在本文中,您将会了解到关于android如何旋转画布rect的新资讯,同时我们还将为您解释android旋转的相关在本文中,我们将带你探索android如何旋转画布rect的奥秘,分析android旋
在本文中,您将会了解到关于android如何旋转画布rect的新资讯,同时我们还将为您解释android 旋转的相关在本文中,我们将带你探索android如何旋转画布rect的奥秘,分析android 旋转的特点,并给出一些关于An Overview of the Android Architecture (Android Studio)、Android canvas画图操作之切割画布实现方法(clipRect)、Android Material Design Ripple Effect 在 Android5.0(SDK=21)以下 Android 版本崩溃问题解决、Android Studio如何旋转按钮并使它们与父视图的右侧/左侧对齐?的实用技巧。
本文目录一览:- android如何旋转画布rect(android 旋转)
- An Overview of the Android Architecture (Android Studio)
- Android canvas画图操作之切割画布实现方法(clipRect)
- Android Material Design Ripple Effect 在 Android5.0(SDK=21)以下 Android 版本崩溃问题解决
- Android Studio如何旋转按钮并使它们与父视图的右侧/左侧对齐?
android如何旋转画布rect(android 旋转)
paint.setAntiAlias(true);
paint.setstrokeWidth(2);
paint.setColor(Color.BLUE);
paint.setAlpha(75);
Path path = new Path();
path.addRect(166,748,314,890,Path.Direction.CW);
canvas.rotate(45);
canvas.drawPath(path,paint);
解决方法
canvas.save(); canvas.rotate(45); canvas.drawRect(166,paint); canvas.restore();
Path.Direction与旋转变换无关.从docs:
Specifies how closed shapes (e.g. rects,ovals) are oriented when they are added to a path.

An Overview of the Android Architecture (Android Studio)
http://www.techotopia.com/index.php/An_Overview_of_the_Android_Architecture_(Android_Studio)
So far in this book, steps have been taken to set up an environment suitable for the development of Android applications using Android Studio. An initial step has also been taken into the process of application development through the creation of a simple Android Studio application project.
Before delving further into the practical matters of Android application development, however, it is important to gain an understanding of some of the more abstract concepts of both the Android SDK and Android development in general. Gaining a clear understanding of these concepts now will provide a sound foundation on which to build further knowledge.Starting with an overview of the Android architecture in this chapter, and continuing in the next few chapters of this book, the goal is to provide a detailed overview of the fundamentals of Android development.
The Android Software Stack
Android is structured in the form of a software stack comprising applications, an operating system, run-time environment, middleware, services and libraries. This architecture can, perhaps, best be represented visually as outlined in Figure 8-1. Each layer of the stack, and the corresponding elements within each layer, are tightly integrated and carefully tuned to provide the optimal application development and execution environment for mobile devices.
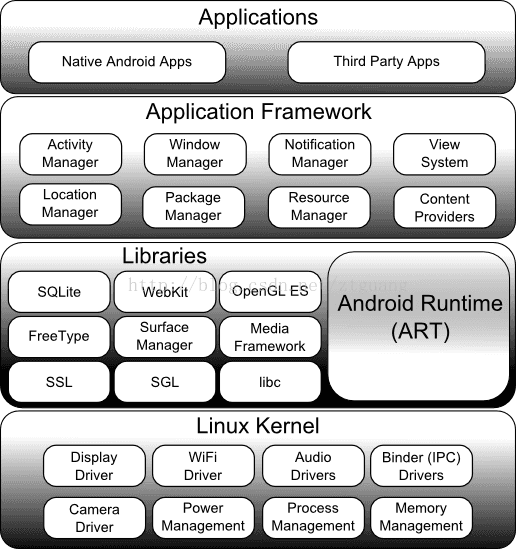
Figure 8-1
The remainder of this chapter will work through the different layers of the Android stack, starting at the bottom with the Linux Kernel.
The Linux Kernel
Positioned at the bottom of the Android software stack, the Linux Kernel provides a level of abstraction between the device hardware and the upper layers of the Android software stack. Based on Linux version 2.6, the kernel provides preemptive multitasking, low-level core system services such as memory, process and power management in addition to providing a network stack and device drivers for hardware such as the device display, Wi-Fi and audio.
The original Linux kernel was developed in 1991 by Linus Torvalds and was combined with a set of tools, utilities and compilers developed by Richard Stallman at the Free Software Foundation to create a full operating system referred to as GNU/Linux. Various Linux distributions have been derived from these basic underpinnings such as Ubuntu and Red Hat Enterprise Linux.
