要花 8 元
如果有 2 个人买票,单张门票的价格为 : Ki * 2 + Bi = 6
所以这 2 个人游玩该项目要花 6 * 2 = 12 元
如果有 5 个人买票,单张门票的价格为 : Ki * 2 + Bi = 0
所以这 5 个人游玩该项目要花 0 * 5 = 0 元
如果有更多人买票,都认为花 0 元 (因为你让项目倒贴钱实在是太操蛋了)
于是可以认为,如果有 x 个人买票,单张门票的价格为 : Ki * x + Bi
x 个人游玩这个项目的总花费是 : max {(Ki * x + Bi) * x , 0 }
你作为领导,单位一共有 n 个人,每个人最多可以选 1 个项目来游玩,也可以不选任何项目
所有员工将在明晚提交选择,然后由你去按照上面的规则,统一花钱,统一购票
但是现在,你想知道自己需要准备多少钱,就可以应付可能的各种情况,
支持各种可能下的开销,返回这个最保险的钱数。
数据量描述 :
1 <= N、M、Bi <= 10^5,
-(10^5) <= Ki < 0。
来自左程云。
答案 2023-08-10:
步骤描述:
1. 创建一个优先队列(堆)h,用于存储游戏项目。我们使用 GameHeap 类型来定义优先队列,并实现 Len、Less、Swap、Push 和 Pop 方法。
2. 遍历每个项目 g,在遍历过程中将 Ki 和 Bi 作为参数创建 Game 结构体 game,并将其添加到优先队列 h 中。
3. 初始化结果变量 ans 为 0,用于记录总花费。
4. 迭代 n 次,表示有 n 个人进行选择游戏项目的操作。
4.1. 检查当前优先队列 h 的第一个项目的 Earn 值(单张门票的价格乘以人数)。如果 Earn 值小于等于 0,即项目不再划算,跳出循环。
4.2. 从优先队列 h 中弹出一个项目,并将其赋值给变量 cur。
4.3. 将当前项目的 Earn 值累加到结果变量 ans 中。
4.4. 增加当前项目的人数 cur.People。
4.5. 将更新后的项目 cur 添加回优先队列 h 中。
5. 返回结果变量 ans,即准备的最保险的金额。
总的时间复杂度:O (nlog (m)),其中 n 为人数,m 为项目数。遍历 n 次,每次从优先队列中弹出最大值,时间复杂度为 log (m)。
总的空间复杂度:O (m),优先队列 h 的大小取决于项目数 m。
go 完整代码如下:
package main
import (
"container/heap"
"fmt"
)
type Game struct {
Ki int
Bi int
People int
}
type GameHeap []Game
func (h GameHeap) Len () int return len (h) }
func (h GameHeap) Less (i, j int ) bool return h[i].Earn() > h[j].Earn() }
