想了解springboot基于shiro/springsecurity实现自定义登录的新动态吗?本文将为您提供详细的信息,我们还将为您解答关于springsecurity自定义登录页面的相关问题,此外
想了解spring boot 基于 shiro /spring security 实现自定义登录的新动态吗?本文将为您提供详细的信息,我们还将为您解答关于spring security 自定义登录页面的相关问题,此外,我们还将为您介绍关于4. Spring Boot 中 Spring Security 自定义用户认证、Spring Boot + Spring Security 实现自动登录功能、Spring Boot + Spring Security自定义用户认证、Spring Boot 整合 Spring Security + JWT(实现无状态登录)的新知识。
本文目录一览:- spring boot 基于 shiro /spring security 实现自定义登录(spring security 自定义登录页面)
- 4. Spring Boot 中 Spring Security 自定义用户认证
- Spring Boot + Spring Security 实现自动登录功能
- Spring Boot + Spring Security自定义用户认证
- Spring Boot 整合 Spring Security + JWT(实现无状态登录)

spring boot 基于 shiro /spring security 实现自定义登录(spring security 自定义登录页面)
shiro
shiro 配置文件
/**
* Shiro配置
*
* @see ShiroAutoConfiguration
*/
@Configuration
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class ShiroConf extends AbstractShiroConfiguration {
private final UserDetailService userDetailService;
private final TokenService tokenService;
private final CaptchaService captchaService;
private final Gson gson;
/**
* 自定义权限管理
*
* @see ShiroConfiguration
* @see DefaultSecurityManager
*/
@Bean
public DefaultWebSecurityManager securityManager(List<Realm> realms) {
DefaultWebSecurityManager securityManager = new DefaultWebSecurityManager();
securityManager.setRealms(realms);
securityManager.setSubjectDAO(subjectDAO());
ModularRealmAuthenticator authenticator = (ModularRealmAuthenticator) securityManager.getAuthenticator();
authenticator.setAuthenticationStrategy(authenticationStrategy());
return securityManager;
}
@Override
protected AuthenticationStrategy authenticationStrategy() {
// multiple realms none exception captured
return new FirstExceptionStrategy();
}
@Override
protected SessionStorageEvaluator sessionStorageEvaluator() {
DefaultSessionStorageEvaluator defaultSessionStorageEvaluator = new DefaultSessionStorageEvaluator();
// disable session
defaultSessionStorageEvaluator.setSessionStorageEnabled(false);
return defaultSessionStorageEvaluator;
}
@Bean
public Realm userAuthenticatingRealm() {
UserAuthenticatingRealm userAuthenticatingRealm = new UserAuthenticatingRealm();
userAuthenticatingRealm.setUserDetailService(userDetailService);
userAuthenticatingRealm.setCaptchaService(captchaService);
PasswordMatcher passwordMatcher = new PasswordMatcher();
passwordMatcher.setPasswordService(passwordService());
userAuthenticatingRealm.setCredentialsMatcher(passwordMatcher);
return userAuthenticatingRealm;
}
@Bean
public Realm tokenAuthorizingRealm() {
TokenAuthorizingRealm tokenAuthorizingRealm = new TokenAuthorizingRealm();
tokenAuthorizingRealm.setTokenService(tokenService);
return tokenAuthorizingRealm;
}
@Bean(name = "user_authc")
public UserFilter userAuthenticatingFilter() {
UserFilter userFilter = new UserFilter();
userFilter.setTokenService(tokenService);
userFilter.setGson(gson);
return userFilter;
}
@Bean(name = "token_authc")
public TokenFilter tokenAuthenticatingFilter() {
return new TokenFilter();
}
/**
* @see DefaultFilter
*/
@Bean(name = "shiroFilterChainDefinition")
public ShiroFilterChainDefinition shiroFilterChainDefinition() {
DefaultShiroFilterChainDefinition chainDefinition = new DefaultShiroFilterChainDefinition();
chainDefinition.addPathDefinition("/sys/login", "user_authc");
chainDefinition.addPathDefinition("/sys/logout", "anon");
chainDefinition.addPathDefinition("/sys/**", "token_authc");
chainDefinition.addPathDefinition("/manage/**", "anon");
chainDefinition.addPathDefinition("/wx/**", "anon");
chainDefinition.addPathDefinition("/**", "anon");
return chainDefinition;
}
@Bean(name = "shiroFilterFactoryBean")
public ShiroFilterFactoryBean shiroFilterFactoryBean(SecurityManager securityManager,
ShiroFilterChainDefinition shiroFilterChainDefinition,
Map<String, Filter> filterMap) {
ShiroFilterFactoryBean filterFactoryBean = new ShiroFilterFactoryBean();
filterFactoryBean.setSecurityManager(securityManager);
filterFactoryBean.setFilterChainDefinitionMap(shiroFilterChainDefinition.getFilterChainMap());
filterFactoryBean.setFilters(filterMap);
return filterFactoryBean;
}
@Bean
@DependsOn("lifecycleBeanPostProcessor")
public DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator defaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator() {
DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator proxyCreator = new DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator();
// 非接口使用 cglib, 防止额外的 aop 导致 @RequiresPermissions 注解失效
proxyCreator.setProxyTargetClass(true);
return proxyCreator;
}
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
@Bean
public PasswordService passwordService() {
return new DefaultPasswordService();
}
}AbstractAuthenticationStrategy
/**
* {@link org.apache.shiro.authc.pam.AuthenticationStrategy} implementation that throws the first exception it gets
* and ignores all subsequent realms. If there is no exceptions it works as the {@link FirstSuccessfulStrategy}
* <p>
* WARN: This approach works fine as long as there is ONLY ONE Realm per Token type.