It is important to note, however, that Android only uses the Linux kernel. That said, it is worth noting that the Linux kernel was originally developed for use in traditional computers in the form of desktops and servers. In fact, Linux is now most widely deployed in mission critical enterprise server environments. It is a testament to both the power of today’s mobile devices and the efficiency and performance of the Linux kernel that we find this software at the heart of the Android software stack.
Android Runtime - ART
When an Android app is built within Android Studio it is compiled into an intermediate bytecode format (referred to as DEX format). When the application is subsequently loaded onto the device, the Android Runtime (ART) uses a process referred to as Ahead-of-Time (AOT) compilation to translate the bytecode down to the native instructions required by the device processor. This format is known as Executable and Linkable Format (ELF).
Each time the application is subsequently launched, the ELF executable version is run, resulting in faster application performance and improved battery life.
This contrasts with the Just-in-Time (JIT) compilation approach used in older Android implementations whereby the bytecode was translated within a virtual machine (VM) each time the application was launched.
Android Libraries
In addition to a set of standard Java development libraries (providing support for such general purpose tasks as string handling, networking and file manipulation), the Android development environment also includes the Android Libraries. These are a set of Java-based libraries that are specific to Android development. Examples of libraries in this category include the application framework libraries in addition to those that facilitate user interface building, graphics drawing and database access.
A summary of some key core Android libraries available to the Android developer is as follows:- android.app – Provides access to the application model and is the cornerstone of all Android applications.
- android.content – Facilitates content access, publishing and messaging between applications and application components.
- android.database – Used to access data published by content providers and includes SQLite database management classes.
- android.graphics – A low-level 2D graphics drawing API including colors, points, filters, rectangles and canvases.
- android.hardware – Presents an API providing access to hardware such as the accelerometer and light sensor.
- android.opengl – A Java interface to the OpenGL ES 3D graphics rendering API.
- android.os – Provides applications with access to standard operating system services including messages, system services and inter-process communication.
- android.media – Provides classes to enable playback of audio and video.
- android.net – A set of APIs providing access to the network stack. Includes android.net.wifi, which provides access to the device’s wireless stack.
- android.print – Includes a set of classes that enables content to be sent to configured printers from within Android applications.
- android.provider – A set of convenience classes that provide access to standard Android content provider databases such as those maintained by the calendar and contact applications.
- android.text – Used to render and manipulate text on a device display.
- android.util – A set of utility classes for performing tasks such as string and number conversion, XML handling and date and time manipulation.
- android.view – The fundamental building blocks of application user interfaces.
- android.widget - A rich collection of pre-built user interface components such as buttons, labels, list views, layout managers, radio buttons etc.
- android.webkit – A set of classes intended to allow web-browsing capabilities to be built into applications.
Having covered the Java-based libraries in the Android runtime, it is now time to turn our attention to the C/C++ based libraries contained in this layer of the Android software stack.
C/C++ Libraries
The Android runtime core libraries outlined in the preceding section are Java-based and provide the primary APIs for developers writing Android applications. It is important to note, however, that the core libraries do not actually perform much of the actual work and are, in fact, essentially Java “wrappers” around a set of C/C++ based libraries. When making calls, for example, to the android.opengl library to draw 3D graphics on the device display, the library actually ultimately makes calls to the OpenGL ES C++ library which, in turn, works with the underlying Linux kernel to perform the drawing tasks.C/C++ libraries are included to fulfill a wide and diverse range of functions including 2D and 3D graphics drawing, Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) communication, SQLite database management, audio and video playback, bitmap and vector font rendering, display subsystem and graphic layer management and an implementation of the standard C system library (libc).
In practice, the typical Android application developer will access these libraries solely through the Java based Android core library APIs. In the event that direct access to these libraries is needed, this can be achieved using the Android Native Development Kit (NDK), the purpose of which is to call the native methods of non-Java programming languages (such as C and C++) from within Java code using the Java Native Interface (JNI).
Application Framework
The Application Framework is a set of services that collectively form the environment in which Android applications run and are managed. This framework implements the concept that Android applications are constructed from reusable, interchangeable and replaceable components. This concept is taken a step further in that an application is also able to publish its capabilities along with any corresponding data so that they can be found and reused by other applications.
The Android framework includes the following key services:
- Activity Manager – Controls all aspects of the application lifecycle and activity stack.
- Content Providers – Allows applications to publish and share data with other applications.
- Resource Manager – Provides access to non-code embedded resources such as strings, color settings and user interface layouts.
- Notifications Manager – Allows applications to display alerts and notifications to the user.
- View System – An extensible set of views used to create application user interfaces.
- Package Manager – The system by which applications are able to find out information about other applications currently installed on the device.
- Telephony Manager – Provides information to the application about the telelphony services available on the device such as status and subscriber information.
