本文将介绍javaThreadGroup源码分析的详细情况,特别是关于javathread类源码的相关信息。我们将通过案例分析、数据研究等多种方式,帮助您更全面地了解这个主题,同时也将涉及一些关于co
本文将介绍java ThreadGroup源码分析的详细情况,特别是关于java thread类源码的相关信息。我们将通过案例分析、数据研究等多种方式,帮助您更全面地了解这个主题,同时也将涉及一些关于com.sun.jdi.ThreadGroupReference的实例源码、Golang WaitGroup源码分析、java ThreadGroup 作用 方法解析(转)、Java Thread源码分析的知识。
本文目录一览:- java ThreadGroup源码分析(java thread类源码)
- com.sun.jdi.ThreadGroupReference的实例源码
- Golang WaitGroup源码分析
- java ThreadGroup 作用 方法解析(转)
- Java Thread源码分析

java ThreadGroup源码分析(java thread类源码)
使用:


1 import javax.swing.text.html.HTMLDocument.HTMLReader.IsindexAction;
2
3 public class Test {
4
5 public static void main(String[] args) {
6
7 ThreadGroup tg = new ThreadGroup("threadGroup-001");
8
9 Thread t1 = new Thread(tg, new MyThread());
10 t1.start();
11
12 Thread t2 = new Thread(tg, new MyThread());
13 t2.start();
14
15 // 返回线程组中活动线程的估计数
16 System.out.println("active thread group: " + tg.activeCount());
17 // 返回此线程组中活动线程组的估计数
18 System.out.println("activeGroupCount: " + tg.activeGroupCount());
19 // 检查当前运行的线程是否有权修改此线程组
20 tg.checkAccess();
21 // 设置线程组的最高优先级
22 tg.setMaxPriority(6);
23 // 返回此线程组的最高优先级
24 System.out.println("maxPriority: " + tg.getMaxPriority());
25 // 返回此线程组的名称
26 System.out.println("thread group name: " + tg.getName());
27 // 返回此线程组的父线程组
28 System.out.println(tg.getParent());
29 // 中断此线程组中的所有线程
30 tg.interrupt();
31 // 更改此线程组的后台程序状态
32 tg.setDaemon(true);
33 // 测试此线程组是否为一个后台程序线程组
34 System.out.println("is daemon: " + tg.isDaemon());
35 // 测试此线程组是否为线程组参数或其祖先线程组之一
36 System.out.println("is parent: "+ tg.getParent().parentOf(tg));
37 // 打印线程组信息
38 tg.list();
39 // 返回线程组的字符串表示形式
40 System.out.println(tg.toString());
41 // 销毁此线程组及其所有子组
42 tg.destroy();
43 // 测试此线程组是否已经销毁
44 System.out.println(tg.isDestroyed());
45 // System.out.println(tg.);
46 }
47
48 private static class MyThread extends Thread {
49 @Override
50 public void run() {
51 System.out.println("thread name: " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
52 }
53 }
54
55 }一、构造函数
两种构造函数:
ThreadGroup(String name)
ThreadGroup(ThreadGroup parent, String name)


public ThreadGroup(String name) {
this(Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup(), name);
}

1 public ThreadGroup(ThreadGroup parent, String name) {
2 this(checkParentAccess(parent), parent, name);
3 }

1 private ThreadGroup(Void unused, ThreadGroup parent, String name) {
2 this.name = name;
3 this.maxPriority = parent.maxPriority;
4 this.daemon = parent.daemon;
5 this.parent = parent;
6 parent.add(this);
7 }

1 private final void add(ThreadGroup g){
2 synchronized (this) {
3 if (destroyed) {
4 throw new IllegalThreadStateException();
5 }
6 // 添加一个线程组到此线程组的groups数组中,groups初始容量为4,每次容量耗尽之后按2倍扩增。
7 if (groups == null) {
8 groups = new ThreadGroup[4];
9 } else if (ngroups == groups.length) {
10 groups = Arrays.copyOf(groups, ngroups * 2);
11 }
12 groups[ngroups] = g;
13
14 // This is done last so it doesn''t matter in case the
15 // thread is killed
16 ngroups++;
17 }
18 }二、添加线程到线程组


1 ThreadGroup tg = new ThreadGroup("threadGroup-001");
2 Thread t1 = new Thread(tg, new MyThread());
3 t1.start();new Thread(tg, new MyThread()); 调用后,关于线程组相关的操作设置可在 private Thread(ThreadGroup g, Runnable target, String name,long stackSize, AccessControlContext acc,boolean inheritThreadLocals)看到:
1 private Thread(ThreadGroup g, Runnable target, String name,
2 long stackSize, AccessControlContext acc,
3 boolean inheritThreadLocals) {
4 if (name == null) {
5 throw new NullPointerException("name cannot be null");
6 }
7
8 this.name = name;
9
10 Thread parent = currentThread();
11 SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();
12 if (g == null) {
13 /* Determine if it''s an applet or not */
14
15 /* If there is a security manager, ask the security manager
16 what to do. */
17 if (security != null) {
18 g = security.getThreadGroup();
19 }
20
21 /* If the security manager doesn''t have a strong opinion
22 on the matter, use the parent thread group. */
23 // 此线程没有明确指定线程组时,为其指定当前线程所在的线程组
24 if (g == null) {
25 g = parent.getThreadGroup();
26 }
27 }
28
29 /* checkAccess regardless of whether or not threadgroup is
30 explicitly passed in. */
31 g.checkAccess();
32
33 /*
34 * Do we have the required permissions?
35 */
36 if (security != null) {
37 if (isCCLOverridden(getClass())) {
38 security.checkPermission(
39 SecurityConstants.SUBCLASS_IMPLEMENTATION_PERMISSION);
40 }
41 }
42
43 // 调用类ThreadGroup的addUnstarted函数, 添加一个未启用的线程到线程组
44 g.addUnstarted();
45
46 // 设置当前线程的线程组
47 this.group = g;
48 this.daemon = parent.isDaemon();
49 this.priority = parent.getPriority();
50 if (security == null || isCCLOverridden(parent.getClass()))
51 this.contextClassLoader = parent.getContextClassLoader();
52 else
53 this.contextClassLoader = parent.contextClassLoader;
54 this.inheritedAccessControlContext =
55 acc != null ? acc : AccessController.getContext();
56 this.target = target;
57 setPriority(priority);
58 if (inheritThreadLocals && parent.inheritableThreadLocals != null)
59 this.inheritableThreadLocals =
60 ThreadLocal.createInheritedMap(parent.inheritableThreadLocals);
61 /* Stash the specified stack size in case the VM cares */
62 this.stackSize = stackSize;
63
64 /* Set thread ID */
65 this.tid = nextThreadID();
66 }主要操作:设置此线程的线程组,将线程组的未启动线程数加1(addUnstarted() 即nUnstartedThreads++)。
随后启动一个线程(t1.start()):
1 public synchronized void start() {
2 /**
3 * This method is not invoked for the main method thread or "system"
4 * group threads created/set up by the VM. Any new functionality added
5 * to this method in the future may have to also be added to the VM.
6 *
7 * A zero status value corresponds to state "NEW".
8 */
9 if (threadStatus != 0)
10 throw new IllegalThreadStateException();
11
12 /* Notify the group that this thread is about to be started
13 * so that it can be added to the group''s list of threads
14 * and the group''s unstarted count can be decremented. */
15 group.add(this);
16
17 boolean started = false;
18 try {
19 start0();
20 started = true;
21 } finally {
22 try {
23 if (!started) {
24 group.threadStartFailed(this);
25 }
26 } catch (Throwable ignore) {
27 /* do nothing. If start0 threw a Throwable then
28 it will be passed up the call stack */
29 }
30 }
31 }start()中的先调用 group.add(this)。然后线程启动失败后调用 group.threadStartFailed(this) 。
源码如下:


1 void add(Thread t) {
2 synchronized (this) {
3 if (destroyed) {
4 throw new IllegalThreadStateException();
5 }
6 // ThreadGroup维护了一个数组,用来存放线程。
7 if (threads == null) {
8 threads = new Thread[4];
9 } else if (nthreads == threads.length) {
10 threads = Arrays.copyOf(threads, nthreads * 2);
11 }
12 // 添加线程到数组中
13 threads[nthreads] = t;
14
15 // This is done last so it doesn''t matter in case the
16 // thread is killed
17 // 线程数组中线程数量增加1
18 nthreads++;
19
20 // The thread is now a fully fledged member of the group, even
21 // though it may, or may not, have been started yet. It will prevent
22 // the group from being destroyed so the unstarted Threads count is
23 // decremented.
24 // 未启动线程数减1
25 nUnstartedThreads--;
26 }
27 }

1 void threadStartFailed(Thread t) {
2 synchronized(this) {
3 // 线程组中移除线程t
4 remove(t);
5 // 未启动线程数增加1
6 nUnstartedThreads++;
7 }
8 }

1 private void remove(Thread t) {
2 synchronized (this) {
3 if (destroyed) {
4 return;
5 }
6 // 循环遍历查找线程t,并移除
7 for (int i = 0 ; i < nthreads ; i++) {
8 if (threads[i] == t) {
9 System.arraycopy(threads, i + 1, threads, i, --nthreads - i);
10 // Zap dangling reference to the dead thread so that
11 // the garbage collector will collect it.
12 threads[nthreads] = null;
13 break;
14 }
15 }
16 }
17 }由上可见:只有调用start()成功启动的线程才会被它的线程组保存。
三、ThreadGroup的一些函数
1、destory() 销毁此线程组及其所有子组


1 // 销毁此线程组及其所有子线程组
2 public final void destroy() {
3 int ngroupsSnapshot;
4 ThreadGroup[] groupsSnapshot;
5 synchronized (this) {
6 checkAccess();
7 if (destroyed || (nthreads > 0)) {
8 throw new IllegalThreadStateException();
9 }
10 // 子线程组数量
11 ngroupsSnapshot = ngroups;
12 // 子线程组数组
13 if (groups != null) {
14 groupsSnapshot = Arrays.copyOf(groups, ngroupsSnapshot);
15 } else {
16 groupsSnapshot = null;
17 }
18 // 置空子线程数量、子线程组、子线程组数量、子线程组数组
19 if (parent != null) {
20 destroyed = true;
21 ngroups = 0;
22 groups = null;
23 nthreads = 0;
24 threads = null;
25 }
26 }
27 // 递归子线程组
28 for (int i = 0 ; i < ngroupsSnapshot ; i += 1) {
29 groupsSnapshot[i].destroy();
30 }
31 // 从父线程组中移除此线程组
32 if (parent != null) {
33 parent.remove(this);
34 }
35 }2、interrupt() 中断此线程组中的所有线程(包括子线程组中的线程)


1 // 中断此线程组中的所有线程(包括子线程组中的线程)
2 public final void interrupt() {
3 int ngroupsSnapshot;
4 ThreadGroup[] groupsSnapshot;
5 synchronized (this) {
6 checkAccess();
7 // 循环遍历线程组中的子线程,中断线程
8 for (int i = 0 ; i < nthreads ; i++) {
9 threads[i].interrupt();
10 }
11 ngroupsSnapshot = ngroups;
12 if (groups != null) {
13 groupsSnapshot = Arrays.copyOf(groups, ngroupsSnapshot);
14 } else {
15 groupsSnapshot = null;
16 }
17 }
18 // 递归去子线程组执行interrupt()
19 for (int i = 0 ; i < ngroupsSnapshot ; i++) {
20 groupsSnapshot[i].interrupt();
21 }
22 }3、setMaxPriority 设置线程组(包括子线程组)的最高优先级


1 // 设置线程组(包括子线程组)的最高优先级
2 public final void setMaxPriority(int pri) {
3 int ngroupsSnapshot;
4 ThreadGroup[] groupsSnapshot;
5 synchronized (this) {
6 checkAccess();
7 // 检验优先级大小是否合规
8 if (pri < Thread.MIN_PRIORITY || pri > Thread.MAX_PRIORITY) {
9 return;
10 }
11 // 最高优先级不能大于父线程组
12 maxPriority = (parent != null) ? Math.min(pri, parent.maxPriority) : pri;
13 ngroupsSnapshot = ngroups;
14 if (groups != null) {
15 groupsSnapshot = Arrays.copyOf(groups, ngroupsSnapshot);
16 } else {
17 groupsSnapshot = null;
18 }
19 }
20 // 递归设置子线程组的最高优先级
21 for (int i = 0 ; i < ngroupsSnapshot ; i++) {
22 groupsSnapshot[i].setMaxPriority(pri);
23 }
24 }4、parentOf 判断是否为当前线程组的祖先线程组(或是否是当前线程组)


1 // 判断g是否为当前线程组的祖先线程组(或是否是当前线程组)
2 public final boolean parentOf(ThreadGroup g) {
3 // 向上查找父线程组,直到父线程组为空,判断g是否为当前线程组的祖先线程组(或是否是当前线程组)
4 for (; g != null ; g = g.parent) {
5 if (g == this) {
6 return true;
7 }
8 }
9 return false;
10 }5、activeCount 返回线程组中活动线程的估计数


1 // 返回线程组中活动线程的估计数
2 public int activeCount() {
3 int result;
4 // Snapshot sub-group data so we don''t hold this lock
5 // while our children are computing.
6 int ngroupsSnapshot;
7 ThreadGroup[] groupsSnapshot;
8 synchronized (this) {
9 if (destroyed) {
10 return 0;
11 }
12 // 线程组中的线程数
13 result = nthreads;
14 // 子线程组
15 ngroupsSnapshot = ngroups;
16 if (groups != null) {
17 groupsSnapshot = Arrays.copyOf(groups, ngroupsSnapshot);
18 } else {
19 groupsSnapshot = null;
20 }
21 }
22 // 递归子孙线程组
23 for (int i = 0 ; i < ngroupsSnapshot ; i++) {
24 result += groupsSnapshot[i].activeCount();
25 }
26 return result;
27 }6、activeGroupCount 返回此线程组中活动线程组的估计数