*/
public class FirstExceptionStrategy extends FirstSuccessfulStrategy {
@Override
public AuthenticationInfo afterAttempt(Realm realm, AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo singleRealmInfo, AuthenticationInfo aggregateInfo, Throwable t) throws AuthenticationException {
if ((t instanceof AuthenticationException)) throw (AuthenticationException) t;
return super.afterAttempt(realm, token, singleRealmInfo, aggregateInfo, t);
}
}认证
/**
* AuthenticationToken —— 待认证 token
*/
public class UserAuthentication implements AuthenticationToken {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private final Object principal;
private Object credentials;
/**
* 验证码
*/
private String captcha;
private String uuid;
private boolean refresh;
/**
* 需要进行认证
*/
public UserAuthentication(Object principal, Object credentials) {
this.principal = principal;
this.credentials = credentials;
}
/**
* 需要进行认证(附带验证码)
*/
public UserAuthentication(Object principal, Object credentials, String captcha) {
this.principal = principal;
this.credentials = credentials;
this.captcha = captcha;
}
/**
* 需要进行认证(附带验证码)
*/
public UserAuthentication(Object principal, Object credentials, String captcha, String uuid) {
this.principal = principal;
this.credentials = credentials;
this.captcha = captcha;
this.uuid = uuid;
}
/**
* 以旧换新, 无须通过密码校验
*/
public UserAuthentication(Object principal, boolean refresh) {
this.principal = principal;
this.refresh = refresh;
}
@Override
public Object getPrincipal() {
return principal;
}
@Override
public Object getCredentials() {
return credentials;
}
public String getCaptcha() {
return captcha;
}
public String getUuid() {
return uuid;
}
}filter
/**
* 自定义 AuthenticatingFilter 认证过滤器
* <p>
* 登录认证
*/
@Slf4j
public class UserFilter extends AuthenticatingFilter {
private SysUserTokenService sysUserTokenService;
private Gson gson;
/**
* 返回待 AuthorizingRealm 认证的 AuthenticationToken, 参见 {@link UserAuthenticatingRealm#doGetAuthenticationInfo}
*/
@Override
protected AuthenticationToken createToken(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest req = (HttpServletRequest) request;
ServletInputStream inputStream = req.getInputStream();
InputStreamReader reader = new InputStreamReader(inputStream);
JsonObject jsonObject = getGson().fromJson(reader, JsonObject.class);
String principle = jsonObject.get(obtainUsernameParam()).getAsString();
String credentials = jsonObject.get(obtainPasswordParam()).getAsString();
String captcha = jsonObject.get(obtainCaptchaParam()).getAsString();
String uuid = jsonObject.get(obtainUuidParam()).getAsString();
return new UserAuthentication(principle, credentials, captcha, uuid);
}
/**
* 判断是否是登录请求
*/
@Override
public String getLoginUrl() {
return SecurityConstant.loginUrl;
}
/**
* 放行非登录请求(如 logout)
*/
@Override
protected boolean isAccessAllowed(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, Object mappedValue) {
return super.isAccessAllowed(request, response, mappedValue);
}
/**
* 拦截登录请求 —> 执行
*/
@Override
protected boolean onAccessDenied(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response) throws Exception {
if (isLoginRequest(request, response)) {
if (isLoginSubmission(request, response)) {
super.executeLogin(request, response);
} else {
//可能是登录页,故不禁止访问
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* 登录失败回调
*/
@SuppressWarnings("Duplicates")
@SneakyThrows
@Override
protected boolean onLoginFailure(AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationException exp, ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response) {
HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse = (HttpServletResponse) response;
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
String errorMsg = "未知异常";
int errorCode = 500;
if (exp instanceof CaptchaInvalidException) {
errorMsg = "验证码填写错误";
} else if (exp instanceof UnknownAccountException) {
errorMsg = "账号不存在";
} else if (exp instanceof CredentialsException) {
errorMsg = "密码错误";
} else if (exp instanceof LockedAccountException) {
errorMsg = "账号已锁定";
} else {
log.error("login fail {}", exp.getMessage());
}
map.put("code", errorCode);
map.put("msg", errorMsg);
map.put("success", false);
httpServletResponse.setContentType("application/json");
httpServletResponse.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_OK);
try {
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
mapper.writeValue(httpServletResponse.getOutputStream(), map);
} catch (Exception er) {
throw new ServletException();
}
// 尝试重新登录
return true;
}
/**
* 登录成功回调
*/
@SuppressWarnings("Duplicates")
@Override
protected boolean onLoginSuccess(AuthenticationToken token, Subject subject, ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse = (HttpServletResponse) response;
SysUserEntity userEntity = (SysUserEntity) SecurityUtils.getSubject().getPrincipal();
Result r = getSysUserTokenService().createToken(userEntity.getUserId());
httpServletResponse.setContentType("application/json");
httpServletResponse.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_OK);
try {
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
mapper.writeValue(httpServletResponse.getOutputStream(), r);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new ServletException();
}
return true;
}
protected String obtainUsernameParam() {
return "username";
}
protected String obtainPasswordParam() {
return "password";
}
protected String obtainCaptchaParam() {
return "captcha";
}
protected String obtainUuidParam() {
return "uuid";
}
protected boolean isLoginSubmission(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response) {
return (request instanceof HttpServletRequest) && WebUtils.toHttp(request).getMethod().equalsIgnoreCase(POST_METHOD);
}
public SysUserTokenService getSysUserTokenService() {
Assert.notNull(this.sysUserTokenService, "sysUserTokenService is needed");
return sysUserTokenService;
}
public void setSysUserTokenService(SysUserTokenService sysUserTokenService) {
this.sysUserTokenService = sysUserTokenService;
}
public Gson getGson() {
Assert.notNull(this.gson, "gson is needed");
return gson;
}
public void setGson(Gson gson) {
this.gson = gson;
}
}AuthenticatingRealm
/**
* 用户登录认证
*/
public class UserAuthenticatingRealm extends AuthenticatingRealm {
private ShiroService shiroService;
private SysCaptchaService sysCaptchaService;
public void setShiroService(ShiroService shiroService) {
this.shiroService = shiroService;
}
public SysCaptchaService getSysCaptchaService() {
Assert.notNull(this.sysCaptchaService, "getSysCaptchaService is needed");
return sysCaptchaService;
}
public void setSysCaptchaService(SysCaptchaService sysCaptchaService) {
this.sysCaptchaService = sysCaptchaService;
}
@Override
public boolean supports(AuthenticationToken token) {
return token instanceof UserAuthentication;
}
/**
* 认证
* <p>
* 从数据库查询真实个人信息
*
* @see org.apache.shiro.realm.AuthenticatingRealm#getAuthenticationInfo
* @see org.apache.shiro.realm.AuthenticatingRealm#assertCredentialsMatch
*/
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException {
// 校验验证码
UserAuthentication userAuthentication = (UserAuthentication) authenticationToken;
String captcha = userAuthentication.getCaptcha();
String uuid = userAuthentication.getUuid();
boolean validated = getSysCaptchaService().validate(uuid, captcha);
if (!validated) {
throw new CaptchaInvalidException("验证码无效");
}
String username = (String) authenticationToken.getPrincipal();
SysUserEntity user = shiroService.queryByUsername(username);
if (user == null) {
throw new UnknownAccountException("账号不存在");
} else if (user.getStatus() == 0) {
throw new LockedAccountException("账号已被锁定, 请联系管理员");
}
return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(user, user.getPassword(), getName());
}
}AuthenticationException
public class CaptchaInvalidException extends AuthenticationException {
public CaptchaInvalidException(String msg) {
super(msg);
}
}
鉴权与授权
/**
* AuthenticationToken —— 待认证 token
*/
public class XxAuthenticationToken implements AuthenticationToken {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private final String token;
public XxAuthenticationToken(String token) {
this.token = token;
}
@Override
public Object getPrincipal() {
return token;
}
@Override
public Object getCredentials() {
return token;
}
public String getToken() {
return token;
}
}filter
@Slf4j
public class TokenFilter extends AuthenticatingFilter {