- Location Manager – Provides access to the location services allowing an application to receive updates about location changes.
Applications
Located at the top of the Android software stack are the applications. These comprise both the native applications provided with the particular Android implementation (for example web browser and email applications) and the third party applications installed by the user after purchasing the device.
Summary
A good Android development knowledge foundation requires an understanding of the overall architecture of Android. Android is implemented in the form of a software stack architecture consisting of a Linux kernel, a runtime environment and corresponding libraries, an application framework and a set of applications. Applications are predominantly written in Java and compiled down to bytecode format within the Android Studio build environment. When the application is subsequently installed on a device, this bytecode is compiled down by the Android Runtime (ART) to the native format used by the CPU. The key goals of the Android architecture are performance and efficiency, both in application execution and in the implementation of reuse in application design.

Android canvas画图操作之切割画布实现方法(clipRect)
本文实例讲述了Android canvas画图操作之切割画布实现方法。分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下:
android切割画布的历程不算很难,可是理解起来也比较麻烦,这里写一下我的理解 但是不一定正确:
canvas.clipRect(30,30,70,Region.Op.XOR);
最后一个参数有多个选择分别是:
//DIFFERENCE是第一次不同于第二次的部分显示出来
//REPLACE是显示第二次的
//REVERSE_DIFFERENCE 是第二次不同于第一次的部分显示
//INTERSECT交集显示
//UNION全部显示
//XOR补集 就是全集的减去交集生育部分显示

import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.graphics.Paint;
import android.graphics.Path;
import android.graphics.Region;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.View;
public class sBook extends View{
Context mContext;
Paint mPaint;
Path mPath;
public sBook(Context context) {
super(context);
init();
}
public sBook(Context context,AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context,attrs);
init();
}
public sBook(Context context,AttributeSet attrs,int defStyle) {
super(context,attrs,defStyle);
init();
}
private void init(){
mPaint = new Paint();
mPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
mPaint.setstrokeWidth(6);
mPaint.setTextSize(16);
mPaint.setTextAlign(Paint.Align.RIGHT);
mPath = new Path();
}
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas){
canvas.drawColor(Color.GRAY);
canvas.save();
canvas.translate(10,10);
drawScene(canvas);
canvas.restore();
canvas.save();
canvas.translate(160,10);
canvas.clipRect(10,10,90,90);
canvas.clipRect(30,Region.Op.XOR);
drawScene(canvas);
canvas.restore();
canvas.save();
canvas.translate(10,160);
mPath.reset();
// canvas.clipPath(mPath); // makes the clip empty
// mPath.addCircle(50,50,Path.Direction.ccw);
mPath.cubicTo(0,100,100);
mPath.cubicTo(100,0);
canvas.clipPath(mPath,Region.Op.REPLACE);
drawScene(canvas);
canvas.restore();
canvas.save();
canvas.translate(160,160);
canvas.clipRect(0,60,60);
canvas.clipRect(40,40,Region.Op.UNION);
drawScene(canvas);
canvas.restore();
canvas.save();
canvas.translate(10,310);
canvas.clipRect(0,Region.Op.XOR);
drawScene(canvas);
canvas.restore();
canvas.save();
canvas.translate(160,Region.Op.REVERSE_DIFFERENCE);
drawScene(canvas);
canvas.restore();
}
private void drawScene(Canvas canvas) {
canvas.clipRect(0,100);
canvas.drawColor(Color.WHITE);
mPaint.setColor(Color.RED);
canvas.drawLine(0,mPaint);
mPaint.setColor(Color.GREEN);
canvas.drawCircle(30,mPaint);
mPaint.setColor(Color.BLUE);
canvas.drawText("Clipping",mPaint);
}
}
更多关于Android相关内容感兴趣的读者可查看本站专题:《Android图形与图像处理技巧总结》、《Android开发入门与进阶教程》、《Android调试技巧与常见问题解决方法汇总》、《Android多媒体操作技巧汇总(音频,视频,录音等)》、《Android基本组件用法总结》、《Android视图View技巧总结》、《Android布局layout技巧总结》及《Android控件用法总结》
希望本文所述对大家Android程序设计有所帮助。

Android Material Design Ripple Effect 在 Android5.0(SDK=21)以下 Android 版本崩溃问题解决
Android Material Design Ripple Effect 在 Android5.0(SDK=21)以下 Android 版本崩溃问题解决
附录 1 的 Android Ripple Effect 水波波纹荡漾的视觉交互设计,在 Android SDK 版本 21 上运作良好,但是放到 21 版本以下,比如 Android 4.0.3(SDK=15),就会导致整个 APP 崩溃,其中一个解决方案:以附录文章 1 为例,不仅需要在 drawable-v21 中写好 ripple_effect.xml,同时需要再在普通的 res/drawable 下面放一个同名 ripple_effect.xml 文件,在 res/drawable 目录下放的 ripple_effect.xml,目的就是为了向下兼容到低版本的 Android 设备,但是在 Android 低版本设备中,我把 ripple effect 退化成一个简单的点击背景变灰色的交互设计:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<selector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<item android:drawable="@android:color/white" android:state_window_focused="false" />
<item android:drawable="@android:color/darker_gray" android:state_pressed="true" />
<item android:drawable="@android:color/darker_gray" android:state_focused="true" />
<item android:drawable="@android:color/transparent" />
</selector>这样就可以正常兼容低版本的 Android 设备了,但这个解决方案的遗憾就是只是解决了代码向下兼容到低版本 Android 设备的问题,代价是牺牲了 Android Material Design 的 Ripple Effect 水波波纹荡漾视觉交互设计效果。
附录:
1,《Android Material Design : Ripple Effect 水波波纹荡漾的视觉交互设计》链接:http://blog.csdn.net/zhangphil/article/details/52451848

Android Studio如何旋转按钮并使它们与父视图的右侧/左侧对齐?