1 public int activeGroupCount() {
2 int ngroupsSnapshot;
3 ThreadGroup[] groupsSnapshot;
4 synchronized (this) {
5 if (destroyed) {
6 return 0;
7 }
8 // 子线程组数量
9 ngroupsSnapshot = ngroups;
10 if (groups != null) {
11 groupsSnapshot = Arrays.copyOf(groups, ngroupsSnapshot);
12 } else {
13 groupsSnapshot = null;
14 }
15 }
16 int n = ngroupsSnapshot;
17 // 递归子孙线程组
18 for (int i = 0 ; i < ngroupsSnapshot ; i++) {
19 n += groupsSnapshot[i].activeGroupCount();
20 }
21 return n;
22 }7、enumerate 所有活动线程复制到指定数组中


1 // rescurse 否还包括作为此线程组的子组的线程组中的线程。
2 // n 是list中已经存在的元素(线程)数量
3 private int enumerate(Thread list[], int n, boolean recurse) {
4 int ngroupsSnapshot = 0;
5 ThreadGroup[] groupsSnapshot = null;
6 synchronized (this) {
7 if (destroyed) {
8 return 0;
9 }
10 // 线程组中的线程
11 int nt = nthreads;
12 // nt不能大于list的可用长度(递归遍历子孙线程组的时候,会带上n,所以此处要减去n)
13 if (nt > list.length - n) {
14 nt = list.length - n;
15 }
16 for (int i = 0; i < nt; i++) {
17 if (threads[i].isAlive()) {
18 list[n++] = threads[i];
19 }
20 }
21 // 子孙线程组
22 if (recurse) {
23 ngroupsSnapshot = ngroups;
24 if (groups != null) {
25 groupsSnapshot = Arrays.copyOf(groups, ngroupsSnapshot);
26 } else {
27 groupsSnapshot = null;
28 }
29 }
30 }
31 // 递归子孙线程组
32 if (recurse) {
33 for (int i = 0 ; i < ngroupsSnapshot ; i++) {
34 n = groupsSnapshot[i].enumerate(list, n, true);
35 }
36 }
37 // 返回已添加到list的线程数量
38 return n;
39 }
com.sun.jdi.ThreadGroupReference的实例源码
public ThreadsCache getThreadsCache() {
synchronized (threadsCollectorLock) {
if (threadsCache == null) {
threadsCache = new ThreadsCache(this);
threadsCache.addPropertychangelistener(new Propertychangelistener() {
// Re-fire the changes
@Override
public void propertyChange(PropertyChangeEvent evt) {
String propertyName = evt.getPropertyName();
if (ThreadsCache.PROP_THREAD_STARTED.equals(propertyName)) {
firePropertyChange(PROP_THREAD_STARTED,null,getThread((ThreadReference) evt.getNewValue()));
}
if (ThreadsCache.PROP_THREAD_DIED.equals(propertyName)) {
firePropertyChange(PROP_THREAD_DIED,getThread((ThreadReference) evt.getoldValue()),null);
}
if (ThreadsCache.PROP_GROUP_ADDED.equals(propertyName)) {
firePropertyChange(PROP_THREAD_GROUP_ADDED,getThreadGroup((ThreadGroupReference) evt.getNewValue()));
}
}
});
}
return threadsCache;
}
}
/**
* Creates a new translated node for given original one.
*
* @param o a node to be translated
* @return a new translated node
*/
private Object createTranslation (Object o) {
switch (translationID) {
case THREAD_ID:
if (o instanceof ThreadReference) {
return new JPDAThreadImpl ((ThreadReference) o,debugger);
} else if (o instanceof ThreadGroupReference) {
return new JPDAThreadGroupImpl ((ThreadGroupReference) o,debugger);
} else {
return null;
}
case LOCALS_ID:
if (o instanceof ArrayType) {
return new JPDAArrayTypeImpl(debugger,(ArrayType) o);
}
if (o instanceof ReferenceType) {
return new JPDAClasstypeImpl(debugger,(ReferenceType) o);
}
default:
throw new IllegalStateException(""+o);
}
}
private void initGroups(ThreadGroupReference group) {
try {
List<ThreadGroupReference> groups = new ArrayList(ThreadGroupReferenceWrapper.threadGroups0(group));
List<ThreadReference> threads = new ArrayList(ThreadGroupReferenceWrapper.threads0(group));
filterThreads(threads);
groupMap.put(group,groups);
threadMap.put(group,threads);
for (ThreadGroupReference g : groups) {
initGroups(g);
}
} catch (ObjectCollectedException e) {
}
}
List<ThreadGroupReference> topLevelThreadGroups() {
List<ThreadGroupReference> groups = null;
try {
Cache local = getCache();
if (local != null) {
groups = local.groups;
}
if (groups == null) {
groups = Arrays.asList(
(ThreadGroupReference[])JDWP.VirtualMachine.TopLevelThreadGroups.
process(vm).groups);
if (local != null) {
local.groups = groups;
if ((vm.traceFlags & VirtualMachine.TRACE_OBJREFS) != 0) {
vm.printTrace(
"Caching top level thread groups (count = " +
groups.size() + ") while VM suspended");
}
}
}
} catch (JDWPException exc) {
throw exc.tojdiException();
}
return groups;
}
public static F3ObjectReference wrap(F3VirtualMachine f3vm,ObjectReference ref) {
if (ref == null) {
return null;
} else if (ref instanceof ArrayReference) {
return f3vm.arrayReference((ArrayReference)ref);
} else if (ref instanceof StringReference) {
return f3vm.stringReference((StringReference)ref);
} else if (ref instanceof ThreadReference) {
return f3vm.threadReference((ThreadReference)ref);
} else if (ref instanceof ThreadGroupReference) {
return f3vm.threadGroupReference((ThreadGroupReference)ref);
} else if (ref instanceof ClassLoaderReference) {
return f3vm.classLoaderReference((ClassLoaderReference)ref);
} else if (ref instanceof ClassObjectReference) {
return f3vm.classObjectReference((ClassObjectReference)ref);
} else {
return f3vm.objectReference(ref);
}
}
public JPDAThreadGroup[] getTopLevelThreadGroups() {
ThreadsCache tc = getThreadsCache();
if (tc == null) {
return new JPDAThreadGroup[0];
}
List<ThreadGroupReference> groupList = tc.getTopLevelThreadGroups();
JPDAThreadGroup[] groups = new JPDAThreadGroup[groupList.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < groups.length; i++) {
groups[i] = getThreadGroup((ThreadGroupReference) groupList.get(i));
}
return groups;
}
public JPDAThreadGroupImpl[] getThreadGroups () {
ThreadsCache tc = debugger.getThreadsCache();
if (tc == null) {
return new JPDAThreadGroupImpl[0];
}
List<ThreadGroupReference> l = tc.getGroups(tgr);
int i,k = l.size ();
JPDAThreadGroupImpl[] ts = new JPDAThreadGroupImpl[k];
for (i = 0; i < k; i++) {
ts [i] = (JPDAThreadGroupImpl) debugger.getThreadGroup(l.get (i));
}
return ts;
}
void notifyToBeResumed(ThreadsCache tc) {
List<ThreadReference> threads = tc.getThreads(tgr);
for (ThreadReference threadRef : threads) {
JPDAThreadImpl thread = debugger.getThread(threadRef);
thread.notifyToBeResumed();
}
List<ThreadGroupReference> groups = tc.getGroups(tgr);
for (ThreadGroupReference groupRef : groups) {
JPDAThreadGroupImpl group = (JPDAThreadGroupImpl) debugger.getThreadGroup(groupRef);
group.notifyToBeResumed(tc);
}
}
void notifySuspended(ThreadsCache tc) {
List<ThreadReference> threads = tc.getThreads(tgr);
for (ThreadReference threadRef : threads) {
JPDAThreadImpl thread = debugger.getThread(threadRef);
thread.notifySuspended();
}
List<ThreadGroupReference> groups = tc.getGroups(tgr);
for (ThreadGroupReference groupRef : groups) {
JPDAThreadGroupImpl group = (JPDAThreadGroupImpl) debugger.getThreadGroup(groupRef);
group.notifySuspended(tc);
}
}
/**
* The invariant in this class is that the top iterator
* on the stack has more elements. If the stack is
* empty,there is no top. This method assures
* this invariant.
*/
private void push(List<ThreadGroupReference> tgl) {
stack.push(tgl.iterator());
while (!stack.isEmpty() && !top().hasNext()) {
stack.pop();
}
}
static ThreadGroupReference find(String name) {
ThreadGroupIterator tgi = new ThreadGroupIterator();