protected static final String AUTHORIZATION_HEADER = "token";
@Override
protected AuthenticationToken createToken(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response) throws Exception {
String token = extractRequestToken(request);
return new XxAuthenticationToken(token);
}
@Override
protected boolean isAccessAllowed(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, Object mappedValue) {
// super.isAccessAllowed 基于 session 级别放行,这里进行重写
// or call org.apache.shiro.mgt.DefaultSessionStorageEvaluator.setSessionStorageEnabled to disable the session
return false;
}
@Override
protected boolean onAccessDenied(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response) throws Exception {
boolean loggedIn = false;
if (isLoginRequest(request, response)) {
loggedIn = executeLogin(request, response);
}
if (!loggedIn) {
//认证失败,提示 token 无效
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
String errorMsg = "invalid token";
int errorCode = 500;
map.put("code", errorCode);
map.put("msg", errorMsg);
map.put("success", false);
HttpServletResponse httpResponse = WebUtils.toHttp(response);
httpResponse.setContentType("application/json");
httpResponse.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_OK);
try {
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
mapper.writeValue(httpResponse.getOutputStream(), map);
} catch (Exception er) {
throw new ServletException();
}
}
return loggedIn;
}
@Override
protected final boolean isLoginRequest(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response) {
return StringUtils.isNotBlank(extractRequestToken(request));
}
private String extractRequestToken(ServletRequest request) {
HttpServletRequest httpRequest = WebUtils.toHttp(request);
String token = httpRequest.getHeader(AUTHORIZATION_HEADER);
if (StringUtils.isBlank(token)) {
token = httpRequest.getParameter(AUTHORIZATION_HEADER);
}
return token;
}
}realm
/**
* 基于 token 的 鉴权与授权
*/
public class TokenAuthorizingRealm extends AuthorizingRealm {
private ShiroService shiroService;
public ShiroService getShiroService() {
Assert.notNull(this.shiroService, "shiroService is needed");
return shiroService;
}
public void setShiroService(ShiroService shiroService) {
this.shiroService = shiroService;
}
@Override
public boolean supports(AuthenticationToken token) {
return token instanceof XxAuthenticationToken;
}
/**
* 认证
*
* 从数据库查询真实个人信息
*
* @see org.apache.shiro.realm.AuthenticatingRealm#getAuthenticationInfo
* @see org.apache.shiro.realm.AuthenticatingRealm#assertCredentialsMatch
*/
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException {
String accessToken = (String) authenticationToken.getPrincipal();
SysUserTokenEntity tokenEntity = shiroService.queryByToken(accessToken);
if (tokenEntity == null || tokenEntity.getExpireTime().getTime() < System.currentTimeMillis()) {
throw new IncorrectCredentialsException("token失效,请重新登录");
}
SysUserEntity user = shiroService.queryUser(tokenEntity.getUserId());
if (user.getStatus() == 0) {
throw new LockedAccountException("账号已被锁定,请联系管理员");
}
return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(user, accessToken, getName());
}
/**
* 授权
*
* 从数据库获取权限信息
*
* @see org.apache.shiro.realm.AuthorizingRealm#isPermitted
*/
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) {
SysUserEntity user = (SysUserEntity) principals.getPrimaryPrincipal();
Long userId = user.getUserId();
//用户权限列表
Set<String> permsSet = getShiroService().getUserPermissions(userId);
SimpleAuthorizationInfo info = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo();
info.setStringPermissions(permsSet);
return info;
}
}
Spring Security
spring security 配置文件
@EnableWebSecurity
@AllArgsConstructor
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true, securedEnabled = true)
public class SecurityConf extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
private TokenAuthenticationConfig tokenAuthenticationConfig;
private CorsFilter corsFilter;
private IPermissionService permissionService;
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
ExpressionUrlAuthorizationConfigurer<HttpSecurity>.ExpressionInterceptUrlRegistry registry = http.csrf().disable()
.addFilterBefore(corsFilter, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class)
.exceptionHandling()
.authenticationEntryPoint(new Http401UnAuthEntryPoint())
.accessDeniedHandler(new XxAccessDeniedHandler())
.and()
.headers()
.frameOptions()
.disable()
// create no session
.and()
.sessionManagement()
.sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS)
.and()
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/doc.htm**", "/service-worker.js",
"/v2/api-docs", "/configuration/ui", "/swagger-resources/**", "/v2/api-docs-ext",
"/configuration/security", "/swagger-ui.html", "/webjars/**",
"/favicon.ico", "/static/**",
"/acc/**", "/third/**", "/public/**"
).permitAll();
registry.antMatchers("/actuator/**")
.hasRole("ADMIN");
plusPermissions(registry);
registry
.anyRequest()
.authenticated()
.and()
.apply(tokenAuthenticationConfig);
}
@Bean
@Override
public AuthenticationManager authenticationManagerBean() throws Exception {
return super.authenticationManagerBean();
}
private void plusPermissions(ExpressionUrlAuthorizationConfigurer<HttpSecurity>.ExpressionInterceptUrlRegistry registry) {
List<Permission> permissions = permissionService.list();
if (CollectionUtil.isNotEmpty(permissions)) {
permissions.forEach(permission -> {
String urls = permission.getUrls();
if (StringUtil.isNotBlank(urls)) {
String[] urlArr = urls.split(",");
String curPerm = "PERMISSION_" + permission.getCode();
String access = String.format("hasRole(''%s'') or hasAuthority(''%s'')", RoleName.ADMIN.getName(), curPerm);
if (urlArr.length > 0) {
registry.antMatchers(urlArr)
.access(access);
}
}
});
}
}
}认证
public class TokenAuthentication extends AbstractAuthenticationToken {
private static final long serialVersionUID = SpringSecurityCoreVersion.SERIAL_VERSION_UID;
private final Object principal;
private Object credentials;
/**
* 认证前
*/
public TokenAuthentication(Object principal, Object credentials) {
super(null);
this.principal = principal;
this.credentials = credentials;
setAuthenticated(false);
}
/**
* 认证后
*/
public TokenAuthentication(Object principal, Object credentials,
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities) {
super(authorities);
this.principal = principal;
this.credentials = credentials;
super.setAuthenticated(true); // must use super, as we override
}
@Override
public Object getCredentials() {
return this.credentials;
}
@Override
public Object getPrincipal() {
return this.principal;
}
@Override
public void eraseCredentials() {
super.eraseCredentials();
credentials = null;
}
@Override
public void setAuthenticated(boolean isAuthenticated) throws IllegalArgumentException {
if (isAuthenticated) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Cannot set this token to trusted - use constructor which takes a GrantedAuthority list instead");
}
super.setAuthenticated(false);
}
}filter
/**
* doFilter 负责预鉴权(验证码,安全码是否一致)
* attemptAuthentication 负责提取 token
*/
@Slf4j
public class TokenAuthenticationFilter extends AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter {
private TokenService tokenService;
public TokenAuthenticationFilter() {
super(new AntPathRequestMatcher(SecurityConstant.LOGIN_URL, "POST"));
}
public void setTokenService(TokenService tokenService) {
this.tokenService = tokenService;
}
public TokenService getTokenService() {
Assert.notNull(this.tokenService, "tokenService is needed");
return this.tokenService;
}
/**
* 鉴权
* - 路由规则匹配
* - 验证码校验(短信验证码或阿里云人机校验)
*/
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest req = (HttpServletRequest) request;
HttpServletResponse res = (HttpServletResponse) response;
// 判断是否是登录请求 LOGIN_URL
if (!requiresAuthentication(req, res)) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
return;
}
try {
// 校验参数与验证码
getTokenService().checkParams(req, res);
} catch (AuthenticationException error) {
unsuccessfulAuthentication(req, res, error);
return;
}
super.doFilter(req, res, chain);
}
/**
* 返回一个待 Provider 认证的 token(TokenAuthentication)
*/
@Override
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws AuthenticationException, IOException, ServletException {
// 拦截非 POST 请求
if (!request.getMethod().equals(HttpMethod.POST.name())) {
throw new AuthenticationServiceException(