func (h GameHeap) Swap (i, j int ) func (h *GameHeap) Push (x interface {}) append (*h, x.(Game)) }
func (h *GameHeap) Pop () interface len (old)
x := old[n-1 ]
*h = old[0 : n-1 ]
return x
}
func (g Game) Earn () int return (2 *g.People+1 )*g.Ki + g.Bi
}
func EnoughMoney (n int , games [][]int ) int for _, g := range games {
game := Game{Ki: g[0 ], Bi: g[1 ]}
heap.Push(h, game)
}
ans := 0
for i := 0 ; i < n; i++ {
if (*h)[0 ].Earn() <= 0 {
break
}
cur := heap.Pop(h).(Game)
ans += cur.Earn()
cur.People++
heap.Push(h, cur)
}
return ans
}
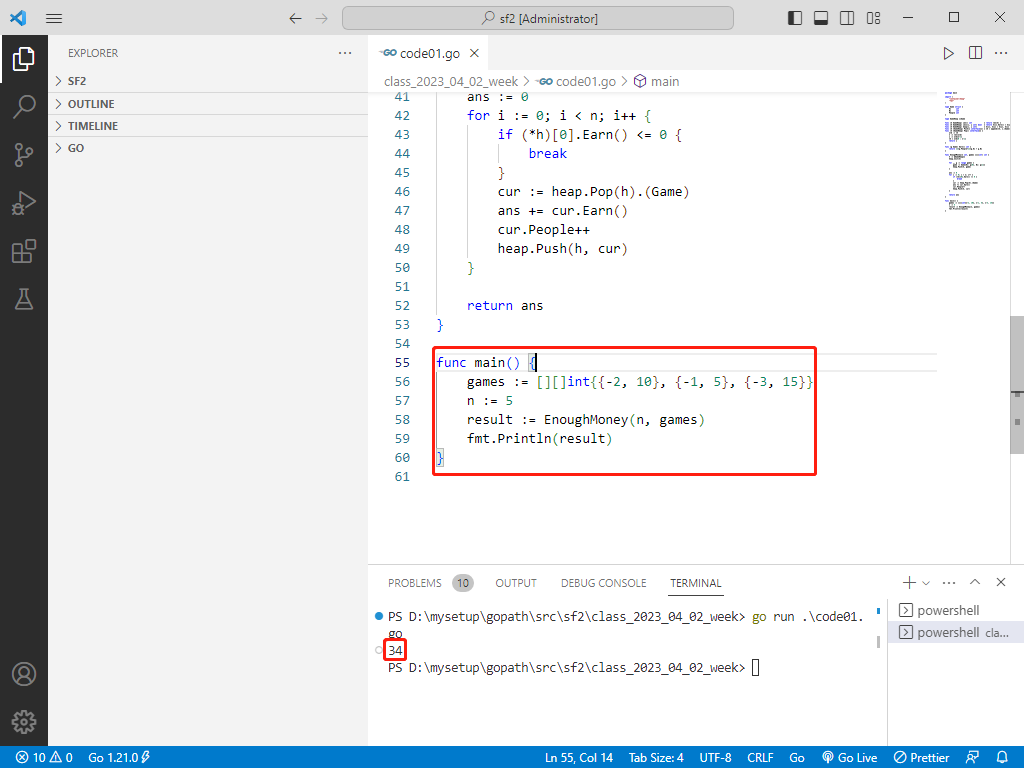
func main () int {{-2 , 10 }, {-1 , 5 }, {-3 , 15 }}
n := 5
result := EnoughMoney(n, games)
fmt.Println(result)
}
c++ 完整代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
using namespace std ;
struct Game {int Ki;
int Bi;
int people;
Game(int k, int b) {
Ki = k;
Bi = b;
people = 0 ;
}
int earn () const return (2 * people + 1 ) * Ki + Bi;
}
};
struct CompareGame {bool operator () (const Game& a, const Game& b) return a.earn() < b.earn();
}
};
int enoughMoney (int n, vector <vector <int >>& games) vector <Game>, CompareGame> heap;
for (auto & g : games) {
heap.push(Game(g[0 ], g[1 ]));
}
int ans = 0 ;
while (n > 0 && heap.top().earn() > 0 ) {