while (tgi.hasNext()) {
ThreadGroupReference tg = tgi.nextThreadGroup();
if (tg.name().equals(name)) {
return tg;
}
}
return null;
}
static ThreadGroupReference group() {
if (group == null) {
// Current thread group defaults to the first top level
// thread group.
setThreadGroup(Env.vm().topLevelThreadGroups().get(0));
}
return group;
}
/**
* The invariant in this class is that the top iterator
* on the stack has more elements. If the stack is
* empty,there is no top. This method assures
* this invariant.
*/
private void push(List<ThreadGroupReference> tgl) {
stack.push(tgl.iterator());
while (!stack.isEmpty() && !top().hasNext()) {
stack.pop();
}
}
static ThreadGroupReference find(String name) {
ThreadGroupIterator tgi = new ThreadGroupIterator();
while (tgi.hasNext()) {
ThreadGroupReference tg = tgi.nextThreadGroup();
if (tg.name().equals(name)) {
return tg;
}
}
return null;
}
static ThreadGroupReference group() {
if (group == null) {
// Current thread group defaults to the first top level
// thread group.
setThreadGroup(Env.vm().topLevelThreadGroups().get(0));
}
return group;
}
/**
* The invariant in this class is that the top iterator
* on the stack has more elements. If the stack is
* empty,there is no top. This method assures
* this invariant.
*/
private void push(List<ThreadGroupReference> tgl) {
stack.push(tgl.iterator());
while (!stack.isEmpty() && !top().hasNext()) {
stack.pop();
}
}
static ThreadGroupReference find(String name) {
ThreadGroupIterator tgi = new ThreadGroupIterator();
while (tgi.hasNext()) {
ThreadGroupReference tg = tgi.nextThreadGroup();
if (tg.name().equals(name)) {
return tg;
}
}
return null;
}
static ThreadGroupReference group() {
if (group == null) {
// Current thread group defaults to the first top level
// thread group.
setThreadGroup(Env.vm().topLevelThreadGroups().get(0));
}
return group;
}
public ThreadGroupReference threadGroup() {
/*
* Thread group can't change,so it's cached once and for all.
*/
if (threadGroup == null) {
try {
threadGroup = JDWP.ThreadReference.ThreadGroup.
process(vm,this).group;
} catch (JDWPException exc) {
throw exc.tojdiException();
}
}
return threadGroup;
}
public String name() {
if (name == null) {
// Does not need synchronization,since worst-case
// static info is fetched twice (Thread group name
// cannot change)
try {
name = JDWP.ThreadGroupReference.Name.
process(vm,this).groupName;
} catch (JDWPException exc) {
throw exc.tojdiException();
}
}
return name;
}
public ThreadGroupReference parent() {
if (!triedParent) {
// Does not need synchronization,since worst-case
// static info is fetched twice (Thread group parent cannot
// change)
try {
parent = JDWP.ThreadGroupReference.Parent.
process(vm,this).parentGroup;
triedParent = true;
} catch (JDWPException exc) {
throw exc.tojdiException();
}
}
return parent;
}
public void suspend() {
for (ThreadReference thread : threads()) {
thread.suspend();
}
for (ThreadGroupReference threadGroup : threadGroups()) {
threadGroup.suspend();
}
}
public void resume() {
for (ThreadReference thread : threads()) {
thread.resume();
}
for (ThreadGroupReference threadGroup : threadGroups()) {
threadGroup.resume();
}
}
/**
* The invariant in this class is that the top iterator
* on the stack has more elements. If the stack is
* empty,there is no top. This method assures
* this invariant.
*/
private void push(List<ThreadGroupReference> tgl) {
stack.push(tgl.iterator());
while (!stack.isEmpty() && !top().hasNext()) {
stack.pop();
}
}
static ThreadGroupReference find(String name) {
ThreadGroupIterator tgi = new ThreadGroupIterator();
while (tgi.hasNext()) {
ThreadGroupReference tg = tgi.nextThreadGroup();
if (tg.name().equals(name)) {
return tg;
}
}
return null;
}
static ThreadGroupReference group() {
if (group == null) {
// Current thread group defaults to the first top level
// thread group.
setThreadGroup(Env.vm().topLevelThreadGroups().get(0));
}
return group;
}
/**
* The invariant in this class is that the top iterator
* on the stack has more elements. If the stack is
* empty,there is no top. This method assures
* this invariant.
*/
private void push(List<ThreadGroupReference> tgl) {
stack.push(tgl.iterator());
while (!stack.isEmpty() && !top().hasNext()) {
stack.pop();
}
}
static ThreadGroupReference find(String name) {
ThreadGroupIterator tgi = new ThreadGroupIterator();
while (tgi.hasNext()) {
ThreadGroupReference tg = tgi.nextThreadGroup();
if (tg.name().equals(name)) {
return tg;
}
}
return null;
}
static ThreadGroupReference group() {
if (group == null) {
// Current thread group defaults to the first top level
// thread group.
setThreadGroup(Env.vm().topLevelThreadGroups().get(0));
}
return group;
}
/**
* The invariant in this class is that the top iterator
* on the stack has more elements. If the stack is
* empty,there is no top. This method assures
* this invariant.
*/
private void push(List<ThreadGroupReference> tgl) {
stack.push(tgl.iterator());
while (!stack.isEmpty() && !top().hasNext()) {
stack.pop();
}
}
static ThreadGroupReference find(String name) {
ThreadGroupIterator tgi = new ThreadGroupIterator();
while (tgi.hasNext()) {
ThreadGroupReference tg = tgi.nextThreadGroup();
if (tg.name().equals(name)) {
return tg;
}
}
return null;
}
static ThreadGroupReference group() {
if (group == null) {
// Current thread group defaults to the first top level
// thread group.
setThreadGroup(Env.vm().topLevelThreadGroups().get(0));
}
return group;
}
public List<ThreadGroupReferenceProxyImpl> threadGroups() {
List<ThreadGroupReference> list = getThreadGroupReference().threadGroups();
List<ThreadGroupReferenceProxyImpl> proxies = new ArrayList<ThreadGroupReferenceProxyImpl>(list.size());
for (Iterator<ThreadGroupReference> iterator = list.iterator(); iterator.hasNext();) {
ThreadGroupReference threadGroupReference = iterator.next();
proxies.add(getVirtualMachineProxy().getThreadGroupReferenceProxy(threadGroupReference));
}
return proxies;
}
public static List<ThreadGroupReference> wrapThreadGroups(F3VirtualMachine f3vm,List<ThreadGroupReference> threadGroups) {
if (threadGroups == null) {
return null;
}
List<ThreadGroupReference> result = new ArrayList<ThreadGroupReference>(threadGroups.size());
for (ThreadGroupReference tref : threadGroups) {
result.add(wrap(f3vm,tref));
}
return result;
}
/**
* The invariant in this class is that the top iterator
* on the stack has more elements. If the stack is
* empty,there is no top. This method assures
* this invariant.
*/
private void push(List<ThreadGroupReference> tgl) {
stack.push(tgl.iterator());
while (!stack.isEmpty() && !top().hasNext()) {
stack.pop();
}
}
static ThreadGroupReference find(VirtualMachine vm,String name) {
ThreadGroupIterator tgi = new ThreadGroupIterator(vm.topLevelThreadGroups());
while (tgi.hasNext()) {
ThreadGroupReference tg = tgi.nextThreadGroup();
if (tg.name().equals(name)) {
return tg;
}
}
return null;
}