"Authentication method not supported: " + request.getMethod());
}
TokenAuthentication tokenAuthentication = new TokenAuthentication(obtainUsername(request), obtainPassword(request));
return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(tokenAuthentication);
}
@Nullable
protected String obtainUsername(HttpServletRequest request) {
return request.getParameter("username");
}
@Nullable
protected String obtainPassword(HttpServletRequest request) {
return request.getParameter("password");
}
}provider
/**
* 认证, 返回已认证的 token(Authentication)
*/
public class TokenAuthenticationProvider implements AuthenticationProvider {
protected final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
private UserDetailsService userDetailsService;
private PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
private BlackTool blackTool;
private static final String USER_NOT_FOUND_PASSWORD = "userNotFoundPassword";
private volatile String userNotFoundEncodedPassword;
private UserDetailsChecker preAuthenticationChecks = new TokenAuthenticationProvider.DefaultPreAuthenticationChecks();
private UserCache userCache = new NullUserCache();
public void setUserDetailsService(UserDetailsService userDetailsService) {
this.userDetailsService = userDetailsService;
}
public void setPasswordEncoder(PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder) {
this.passwordEncoder = passwordEncoder;
}
public void setBlackTool(BlackTool blackTool) {
this.blackTool = blackTool;
}
public UserDetailsService getUserDetailsService() {
Assert.notNull(this.userDetailsService, "userDetailsService could not be null");
return userDetailsService;
}
public PasswordEncoder getPasswordEncoder() {
Assert.notNull(this.passwordEncoder, "passwordEncoder could not be null");
return passwordEncoder;
}
public BlackTool getBlackTool() {
Assert.notNull(this.blackTool, "blackTool could not be null");
return blackTool;
}
/**
* i18n 字符串
*/
protected MessageSourceAccessor messages = SpringSecurityMessageSource.getAccessor();
@Override
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
// 校验 token 的 class 类型
Assert.isInstanceOf(TokenAuthentication.class, authentication,
messages.getMessage(
"SocialAuthenticationProvider.onlySupports",
"Only SocialAuthenticationToken is supported"));
// 通过 username 提取用户信息
String username = (authentication.getPrincipal() == null) ? "NONE_PROVIDED"
: authentication.getName();
//检查是否在黑名单中
checkBlackList(username);
// 从缓存中获取用户信息
boolean cacheWasUsed = true;
UserDetails user = this.userCache.getUserFromCache(username);
// 缓存中没有,则从数据库中获取用户信息
if (user == null) {
cacheWasUsed = false;
try {
user = this.retrieveUser(username, (TokenAuthentication) authentication);
} catch (UsernameNotFoundException notFound) {
logger.debug("User username ''" + username + "'' not found");
throw notFound;
}
Assert.notNull(user,
"retrieveUser returned null - a violation of the interface contract");
}
//检查信息是否匹配有效
try {
preAuthenticationChecks.check(user);
// password check
checkPassword(user, (TokenAuthentication) authentication);
} catch (AuthenticationException exception) {
//重新再试一下
if (cacheWasUsed) {
// There was a problem, so try again after checking
// we''re using latest data (i.e. not from the cache)
cacheWasUsed = false;
user = retrieveUser(username,
(TokenAuthentication) authentication);
preAuthenticationChecks.check(user);
checkPassword(user,
(TokenAuthentication) authentication);
} else {
throw exception;
}
}
// 加入缓存
if (!cacheWasUsed) {
this.userCache.putUserInCache(user);
}
TokenAuthentication authenticationToken = new TokenAuthentication(user, null, user.getAuthorities());
authenticationToken.setDetails(user);
return authenticationToken;
}
/**
* 过滤该 provider 支持认证的 authentication
*/
@Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> authentication) {
return TokenAuthentication.class.isAssignableFrom(authentication);
}
private class DefaultPreAuthenticationChecks implements UserDetailsChecker {
public void check(UserDetails user) {
if (!user.isAccountNonLocked()) {
logger.debug("User account is locked");
throw new LockedException(messages.getMessage(
"AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.locked",
"User account is locked"));
}
if (!user.isEnabled()) {
logger.debug("User account is disabled");
throw new DisabledException(messages.getMessage(
"AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.disabled",
"User is disabled"));
}
if (!user.isAccountNonExpired()) {
logger.debug("User account is expired");
throw new AccountExpiredException(messages.getMessage(
"AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.expired",
"User account has expired"));
}
}
}
public void checkBlackList(String blackKey) {
if (getBlackTool().existInBlackList(blackKey)) {
// 在黑名单中,拒绝访问
throw new AuthFrequentFailException("您已连续5次密码输入错误,请15分钟后再试");
}
}
/**
* 连续多次输入错误,直接禁止登录
*/
public void checkPassword(UserDetails userDetails,
TokenAuthentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
if (authentication.getCredentials() == null) {
logger.debug("Authentication failed: no credentials provided");
throw new BadCredentialsException(messages.getMessage(
"AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.badCredentials",
"Bad credentials"));
}
String blackKey = authentication.getPrincipal().toString();
String presentedPassword = authentication.getCredentials().toString();
if (!getPasswordEncoder().matches(presentedPassword, userDetails.getPassword())) {
logger.debug("Authentication failed: password does not match stored value");
// 黑名单计数
getBlackTool().incr(blackKey);
throw new BadCredentialsException(messages.getMessage(
"AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.badCredentials",
"Bad credentials"));
}
// 黑名单重置
getBlackTool().reset(blackKey);
}
protected final UserDetails retrieveUser(String username,
TokenAuthentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException {
prepareTimingAttackProtection();
try {
UserDetails loadedUser = this.getUserDetailsService().loadUserByUsername(username);
if (loadedUser == null) {
throw new InternalAuthenticationServiceException(
"UserDetailsService returned null, which is an interface contract violation");
}
return loadedUser;
} catch (UsernameNotFoundException ex) {
mitigateAgainstTimingAttack(authentication);
throw ex;
} catch (InternalAuthenticationServiceException ex) {
throw ex;
} catch (Exception ex) {
throw new InternalAuthenticationServiceException(ex.getMessage(), ex);
}
}
private void prepareTimingAttackProtection() {
if (this.userNotFoundEncodedPassword == null) {
this.userNotFoundEncodedPassword = this.passwordEncoder.encode(USER_NOT_FOUND_PASSWORD);
}
}
private void mitigateAgainstTimingAttack(TokenAuthentication authentication) {
if (authentication.getCredentials() != null) {
String presentedPassword = authentication.getCredentials().toString();
this.passwordEncoder.matches(presentedPassword, this.userNotFoundEncodedPassword);
}
}
}TokenAuthenticationConfig
@Component
@AllArgsConstructor
public class TokenAuthenticationConfig extends SecurityConfigurerAdapter<DefaultSecurityFilterChain, HttpSecurity> {
private TokenService tokenService;
private PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
private UserDetailsService userDetailsService;
private BlackTool blackTool;
@Override
public void configure(HttpSecurity http) {
// check filter
TokenCheckFilter checkFilter = new TokenCheckFilter(tokenService);
// handler
TokenFailHandler failHandler = new TokenFailHandler();
TokenSuccessHandler successHandler = new TokenSuccessHandler(tokenService);
// authentication filter
TokenAuthenticationFilter tokenFilter = new TokenAuthenticationFilter();
tokenFilter.setTokenService(tokenService);
tokenFilter.setAuthenticationManager(http.getSharedObject(AuthenticationManager.class));
tokenFilter.setAuthenticationSuccessHandler(successHandler);
tokenFilter.setAuthenticationFailureHandler(failHandler);
// provider
TokenAuthenticationProvider tokenProvider = new TokenAuthenticationProvider();
tokenProvider.setPasswordEncoder(passwordEncoder);
tokenProvider.setUserDetailsService(userDetailsService);
tokenProvider.setBlackTool(blackTool);
http.authenticationProvider(tokenProvider)
.addFilterBefore(checkFilter, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class)
.addFilterAfter(tokenFilter, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class);
}
}401