Game cur = heap.top();
heap.pop();
ans += cur.earn();
cur.people++;
heap.push(cur);
n--;
}
return ans;
}
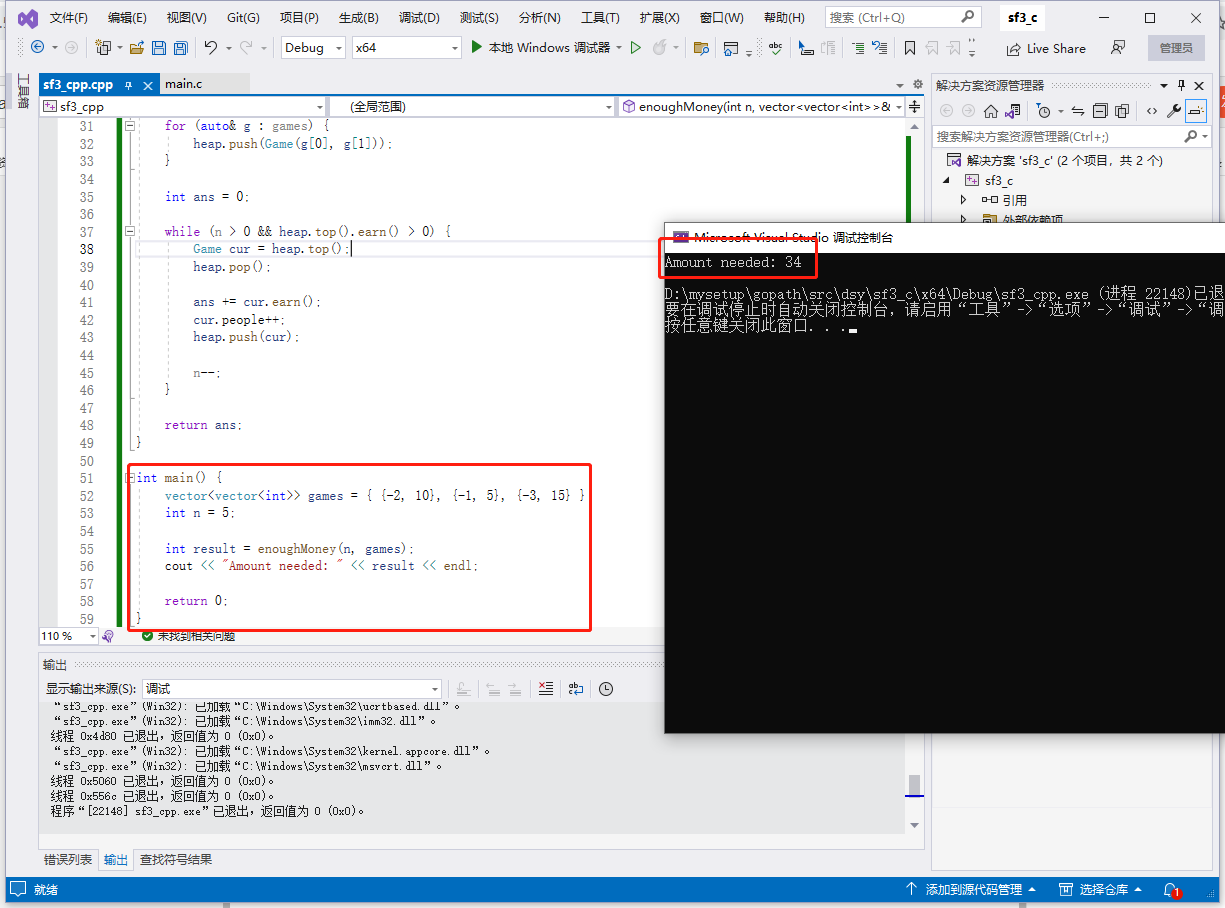
int main () vector <vector <int >> games = { {-2 , 10 }, {-1 , 5 }, {-3 , 15 } };
int n = 5 ;
int result = enoughMoney(n, games);
cout << "Amount needed: " << result << endl ;
return 0 ;
}
c 语言完整代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct Game {int Ki;
int Bi;
int people;
};
typedef struct Game Game ;int cmp (const void * a, const void * b) return (2 * gameB->people + 1 ) * gameB->Ki + gameB->Bi - (2 * gameA->people + 1 ) * gameA->Ki - gameA->Bi;
}
int enoughMoney (int n, int games[][2 ], int m) malloc (m * sizeof (Game));
for (int i = 0 ; i < m; i++) {
heap[i].Ki = games[i][0 ];
heap[i].Bi = games[i][1 ];
heap[i].people = 0 ;
}
qsort(heap, m, sizeof (Game), cmp);
int ans = 0 ;
for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) {
if ((2 * heap[0 ].people + 1 ) * heap[0 ].Ki + heap[0 ].Bi <= 0 ) {
break ;
}
ans += (2 * heap[0 ].people + 1 ) * heap[0 ].Ki + heap[0 ].Bi;
heap[0 ].people++;
qsort(heap, m, sizeof (Game), cmp);
}
free (heap);
return ans;
}
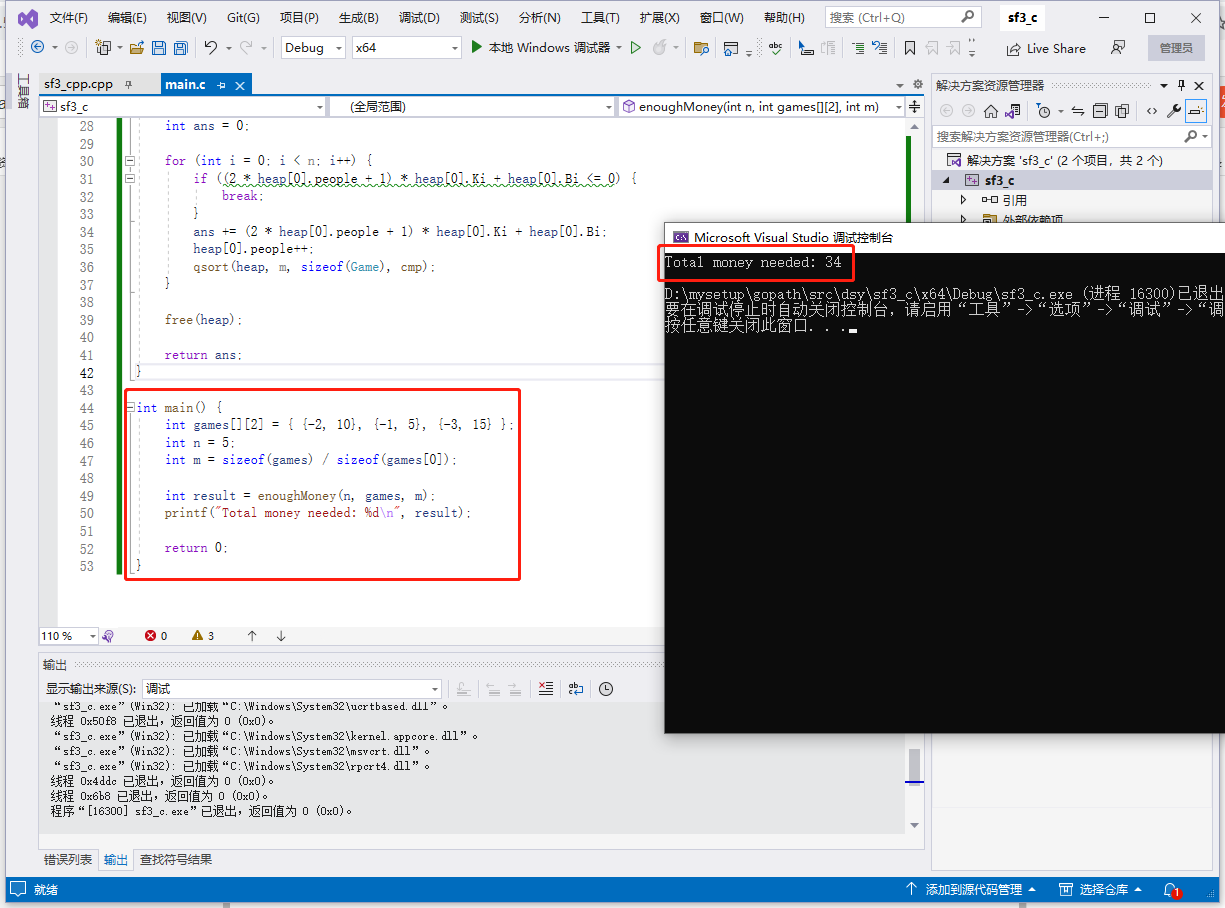
int main () int games[][2 ] = { {-2 , 10 }, {-1 , 5 }, {-3 , 15 } };
int n = 5 ;