如何解决Android Studio如何旋转按钮并使它们与父视图的右侧/左侧对齐??
我想要旋转按钮并将它们与父视图的右/左侧对齐(图1)。 在左侧按钮中,我可以通过将 layout_marginLeft 设置为“ -20dp”来实现。 右键是这里的问题。当我将maring设置为300dp时,按钮不仅会移动到父母的右边(这就是我想要的),而且会变小(图片2)(我不想要那个)
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent">
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:id="@+id/buttons_top">
<Button
android:id="@+id/top_button"
android:layout_width="126dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@drawable/mafia_buttons_background"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
android:textColor="@color/white"
android:textAllCaps="false"
android:rotation="180"
app:autoSizePresetSizes="@array/auto_size_text_sizes"
android:autoSizeTextType="none"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/top_left_button"
android:layout_width="126dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@drawable/mafia_buttons_background"
android:layout_centerVertical="true"
android:layout_alignParentStart="true"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"
android:textColor="@color/white"
android:textAllCaps="false"
android:rotation="145"
app:autoSizePresetSizes="@array/auto_size_text_sizes"
android:autoSizeTextType="none"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/top_right_button"
android:layout_width="126dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@drawable/mafia_buttons_background"
android:layout_centerVertical="true"
android:layout_alignParentEnd="true"
android:layout_marginRight="10dp"
android:textColor="@color/white"
android:textAllCaps="false"
android:rotation="210"
app:autoSizePresetSizes="@array/auto_size_text_sizes"
android:autoSizeTextType="none"
/>
</RelativeLayout>
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:id="@+id/buttons_middle_top"
>
<Button
android:id="@+id/middle_top_left_button"
android:layout_width="126dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@drawable/mafia_buttons_background"
android:layout_centerVertical="true"
android:layout_alignParentStart="true"
android:layout_marginLeft="-20dp"
android:textColor="@color/white"
android:textAllCaps="false"
android:rotation="90"
app:autoSizePresetSizes="@array/auto_size_text_sizes"
android:autoSizeTextType="none"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/middle_top_right_button"
android:layout_width="126dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@drawable/mafia_buttons_background"
android:layout_centerVertical="true"
android:layout_alignParentEnd="true"
android:textColor="@color/white"
android:textAllCaps="false"
android:rotation="270"
app:autoSizePresetSizes="@array/auto_size_text_sizes"
android:autoSizeTextType="none"
/>
</RelativeLayout>
butttons that I want to move
that is happening after I write marginLeft="300dp"
解决方法
暂无找到可以解决该程序问题的有效方法,小编努力寻找整理中!
如果你已经找到好的解决方法,欢迎将解决方案带上本链接一起发送给小编。
小编邮箱:dio#foxmail.com (将#修改为@)
今天关于android如何旋转画布rect和android 旋转的讲解已经结束,谢谢您的阅读,如果想了解更多关于An Overview of the Android Architecture (Android Studio)、Android canvas画图操作之切割画布实现方法(clipRect)、Android Material Design Ripple Effect 在 Android5.0(SDK=21)以下 Android 版本崩溃问题解决、Android Studio如何旋转按钮并使它们与父视图的右侧/左侧对齐?的相关知识,请在本站搜索。
本文标签:



![[转帖]Ubuntu 安装 Wine方法(ubuntu如何安装wine)](https://www.gvkun.com/zb_users/cache/thumbs/4c83df0e2303284d68480d1b1378581d-180-120-1.jpg)