Golang WaitGroup源码分析
针对Golang 1.9的sync.WaitGroup进行分析,与Golang 1.10基本一样除了将panic改为了throw之外其他的都一样。
源代码位置:sync\waitgroup.go。
结构体
type WaitGroup struct {
nocopy nocopy // nocopy可以嵌入到结构中,在第一次使用后不可复制,使用go vet作为检测使用
// 位值:高32位是计数器,低32位是goroution等待计数。
// 64位的原子操作需要64位的对齐,但是32位。编译器不能确保它,所以分配了12个byte对齐的8个byte作为状态。
state1 [12]byte // byte=uint8范围:0~255,只取前8个元素。转为2进制:0000 0000,0000 0000... ...0000 0000
sema uint32 // 信号量,用于唤醒goroution
}
不知道大家是否和我一样,不论是使用Java的CountDownLatch还是Golang的WaitGroup,都会疑问,可以装下多个线程|协程等待呢?看了源码后可以回答了,可以装下
1111 1111 1111 ... 1111 \________32___________/
2^32个辣么多!所以不需要担心单机情况下会被撑爆了。
函数
以下代码已经去掉了与核心代码无关的race代码。
Add
添加或者减少等待goroutine的数量。
参数delta可能是负的,加到WaitGroup计数器,可能出现如下结果
- 如果计数器变为零,所有被阻塞的goroutines都会被释放。
- 如果计数器变成负数,就增加恐慌。
func (wg *WaitGroup) Add(delta int) {
// 获取到wg.state1数组中元素组成的二进制对应的十进制的值
statep := wg.state()
// 高32位是计数器
state := atomic.AddUint64(statep,uint64(delta)<<32)
// 获取计数器
v := int32(state >> 32)
w := uint32(state)
// 计数器为负数,报panic
if v < 0 {
panic("sync: negative WaitGroup counter")
}
// 添加与等待并发调用,报panic
if w != 0 && delta > 0 && v == int32(delta) {
panic("sync: WaitGroup misuse: Add called concurrently with Wait")
}
// 计数器添加成功
if v > 0 || w == 0 {
return
}
// 当等待计数器> 0时,而goroutine设置为0。
// 此时不可能有同时发生的状态突变:
// - 增加不能与等待同时发生,
// - 如果计数器counter == 0,不再增加等待计数器
if *statep != state {
panic("sync: WaitGroup misuse: Add called concurrently with Wait")
}
// Reset waiters count to 0.
*statep = 0
for ; w != 0; w-- {
// 目的是作为一个简单的wakeup原语,以供同步使用。true为唤醒排在等待队列的第一个goroutine
runtime_Semrelease(&wg.sema,false)
}
}
// unsafe.Pointer其实就是类似C的void *,在golang中是用于各种指针相互转换的桥梁。
// uintptr是golang的内置类型,是能存储指针的整型,uintptr的底层类型是int,它和unsafe.Pointer可相互转换。
// uintptr和unsafe.Pointer的区别就是:unsafe.Pointer只是单纯的通用指针类型,用于转换不同类型指针,它不可以参与指针运算;
// 而uintptr是用于指针运算的,GC 不把 uintptr 当指针,也就是说 uintptr 无法持有对象,uintptr类型的目标会被回收。
// state()函数可以获取到wg.state1数组中元素组成的二进制对应的十进制的值
func (wg *WaitGroup) state() *uint64 {
if uintptr(unsafe.Pointer(&wg.state1))%8 == 0 {
return (*uint64)(unsafe.Pointer(&wg.state1))
} else {
return (*uint64)(unsafe.Pointer(&wg.state1[4]))
}
}
Done
相当于Add(-1)。
func (wg *WaitGroup) Done() {
// 计数器减一
wg.Add(-1)
}
Wait
执行阻塞,直到所有的WaitGroup数量变成0。
func (wg *WaitGroup) Wait() {
// 获取到wg.state1数组中元素组成的二进制对应的十进制的值
statep := wg.state()
// cas算法
for {
state := atomic.LoadUint64(statep)
// 高32位是计数器
v := int32(state >> 32)
w := uint32(state)
// 计数器为0,结束等待
if v == 0 {
// Counter is 0,no need to wait.
return
}
// 增加等待goroution计数,对低32位加1,不需要移位
if atomic.CompareAndSwapUint64(statep,state,state+1) {
// 目的是作为一个简单的sleep原语,以供同步使用
runtime_Semacquire(&wg.sema)
if *statep != 0 {
panic("sync: WaitGroup is reused before prevIoUs Wait has returned")
}
return
}
}
}
使用注意事项
- WaitGroup不能保证多个 goroutine 执行次序
- WaitGroup无法指定固定的goroutine数目