int m = sizeof (games) / sizeof (games[0 ]);
int result = enoughMoney(n, games, m);
printf ("Total money needed: %d\n" , result);
return 0 ;
}
24点游戏 题目描述
给出4个正整数操作数,你的任务是使用运算符(+,-,*,/)和括号对
操作数进行计算,分析是否能得到24,每个操作数只能使用1次,运算符和
括号可以多次使用,注意所有的中间结果都是整数。
输入
输入包括多行,每行4个正整数,范围是[1,13],输入以0 0 0 0标记结束
输出
若输入的4个操作数能计算出24,输出Yes,否则输出No
样例输入
1 1 1 1
2 5 7 8
0 0 0 0
样例输出
No
代码如下:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int a[4];
bool Fun(int n)
{
if(n==1)
return a[0]==24;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
{
if(i==j) continue;
int a1=a[i],a2=a[j];
a[i]=a1+a2;
a[j]=a[n-1];
if(Fun(n-1)) return true;
a[i]=a1-a2;
a[j]=a[n-1];
if(Fun(n-1)) return true;
a[i]=a1*a2;
a[j]=a[n-1];
if(Fun(n-1)) return true;
if(a2!=0&&a1%a2==0)
{
a[i]=a1/a2;
a[j]=a[n-1];
if(Fun(n-1)) return true;
}
a[i]=a1;
a[j]=a2;
}
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
while(1)
{
cin>>a[0]>>a[1]>>a[2]>>a[3];
if(a[0]==0&&a[1]==0&&a[2]==0&&a[3]==0) break;
if(Fun(4))
cout<<"Yes"<<endl;
else cout<<"No"<<endl;
}
}
Acer Swift 3笔记本怎么样 Acer Swift 3笔记本上手图赏 Acer Swift 3是宏碁推出的笔记本电脑,具有轻薄时尚等元素,这里为大家带来 Acer Swift 3笔记本上手图赏 ,一起来看看。
14英寸1920*1080的显示屏幕、2.5GHz的英特尔酷睿酷睿i3、i5-7200u/i7处理器、图形128mb英特尔高清显卡620、8GB/256GB的SSD、Windows Hello、指纹识别器,处理速度快可媲美MacBook,售价仅为1398美元(约£1090/1760美元),性价比方面还是不错的。