public class Http401UnAuthEntryPoint implements AuthenticationEntryPoint {
@Override
public void commence(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response,
AuthenticationException authException) throws IOException {
// This is invoked when user tries to access a secured REST resource without supplying any credentials
// We should just send a 401 Unauthorized response because there is no ''login page'' to redirect to
// Here you can place any message you want
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_UNAUTHORIZED, authException.getMessage());
}
}403
@Slf4j
public class XxAccessDeniedHandler implements AccessDeniedHandler {
@Override
public void handle(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, AccessDeniedException e) throws IOException, ServletException {
String requestURI = httpServletRequest.getRequestURI();
log.error("access {} wad denied.", requestURI, e);
httpServletResponse.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_FORBIDDEN);
httpServletResponse.getWriter().write("access denied");
}
}
fail handler
@Slf4j
public class TokenFailHandler implements AuthenticationFailureHandler {
@Override
public void onAuthenticationFailure(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, AuthenticationException exp) throws IOException, ServletException {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
String errorMsg = "未知异常";
int errorCode = 400;
if (exp instanceof UsernameNotFoundException) {
errorMsg = "账号不存在";
} else if (exp instanceof BadCredentialsException) {
errorMsg = "账号或密码错误";
errorCode = 401;
} else if (exp instanceof AuthParamFormatException) {
errorMsg = exp.getMessage();
} else if (exp instanceof AuthEmptyException) {
errorMsg = exp.getMessage();
} else if (exp instanceof AuthFrequentFailException) {
errorMsg = exp.getMessage();
errorCode = 403;
} else if(exp instanceof AuthAfsFailException) {
errorMsg = exp.getMessage();
errorCode = AfsConstant.FAIL_CODE;
} else if (exp instanceof DisabledException) {
errorMsg = "账号已被禁用";
} else if (exp instanceof AccountExpiredException) {
errorMsg = "账号过期";
} else if (exp instanceof LockedException) {
errorMsg = "该账号已被锁定";
} else if (exp instanceof InsufficientAuthenticationException) {
errorMsg = "验证失败";
} else{
log.error("auth error", exp);
}
map.put("code", errorCode);
map.put("msg", errorMsg);
map.put("success", false);
httpServletResponse.setContentType("application/json");
httpServletResponse.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_OK);
try {
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
mapper.writeValue(httpServletResponse.getOutputStream(), map);
} catch (Exception er) {
throw new ServletException();
}
}
}success handler
public class TokenSuccessHandler implements AuthenticationSuccessHandler {
private TokenService tokenService;
public TokenSuccessHandler(TokenService tokenService) {
this.tokenService = tokenService;
}
@Override
public void onAuthenticationSuccess(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, Authentication authentication) throws IOException, ServletException {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("code", 200);
map.put("success", true);
map.put("msg", "成功");
XxRequestToken xxRequestToken = tokenService.generateToken(authentication);
map.put("data", xxRequestToken);
httpServletResponse.setContentType("application/json");
httpServletResponse.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_OK);
try {
XxUserDetails userDetails = SecurityUtil.getUserDetails(authentication);
if (userDetails != null) {
String ipAddr = IPUtil.getIpAddr(httpServletRequest);
SpringUtil.publishEvent(new LoginOkEvent(new LoginInfo(userDetails.getId(), ipAddr)));
}
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
mapper.writeValue(httpServletResponse.getOutputStream(), map);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new ServletException();
}
}
}鉴权与授权
/**
* 校验 token
*/
@Slf4j
public class TokenCheckFilter extends GenericFilterBean {
private static final String AUTHORIZATION_HEADER = "Authorization";
private TokenService tokenService;
public TokenCheckFilter(TokenService tokenService) {
this.tokenService = tokenService;
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest req = (HttpServletRequest) servletRequest;
HttpServletResponse res = (HttpServletResponse) servletResponse;
String tokenKey = resolveToken(req);
String requestURI = req.getRequestURI();
boolean hasAuth = false;
if (StringUtils.hasText(tokenKey) && tokenService.validateToken(tokenKey)) {
Authentication authentication = tokenService.getAuthentication(tokenKey);
if (authentication != null) {
//authentication 中的 principle 可以转换为 XxUserDetails,供 SecurityUtil 提取权限信息
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authentication);
hasAuth = true;
}
}
if (requestURI.startsWith(SecurityConstant.LOGOUT_URL)) {
logout(hasAuth, tokenKey, res);
return;
}
filterChain.doFilter(servletRequest, servletResponse);
}
private String resolveToken(HttpServletRequest request) {
String bearerToken = request.getHeader(AUTHORIZATION_HEADER);
if (StringUtils.hasText(bearerToken) && bearerToken.startsWith("Bearer ")) {
return bearerToken.substring(7);
}
return null;
}
private void logout(boolean isAuthenticated, String tokenKey, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
if (isAuthenticated && tokenService.offline(tokenKey)) {
map.put("code", 200);
map.put("success", true);
map.put("msg", "注销成功");
} else {
map.put("code", 400);
map.put("success", false);
map.put("msg", "注销失败/已注销");
}
response.setContentType("application/json");
response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_OK);
try {
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
mapper.writeValue(response.getOutputStream(), map);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new ServletException();
}
}
}
4. Spring Boot 中 Spring Security 自定义用户认证
自定义认证过程
自定义认证的过程需要实现 Spring Security 提供的 UserDetailService 接口,该接口只有一个抽象方法 loadUserByUsername,源码如下:
public interface UserDetailsService {
UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException;
}loadUserByUsername 方法返回一个 UserDetail 对象,该对象也是一个接口,包含一些用于描述用户信息的方法,源码如下:
public interface UserDetails extends Serializable {
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities();
String getPassword();
String getUsername();
boolean isAccountNonExpired();
boolean isAccountNonLocked();
boolean isCredentialsNonExpired();
boolean isEnabled();
}这些方法的含义如下:
-
getAuthorities获取用户包含的权限,返回权限集合,权限是一个继承了GrantedAuthority的对象; -
getPassword和getUsername用于获取密码和用户名; -
isAccountNonExpired方法返回 boolean 类型,用于判断账户是否未过期,未过期返回 true 反之返回 false; -
isAccountNonLocked方法用于判断账户是否未锁定; -
isCredentialsNonExpired用于判断用户凭证是否没过期,即密码是否未过期; -
isEnabled方法用于判断用户是否可用。
实际中我们可以自定义 UserDetails 接口的实现类,也可以直接使用 Spring Security 提供的 UserDetails 接口实现类 org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User。
说了那么多,下面我们来开始实现 UserDetailService 接口的 loadUserByUsername 方法。
首先创建一个 MyUser 对象,用于存放模拟的用户数据(实际中一般从数据库获取,这里为了方便直接模拟):
public class MyUser implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 3497935890426858541L;
private String userName;
private String password;
private boolean accountNonExpired = true;
private boolean accountNonLocked= true;
private boolean credentialsNonExpired= true;
private boolean enabled= true;
// get,set略
}接着创建 MyUserDetailService 实现 UserDetailService:
@Configuration
public class UserDetailService implements UserDetailsService {
@Autowired
private PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
// 模拟一个用户,替代数据库获取逻辑
MyUser user = new MyUser();
user.setUserName(username);
user.setPassword(this.passwordEncoder.encode("123456"));
// 输出加密后的密码
System.out.println(user.getPassword());
return new User(username, user.getPassword(), user.isEnabled(),
user.isAccountNonExpired(), user.isCredentialsNonExpired(),
user.isAccountNonLocked(), AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList("admin"));
}
}这里我们使用了 org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User 类包含 7 个参数的构造器,其还包含一个三个参数的构造器 User(String username, String password,Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities),由于权限参数不能为空,所以这里先使用 AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList 方法模拟一个 admin 的权限,该方法可以将逗号分隔的字符串转换为权限集合。
此外我们还注入了 PasswordEncoder 对象,该对象用于密码加密,注入前需要手动配置。我们在 BrowserSecurityConfig 中配置它:
@Configuration
public class BrowserSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
...