java ThreadGroup 作用 方法解析(转)
ThreadGroup 线程组,java 对这个类的描述呢就是
“线程组表示一组线程。此外,线程组还可以包括其他线程组。线程组形成一个树,其中除了初始线程组之外的每个线程组都有一个父线程组。
允许线程访问关于其线程组的信息,但不允许访问关于其线程组的父线程组或任何其他线程组的信息。”
ThreadGroup 并不是算是标注容器,因为,最后你会发现这个家伙是没有 public 的 add,remove 方法的。那怎么把线程放到线程组里面呢?
答案是 在 new Thread(参数),将 ThreadGroup 当做参数传进去。
Field
private final ThreadGroup parent;// 线程组的线程组,final 表名 线程组 不可以随便变更
String name; //名字
int maxPriority;//这个线程组 的元素 例如 线程 线程组的最大优先级,具体实现是 当线程或者线程组自身设定优先级的时候,总是取 自己父线程组的优先级和要设定的优先级的最小值
boolean destroyed;//判断是否销毁了
boolean daemon;//当守护进程线程组的最后一个线程停止或最后一个线程组被销毁时,将自动销毁该线程组。
int nUnstartedThreads = 0;
int nthreads;//这个线程组 里面的线程数量
Thread threads[];//线程数组 ,持有 线程的引用
int ngroups;//这个线程组 里面的线程组数量
ThreadGroup groups[];//线程组数组 ,持有 线程组的引用私有构造方法
//创建不在任何线程组中的空线程组。
//此方法用于创建系统线程组。
private ThreadGroup()公共构造方法
//创建一个新线程组。这个新组的父线程组是指定的线程组parent。线程组的 名字 就是name
会对 parent 调用checkAccess() 确定当前运行的线程是否具有修改此线程组的权限(比如 设置setDaemon)。有可能会抛出SecurityException异常
public ThreadGroup(ThreadGroup parent, String name)
//构造一个新线程组。这个新组的父线程组是当前运行线程的线程组。 就是调用上面的方法
public ThreadGroup(String name) {
this(Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup(), name);
}公共方法
public final String getName()//返回线程组名字
//返回父线程组 parent 调用checkAccess() 确定当前运行的线程是否具有修改此线程组的权限。
//有可能会抛出SecurityException异常
public final ThreadGroup getParent()
public final int getMaxPriority() //返回线程组优先级
//测试此线程组是否是守护进程线程组。当守护进程线程组的最后一个线程停止或最后一个线程组被销毁时,将自动销毁该线程组。
public final boolean isDaemon()
public synchronized boolean isDestroyed()//测试该线程组是否已被销毁。
public final void setDaemon(boolean daemon)//将线程组设置成守护线程组 ,会检查 当前线程是否具有权限 修改线程组
//设定当前线程组以及子线程组的 优先级,取pri和当前线程组的父线程组的优先级的较小值为准。
//这个之所以会限制 Thread的最大优先级
//具体实现是 当线程或者线程组自身设定优先级的时候,总是取 自己父线程组的优先级和要设定的优先级的最小值
//会检查 当前线程是否具有权限 修改线程组
public final void setMaxPriority(int pri)
//测试,当前这个线程组是否是 g线程组的父线程 或者参数
public final boolean parentOf(ThreadGroup g)
//检查 当前线程是否具有权限 修改线程组 比如在当前线程中 用线程组自己本身调用它自己的一些方法 ,都会检查
public final void checkAccess()
//返回此线程组及其子线程组中活动线程数量的估计值。递归地遍历此线程组中的所有子组。 如果当前线程组已经destroyed,返回0
public int activeCount()
//将线程组的中线程 活动线程放入list[]里面 会自动扩大这个数组,如果{@code recurse}为{@code true},则此方法递归枚举此线程组的所有子组,并引用这些子组中的每个活动线程
//注意这个声明数组的方式
public int enumerate(Thread list[], boolean recurse)
//和上面方法类似 只不过 下面这个 ThreadGroup
public int enumerate(ThreadGroup list[])
public int enumerate(ThreadGroup list[], boolean recurse)
//返回此线程组及其子组中活动组的数量的估计值。递归地遍历此线程组中的所有子组。
public int activeGroupCount()
//interrupt此线程组中的所有线程。包括 子线程组中的线程
public final void interrupt()特殊的一个方法
public void uncaughtException(Thread t, Throwable e)这个方法呢,作用很简单 使 t 线程 抛出一个 Throwable e 的异常。这个 e 异常 也是你自己定义的。
如果前面设置了,
Thread.setDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler((t, e) -> {
System.out.println("默认的 "+t.getName());
System.out.println("默认的 "+e);
});那么,在上面自定义的 Throwable 会被这个捕获,如果没有设置,就打印标注错误流。对这个方法,存在的意义 比较困惑,,,
Thread.setDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler((t, e) -> {
System.out.println("默认的 "+t.getName());
System.out.println("默认的 "+e);
});
ThreadGroup threadGroup = new ThreadGroup("father");
Thread two = new Thread(threadGroup,"two");
threadGroup.uncaughtException(two,new IllegalAccessException("ssss"));
运行结果
转:https://blog.csdn.net/a1064072510/article/details/87455525