以上就是 Acer Swift 3笔记本上手图赏 相关内容,希望对你有帮助。
Codeforces Round #426 (Div. 2) C. The Meaningless Game C. The Meaningless Game
总结
以上是小编为你收集整理的Codeforces Round #426 (Div. 2) C. The Meaningless Game C. The Meaningless Game全部内容。
如果觉得小编网站内容还不错,欢迎将小编网站推荐给好友。
关于[Swift]LeetCode679. 24点游戏 | 24 Game 和24点游戏6779 的介绍现已完结,谢谢您的耐心阅读,如果想了解更多关于2023-08-10:景区里有 m 个项目,也就是项目数组为 int [][] game,这是一个 m*2 的二维数组 景区的第 i 个项目有如下两个参数: game [i] = { Ki, Bi } Ki 一定是负数,、24点游戏、Acer Swift 3笔记本怎么样 Acer Swift 3笔记本上手图赏、Codeforces Round #426 (Div. 2) C. The Meaningless Game C. The Meaningless Game 的相关知识,请在本站寻找。
![[Swift]LeetCode679. 24点游戏 | 24 Game(24点游戏6779) [Swift]LeetCode679. 24点游戏 | 24 Game(24点游戏6779)](http://www.gvkun.com/zb_users/upload/2025/04/4d6079bf-6887-4c85-982d-233ad90da5cd1744859747354.jpg)

![2023-08-10:景区里有 m 个项目,也就是项目数组为 int [][] game,这是一个 m*2 的二维数组 景区的第 i 个项目有如下两个参数: game [i] = { Ki, Bi } Ki 一定是负数, 2023-08-10:景区里有 m 个项目,也就是项目数组为 int [][] game,这是一个 m*2 的二维数组 景区的第 i 个项目有如下两个参数: game [i] = { Ki, Bi } Ki 一定是负数,](http://www.gvkun.com/zb_users/upload/2025/04/37433d82-26bc-421b-81f5-2070912c0b891744859750397.jpg)












![[转帖]Ubuntu 安装 Wine方法(ubuntu如何安装wine)](https://www.gvkun.com/zb_users/cache/thumbs/4c83df0e2303284d68480d1b1378581d-180-120-1.jpg)