}PasswordEncoder 是一个密码加密接口,而 BCryptPasswordEncoder 是 Spring Security 提供的一个实现方法,我们也可以自己实现 PasswordEncoder。不过 Spring Security 实现的 BCryptPasswordEncoder 已经足够强大,它对相同的密码进行加密后可以生成不同的结果。
这时候重启项目,访问 http://localhost:8080/login,便可以使用任意用户名以及 123456 作为密码登录系统。我们多次进行登录操作,可以看到控制台输出的加密后的密码如下:

可以看到,BCryptPasswordEncoder 对相同的密码生成的结果每次都是不一样的。
替换默认登录页
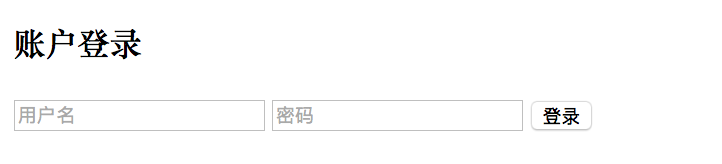
默认的登录页面过于简陋,我们可以自己定义一个登录页面。为了方便起见,我们直接在 src/main/resources/resources 目录下定义一个 login.html(不需要 Controller 跳转):
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>登录</title>
</head>
<body>
<form class="login-page" action="/login" method="post">
<div class="form">
<h3>账户登录</h3>
<input type="text" placeholder="用户名" name="username" required="required" />
<input type="password" placeholder="密码" name="password" required="required" />
<button type="submit">登录</button>
</div>
</form>
</body>
</html>要怎么做才能让 Spring Security 跳转到我们自己定义的登录页面呢?很简单,只需要在 BrowserSecurityConfig 的 configure 中添加一些配置:
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.formLogin() // 表单登录
// http.httpBasic() // HTTP Basic
.loginPage("/login.html")
.loginProcessingUrl("/login")
.and()
.authorizeRequests() // 授权配置
.antMatchers("/login.html").permitAll()
.anyRequest() // 所有请求
.authenticated(); // 都需要认证
}上面代码中.loginPage("/login.html") 指定了跳转到登录页面的请求 URL,.loginProcessingUrl("/login") 对应登录页面 form 表单的 action="/login",.antMatchers("/login.html").permitAll() 表示跳转到登录页面的请求不被拦截,否则会进入无限循环。
这时候启动系统,访问 http://localhost:8080/hello,会看到页面已经被重定向到了 http://localhost:8080/login.html:
输入用户名和密码发现页面报错:

我们先把 CSRF 攻击防御关了,修改 BrowserSecurityConfig 的 configure:
Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.formLogin() // 表单登录
// http.httpBasic() // HTTP Basic
.loginPage("/login.html") // 登录跳转 URL
.loginProcessingUrl("/login") // 处理表单登录 URL
.and()
.authorizeRequests() // 授权配置
.antMatchers("/login.html").permitAll() // 登录跳转 URL 无需认证
.anyRequest() // 所有请求
.authenticated() // 都需要认证
.and().csrf().disable();
}重启项目便可正常登录。
假如现在有这样一个需求:在未登录的情况下,当用户访问 html 资源的时候跳转到登录页,否则返回 JSON 格式数据,状态码为 401。
要实现这个功能我们将 loginPage 的 URL 改为 /authentication/require,并且在 antMatchers 方法中加入该 URL,让其免拦截:
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.formLogin() // 表单登录
// http.httpBasic() // HTTP Basic
.loginPage("/authentication/require") // 登录跳转 URL
.loginProcessingUrl("/login") // 处理表单登录 URL
.and()
.authorizeRequests() // 授权配置
.antMatchers("/authentication/require", "/login.html").permitAll() // 登录跳转 URL 无需认证
.anyRequest() // 所有请求
.authenticated() // 都需要认证
.and().csrf().disable();
}然后定义一个控制器 BrowserSecurityController,处理这个请求:
@RestController
public class BrowserSecurityController {
private RequestCache requestCache = new HttpSessionRequestCache();
private RedirectStrategy redirectStrategy = new DefaultRedirectStrategy();
@GetMapping("/authentication/require")
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED)
public String requireAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
SavedRequest savedRequest = requestCache.getRequest(request, response);
if (savedRequest != null) {
String targetUrl = savedRequest.getRedirectUrl();
if (StringUtils.endsWithIgnoreCase(targetUrl, ".html")) {
redirectStrategy.sendRedirect(request, response, "/login.html");
}
}
return "访问的资源需要身份认证!";
}
}其中 HttpSessionRequestCache 为 Spring Security 提供的用于缓存请求的对象,通过调用它的 getRequest 方法可以获取到本次请求的 HTTP 信息。DefaultRedirectStrategy 的 sendRedirect 为 Spring Security 提供的用于处理重定向的方法。
上面代码获取了引发跳转的请求,根据请求是否以.html 为结尾来对应不同的处理方法。如果是以.html 结尾,那么重定向到登录页面,否则返回” 访问的资源需要身份认证!” 信息,并且 HTTP 状态码为 401(HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED)。
这样当我们访问 http://localhost:8080/hello 的时候页面便会跳转到 http://localhost:8080/authentication/require,并且输出” 访问的资源需要身份认证!”,当我们访问 http://localhost:8080/hello.html 的时候,页面将会跳转到登录页面。
处理成功和失败
Spring Security 有一套默认的处理登录成功和失败的方法:当用户登录成功时,页面会跳转会引发登录的请求,比如在未登录的情况下访问 http://localhost:8080/hello,页面会跳转到登录页,登录成功后再跳转回来;登录失败时则是跳转到 Spring Security 默认的错误提示页面。下面我们通过一些自定义配置来替换这套默认的处理机制。
自定义登录成功逻辑
要改变默认的处理成功逻辑很简单,只需要实现 org.springframework.security.web.authentication.AuthenticationSuccessHandler 接口的 onAuthenticationSuccess 方法即可:
@Component
public class MyAuthenticationSucessHandler implements AuthenticationSuccessHandler {
@Autowired
private ObjectMapper mapper;
@Override
public void onAuthenticationSuccess(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
Authentication authentication) throws IOException, ServletException {
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
response.getWriter().write(mapper.writeValueAsString(authentication));
}
}其中 Authentication 参数既包含了认证请求的一些信息,比如 IP,请求的 SessionId 等,也包含了用户信息,即前面提到的 User 对象。通过上面这个配置,用户登录成功后页面将打印出 Authentication 对象的信息。
要使这个配置生效,我们还的在 BrowserSecurityConfig 的 configure 中配置它:
@Configuration
public class BrowserSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private MyAuthenticationSucessHandler authenticationSucessHandler;
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.formLogin() // 表单登录
// http.httpBasic() // HTTP Basic
.loginPage("/authentication/require") // 登录跳转 URL
.loginProcessingUrl("/login") // 处理表单登录 URL
.successHandler(authenticationSucessHandler) // 处理登录成功
.and()
.authorizeRequests() // 授权配置
.antMatchers("/authentication/require", "/login.html").permitAll() // 登录跳转 URL 无需认证