Java Thread源码分析
一、基本知识
(1)线程特性
- 每个线程均有优先级
- 线程能被标记为守护线程
- 每个线程均分配一个name
(2)创建线程的方法
- 继承Thread类,并重写run方法
// 继承Thread类
class PrimeThread extends Thread {
long minPrime;
PrimeThread(long minPrime) {
this.minPrime = minPrime;
}
public void run() {
// compute primes larger than minPrime
}
}
// 调用
PrimeThread p = new PrimeThread(143);
p.start();- 创建Thread类,并传入构造参数runnable
class PrimeRun implements Runnable {
long minPrime;
PrimeRun(long minPrime) {
this.minPrime = minPrime;
}
public void run() {
// compute primes larger than minPrime
}
}
// 调用
PrimeRun p = new PrimeRun(143);
new Thread(p).start();二、线程状态
public enum State {
NEW,
RUNNABLE,
BLOCKED,
WAITING,
TIMED_WAITING,
TERMINATED;
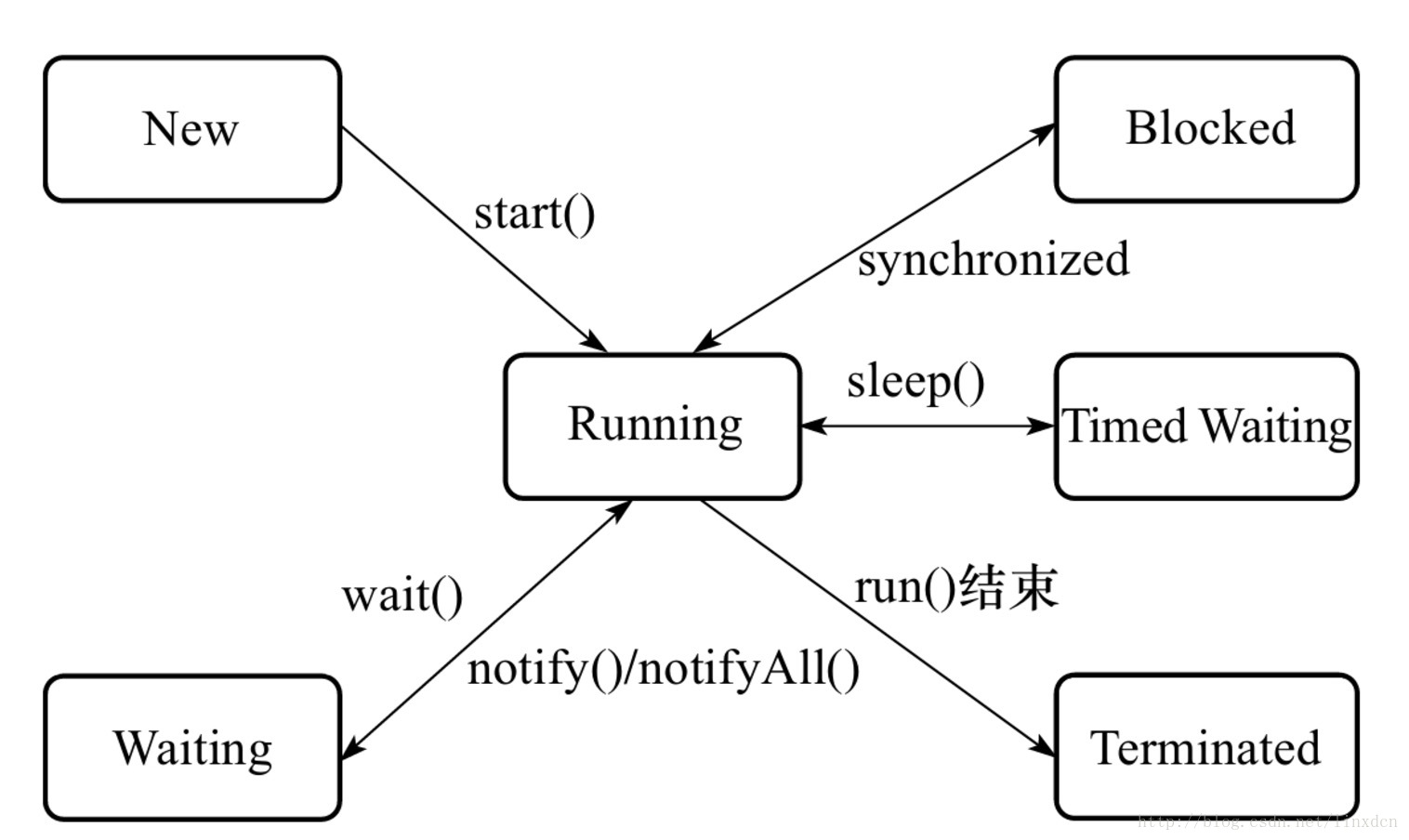
}- NEW 状态是指线程刚创建, 尚未启动
- RUNNABLE 状态是线程正在正常运行中, 当然可能会有某种耗时计算/IO等待的操作/CPU时间片切换等, 这个状态下发生的等待一般是其他系统资源, 而不是锁, Sleep等
- BLOCKED 这个状态下, 是在多个线程有同步操作的场景, 这个事件将在另一个线程放弃了这个锁的时候发生,也就是这里是线程在等待进入临界区
- WAITING(无线等待) 这个状态下是指线程拥有了某个锁之后, 调用了他的wait方法, 等待其他线程/锁拥有者调用 notify / notifyAll 一遍该线程可以继续下一步操作, 这里要区分 BLOCKED 和 WATING 的区别, 一个是在临界点外面等待进入, 一个是在临界点里面wait等待别人notify, 线程调用了join方法 join了另外的线程的时候, 也会进入WAITING状态, 等待被他join的线程执行结束
- TIMED_WAITING 这个状态就是有限的(时间限制)的WAITING, 一般出现在调用wait(long), join(long)等情况下, 另外一个线程sleep后, 也会进入TIMED_WAITING状态
- TERMINATED 这个状态下表示 该线程的run方法已经执行完毕了, 基本上就等于死亡了(当时如果线程被持久持有, 可能不会被回收)
java层次的状态转换图
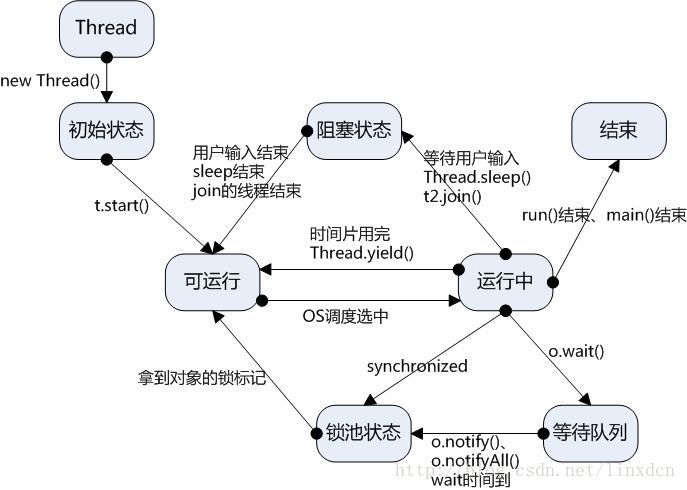
操作系统层次的状态转换图
三、基本属性
// Thread本身也是继承了Runnable接口
public class Thread implements Runnable {
private volatile char name[];
private int priority;
private Thread threadQ;
private long eetop;
private boolean single_step;
private boolean daemon = false;
// 虚拟机状态
private boolean stillborn = false;
// 实际的线程任务
private Runnable target;
private ThreadGroup group;
private ClassLoader contextClassLoader;
private AccessControlContext inheritedAccessControlContext;
// 所有初始化线程的数目
private static int threadInitNumber;
private static synchronized int nextThreadNum() {
return threadInitNumber++;
}
// 这是为ThreadLocal类维护的一些变量
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null;
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap inheritableThreadLocals = null;
private long stackSize;
private long nativeParkEventPointer;
// 线程id相关
private long tid;
private static long threadSeqNumber;
private static synchronized long nextThreadID() {
return ++threadSeqNumber;
}
// 线程状态
private volatile int threadStatus = 0;
volatile Object parkBlocker;
private volatile Interruptible blocker;
private final Object blockerLock = new Object();
void blockedOn(Interruptible b) {
synchronized (blockerLock) {
blocker = b;
}
}
// java中的线程总共分了10个优先级
// 最小优先级为1,最大为10,默认为5
public final static int MIN_PRIORITY = 1;
public final static int NORM_PRIORITY = 5;
public final static int MAX_PRIORITY = 10;
}四、构造函数
// 最主要的辅助构造函数,所有的构造函数均调用init函数
private void init(ThreadGroup g, Runnable target, String name,
long stackSize, AccessControlContext acc) {
if (name == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("name cannot be null");
}
this.name = name.toCharArray();
Thread parent = currentThread();
SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();
if (g == null) {
/* Determine if it''s an applet or not */
/* If there is a security manager, ask the security manager
what to do. */
if (security != null) {
g = security.getThreadGroup();
}
/* If the security doesn''t have a strong opinion of the matter
use the parent thread group. */
if (g == null) {
g = parent.getThreadGroup();
}
}
/* checkAccess regardless of whether or not threadgroup is
explicitly passed in. */
g.checkAccess();
/*
* Do we have the required permissions?
*/
if (security != null) {
if (isCCLOverridden(getClass())) {
security.checkPermission(SUBCLASS_IMPLEMENTATION_PERMISSION);
}
}
g.addUnstarted();
this.group = g;
// 子线程继承父线程的优先级和守护属性
this.daemon = parent.isDaemon();
this.priority = parent.getPriority();
if (security == null || isCCLOverridden(parent.getClass()))
this.contextClassLoader = parent.getContextClassLoader();
else
this.contextClassLoader = parent.contextClassLoader;
this.inheritedAccessControlContext =
acc != null ? acc : AccessController.getContext();
this.target = target;