.anyRequest() // 所有请求
.authenticated() // 都需要认证
.and().csrf().disable();
}
}我们将 MyAuthenticationSucessHandler 注入进来,并通过 successHandler 方法进行配置。
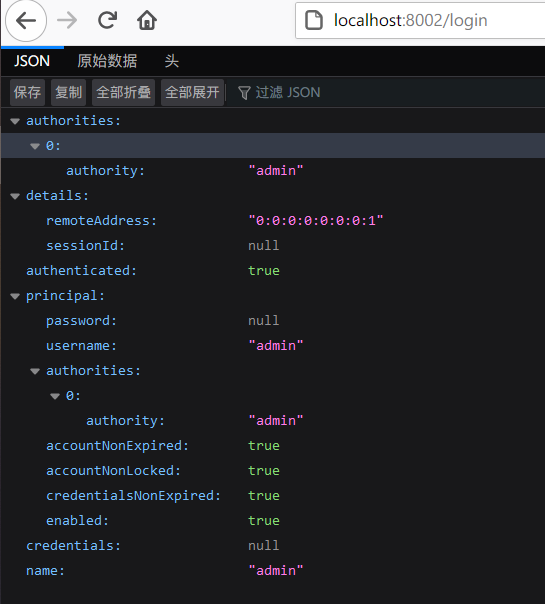
这时候重启项目登录后页面将会输出如下 JSON 信息:
{
"authorities": [{
"authority": "admin"
}],
"details": {
"remoteAddress": "127.0.0.1",
"sessionId": "2131709E2D8F89FEBC3DB7A62B76B243"
},
"authenticated": true,
"principal": {
"password": null,
"username": "111",
"authorities": [{
"authority": "admin"
}],
"accountNonExpired": true,
"accountNonLocked": true,
"credentialsNonExpired": true,
"enabled": true
},
"credentials": null,
"name": "111"
}像 password,credentials 这些敏感信息,Spring Security 已经将其屏蔽。
除此之外,我们也可以在登录成功后做页面的跳转,修改 MyAuthenticationSucessHandler:
@Component
public class MyAuthenticationSucessHandler implements AuthenticationSuccessHandler {
private RequestCache requestCache = new HttpSessionRequestCache();
private RedirectStrategy redirectStrategy = new DefaultRedirectStrategy();
@Override
public void onAuthenticationSuccess(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
Authentication authentication) throws IOException {
SavedRequest savedRequest = requestCache.getRequest(request, response);
redirectStrategy.sendRedirect(request, response, savedRequest.getRedirectUrl());
}
}通过上面配置,登录成功后页面将跳转回引发跳转的页面。如果想指定跳转的页面,比如跳转到 /index,可以将 savedRequest.getRedirectUrl() 修改为 /index:
@Component
public class MyAuthenticationSucessHandler implements AuthenticationSuccessHandler {
private RedirectStrategy redirectStrategy = new DefaultRedirectStrategy();
@Override
public void onAuthenticationSuccess(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
Authentication authentication) throws IOException {
redirectStrategy.sendRedirect(request, response, "/index");
}
}然后在 TestController 中定义一个处理该请求的方法:
@RestController
public class TestController {
@GetMapping("index")
public Object index(){
return SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
}
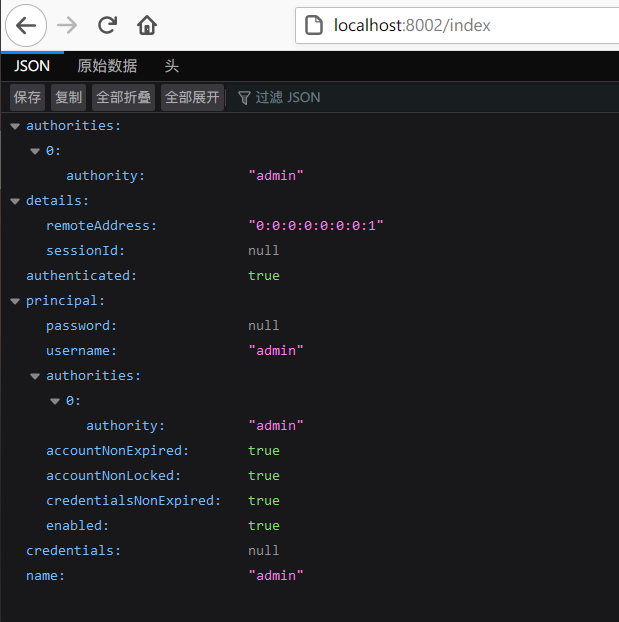
}登录成功后,便可以使用 SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication() 获取到 Authentication 对象信息。除了通过这种方式获取 Authentication 对象信息外,也可以使用下面这种方式:
@RestController
public class TestController {
@GetMapping("index")
public Object index(Authentication authentication) {
return authentication;
}
}重启项目,登录成功后,页面将跳转到 http://localhost:8080/index:

自定义登录失败逻辑
和自定义登录成功处理逻辑类似,自定义登录失败处理逻辑需要实现 org.springframework.security.web.authentication.AuthenticationFailureHandler 的 onAuthenticationFailure 方法:
@Component
public class MyAuthenticationFailureHandler implements AuthenticationFailureHandler {
@Override
public void onAuthenticationFailure(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
AuthenticationException exception) throws IOException {
}
}onAuthenticationFailure 方法的 AuthenticationException 参数是一个抽象类,Spring Security 根据登录失败的原因封装了许多对应的实现类,查看 AuthenticationException 的 Hierarchy:

不同的失败原因对应不同的异常,比如用户名或密码错误对应的是 BadCredentialsException,用户不存在对应的是 UsernameNotFoundException,用户被锁定对应的是 LockedException 等。
假如我们需要在登录失败的时候返回失败信息,可以这样处理:
@Component
public class MyAuthenticationFailureHandler implements AuthenticationFailureHandler {
@Autowired
private ObjectMapper mapper;
@Override
public void onAuthenticationFailure(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
AuthenticationException exception) throws IOException {
response.setStatus(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.value());
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
response.getWriter().write(mapper.writeValueAsString(exception.getMessage()));
}
}状态码定义为 500(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.value()),即系统内部异常。
同样的,我们需要在 BrowserSecurityConfig 的 configure 中配置它:
@Configuration
public class BrowserSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private MyAuthenticationSucessHandler authenticationSucessHandler;
@Autowired
private MyAuthenticationFailureHandler authenticationFailureHandler;
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.formLogin() // 表单登录
// http.httpBasic() // HTTP Basic
.loginPage("/authentication/require") // 登录跳转 URL
.loginProcessingUrl("/login") // 处理表单登录 URL
.successHandler(authenticationSucessHandler) // 处理登录成功
.failureHandler(authenticationFailureHandler) // 处理登录失败
.and()
.authorizeRequests() // 授权配置
.antMatchers("/authentication/require", "/login.html").permitAll() // 登录跳转 URL 无需认证
.anyRequest() // 所有请求
.authenticated() // 都需要认证
.and().csrf().disable();
}
}重启项目,当输入错误的密码时,页面输出如下:

源码:https://gitee.com/hekang_admin/security-demo1.git

Spring Boot + Spring Security 实现自动登录功能
今日干货

公众号后台回复 ssm,免费获取松哥纯手敲的 SSM 框架学习干货。
自动登录是我们在软件开发时一个非常常见的功能,例如我们登录 QQ 邮箱:
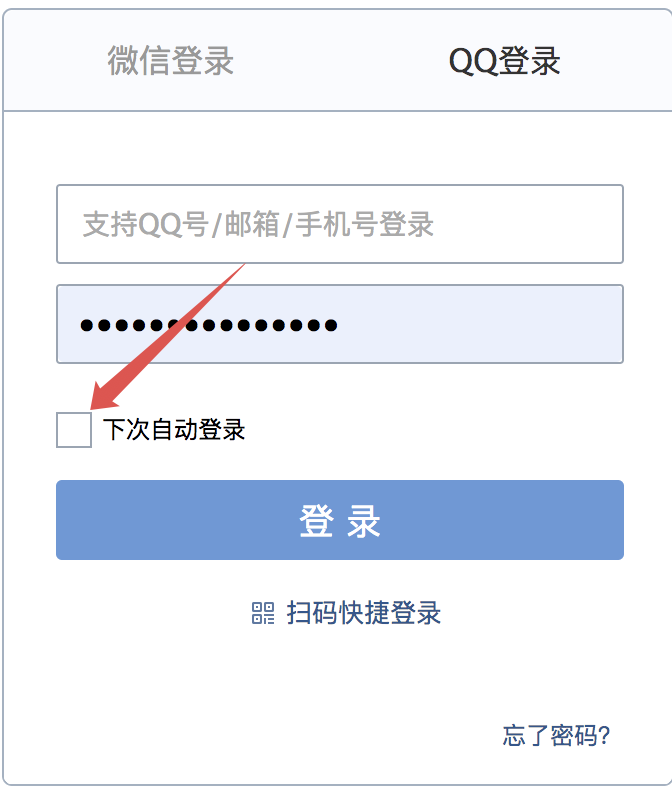
很多网站我们在登录的时候都会看到类似的选项,毕竟总让用户输入用户名密码是一件很麻烦的事。
自动登录功能就是,用户在登录成功后,在某一段时间内,如果用户关闭了浏览器并重新打开,或者服务器重启了,都不需要用户重新登录了,用户依然可以直接访问接口数据。
作为一个常见的功能,我们的 Spring Security 肯定也提供了相应的支持,本文我们就来看下 Spring Security 中如何实现这个功能。
本文是松哥最近在连载的 Spring Security 系列第 8 篇,阅读本系列前面的文章可以更好的理解本文(如果大家对松哥录制的 Spring Security 视频感兴趣,也可以看看这里:SpringBoot+Vue+微人事视频教程):
-
挖一个大坑,Spring Security 开搞! -
松哥手把手带你入门 Spring Security,别再问密码怎么解密了 -
手把手教你定制 Spring Security 中的表单登录 -
Spring Security 做前后端分离,咱就别做页面跳转了!统统 JSON 交互 -
Spring Security 中的授权操作原来这么简单 -
Spring Security 如何将用户数据存入数据库? -
Spring Security+Spring Data Jpa 强强联手,安全管理只有更简单!