setPriority(priority);
if (parent.inheritableThreadLocals != null)
this.inheritableThreadLocals =
ThreadLocal.createInheritedMap(parent.inheritableThreadLocals);
/* Stash the specified stack size in case the VM cares */
this.stackSize = stackSize;
// 获取唯一的线程id,此函数为synchronize
tid = nextThreadID();
}
// 所有的构造函数本质上都是调用init方法
public Thread() {
init(null, null, "Thread-" + nextThreadNum(), 0);
}
public Thread(Runnable target) {
init(null, target, "Thread-" + nextThreadNum(), 0);
}
Thread(Runnable target, AccessControlContext acc) {
init(null, target, "Thread-" + nextThreadNum(), 0, acc);
// 省略许多构造函数五、主要方法
// 启动一个线程
public synchronized void start() {
// 线程不能重复start
if (threadStatus != 0)
throw new IllegalThreadStateException();
group.add(this);
boolean started = false;
try {
// 未native方法
start0();
started = true;
} finally {
try {
if (!started) {
group.threadStartFailed(this);
}
} catch (Throwable ignore) {
}
}
}
private native void start0();
// Thread也实现了Runnable接口
@Override
public void run() {
if (target != null) {
target.run();
}
}
// 由系统调用,可以使Thread在销毁前释放资源
private void exit() {
if (group != null) {
group.threadTerminated(this);
group = null;
}
target = null;
threadLocals = null;
inheritableThreadLocals = null;
inheritedAccessControlContext = null;
blocker = null;
uncaughtExceptionHandler = null;
}
// 中断
public void interrupt() {
if (this != Thread.currentThread())
checkAccess();
synchronized (blockerLock) {
Interruptible b = blocker;
if (b != null) {
// 只是设置了中断标志位
interrupt0();
b.interrupt(this);
return;
}
}
interrupt0();
}
public final synchronized void join(long millis)
throws InterruptedException {
long base = System.currentTimeMillis();
long now = 0;
if (millis < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("timeout value is negative");
}
if (millis == 0) {
while (isAlive()) {
wait(0);
}
} else {
while (isAlive()) {
long delay = millis - now;
if (delay <= 0) {
break;
}
wait(delay);
now = System.currentTimeMillis() - base;
}
}
}
// 一些静态native方法,由jvm实现
public static native Thread currentThread();
public static native void yield();
public static native void sleep(long millis) throws InterruptedException;
// 还有一些已经不推荐使用的方法
@Deprecated
public final void stop() { }
@Deprecated
public final void stop() { }
@Deprecated
public void destroy() {
throw new NoSuchMethodError();
}
@Deprecated
public final void suspend() {
checkAccess();
suspend0();
}
@Deprecated
public final void resume() {
checkAccess();
resume0();
}六、总结
(1)线程复用
像线程池类高效的原因在于,线程池中的线程在完成任务后,不会销毁,而且缓存起来,每当用户请求一个线程处理任务时,线程池可以利用缓存的空闲线程来处理用户任务,这样避免了线程创建销毁带来的开销。
在Thread类中有一个Runnable target的域,只需将target替换成新的Runnable即可。
(2)wait()和notify/notifyAll()方法
wait()方法
- 线程进入WAITING状态,并且释放掉它所占有的“锁标志”,从而使别的线程有机会抢占该锁,等待其他线程调用“锁标志“对象的notify或notifyAll方法恢复
- wait方法是一个本地方法,其底层是通过一个叫做监视器锁的对象来完成的,所以调用wait方式时必须获取到monitor对象的所有权即通过Synchronized关键字,否则抛出IllegalMonitorStateException异常
notify/notifyAll()方法
- 在同一对象上去调用notify/notifyAll方法,就可以唤醒对应对象monitor上等待的线程了。notify和notifyAll的区别在于前者只能唤醒monitor上的一个线程,对其他线程没有影响,而notifyAll则唤醒所有的线程
(3)sleep/yield/join方法解析
sleep
- sleep方法的作用是让当前线程暂停指定的时间(毫秒)
- wait方法依赖于同步,而sleep方法可以直接调用
- sleep方法只是暂时让出CPU的执行权,并不释放锁。而wait方法则需要释放锁
yield
- yield方法的作用是暂停当前线程,以便其他线程有机会执行,不过不能指定暂停的时间,并且也不能保证当前线程马上停止
- yield只能使同优先级或更高优先级的线程有执行的机会
join
- 等待调用join方法的线程结束,再继续执行。如:t.join(),主要用于等待t线程运行结束
- 作用是父线程等待子线程执行完成后再执行,换句话说就是将异步执行的线程合并为同步的线程
(4)不推荐使用方法解释
参考:Why Are Thread.stop, Thread.suspend, Thread.resume and Runtime.runFinalizersOnExit Deprecated?
suspend()和resume()
- 这两个方法是配套使用的,suspend()是暂停线程,但并不释放资源,容易造成死锁情况
stop()
- 因为调用stop会使线程释放所有的锁,导致不安全情况,在调用stop时候,由锁保护的临界区可能处于状态不一致的情况,这不一致状态将暴露给其他线程
- 推荐的做法是,维护一个状态变量,当线程需要停止时更改这一状态变量,该线程应检查这一状态变量,看该线程是否应该终止了
(5)关于interrupt()中断函数
- 其实调用这个函数并不是真的中断线程,这个函数只是将Thread中的interrupt标志设置为true,用户需自行检测这一变量,停止线程,这种做法避免了stop带来的问题
(6)更深入学习
Thread类中有许多native方法,更深入的学习后续还需研究研究jvm的源码
今天关于java ThreadGroup源码分析和java thread类源码的讲解已经结束,谢谢您的阅读,如果想了解更多关于com.sun.jdi.ThreadGroupReference的实例源码、Golang WaitGroup源码分析、java ThreadGroup 作用 方法解析(转)、Java Thread源码分析的相关知识,请在本站搜索。
本文标签:



![[转帖]Ubuntu 安装 Wine方法(ubuntu如何安装wine)](https://www.gvkun.com/zb_users/cache/thumbs/4c83df0e2303284d68480d1b1378581d-180-120-1.jpg)