这个功能实现起来简单,但是还是会涉及到很多细节,所以我会分两篇文章来逐一介绍,本文是第一篇。
1.实战代码
首先,要实现记住我这个功能,其实只需要其实只需要在 Spring Security 的配置中,添加如下代码即可:
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.and()
.rememberMe()
.and()
.csrf().disable();
}
大家看到,这里只需要添加一个 .rememberMe() 即可,自动登录功能就成功添加进来了。
接下来我们随意添加一个测试接口:
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
return "hello";
}
}
重启项目,我们访问 hello 接口,此时会自动跳转到登录页面:
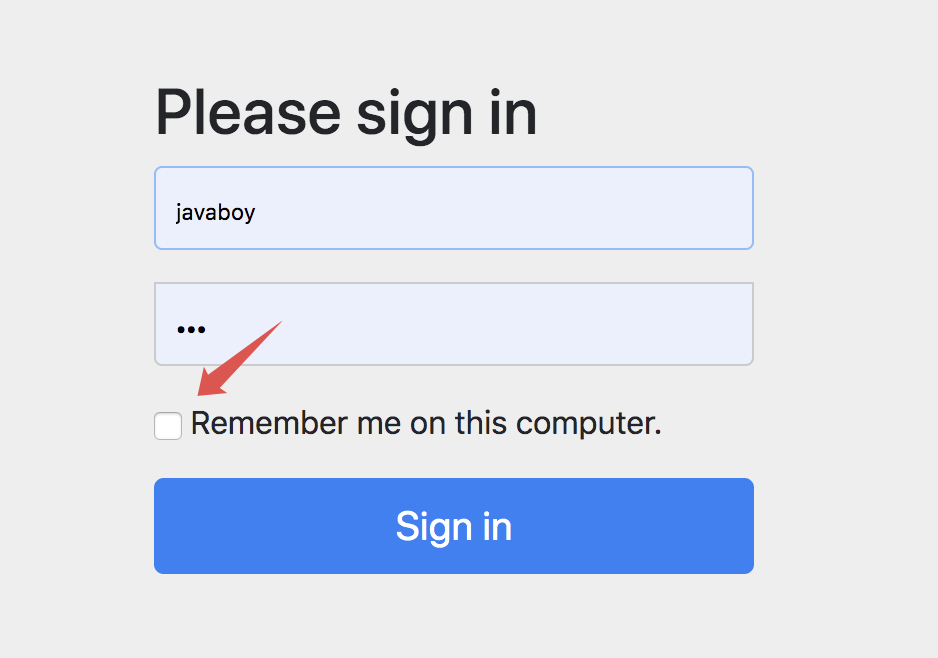
这个时候大家发现,默认的登录页面多了一个选项,就是记住我。我们输入用户名密码,并且勾选上记住我这个框,然后点击登录按钮执行登录操作:
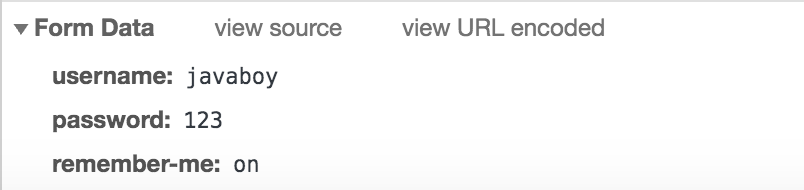
可以看到,登录数据中,除了 username 和 password 之外,还有一个 remember-me,之所以给大家看这个,是想告诉大家,如果你你需要自定义登录页面,RememberMe 这个选项的 key 该怎么写。
登录成功之后,就会自动跳转到 hello 接口了。我们注意,系统访问 hello 接口的时候,携带的 cookie:

大家注意到,这里多了一个 remember-me,这就是这里实现的核心,关于这个 remember-me 我一会解释,我们先来测试效果。
接下来,我们关闭浏览器,再重新打开浏览器。正常情况下,浏览器关闭再重新打开,如果需要再次访问 hello 接口,就需要我们重新登录了。但是此时,我们再去访问 hello 接口,发现不用重新登录了,直接就能访问到,这就说明我们的 RememberMe 配置生效了(即下次自动登录功能生效了)。
2.原理分析
按理说,浏览器关闭再重新打开,就要重新登录,现在竟然不用等了,那么这个功能到底是怎么实现的呢?
首先我们来分析一下 cookie 中多出来的这个 remember-me,这个值一看就是一个 Base64 转码后的字符串,我们可以使用网上的一些在线工具来解码,可以自己简单写两行代码来解码:
@Test
void contextLoads() throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
String s = new String(Base64.getDecoder().decode("amF2YWJveToxNTg5MTA0MDU1MzczOjI1NzhmZmJjMjY0ODVjNTM0YTJlZjkyOWFjMmVmYzQ3"), "UTF-8");
System.out.println("s = " + s);
}
执行这段代码,输出结果如下:
s = javaboy:1589104055373:2578ffbc26485c534a2ef929ac2efc47
可以看到,这段 Base64 字符串实际上用 : 隔开,分成了三部分:
-
第一段是用户名,这个无需质疑。 -
第二段看起来是一个时间戳,我们通过在线工具或者 Java 代码解析后发现,这是一个两周后的数据。 -
第三段我就不卖关子了,这是使用 MD5 散列函数算出来的值,他的明文格式是 username + ":" + tokenExpiryTime + ":" + password + ":" + key,最后的 key 是一个散列盐值,可以用来防治令牌被修改。
了解到 cookie 中 remember-me 的含义之后,那么我们对于记住我的登录流程也就很容易猜到了了。
在浏览器关闭后,并重新打开之后,用户再去访问 hello 接口,此时会携带着 cookie 中的 remember-me 到服务端,服务到拿到值之后,可以方便的计算出用户名和过期时间,再根据用户名查询到用户密码,然后通过 MD5 散列函数计算出散列值,再将计算出的散列值和浏览器传递来的散列值进行对比,就能确认这个令牌是否有效。
流程就是这么个流程,接下来我们通过分析源码来验证一下这个流程对不对。
3.源码分析
接下来,我们通过源码来验证一下我们上面说的对不对。
这里主要从两个方面来介绍,一个是 remember-me 这个令牌生成的过程,另一个则是它解析的过程。
3.1 生成
生成的核心处理方法在:TokenBasedRememberMeServices#onLoginSuccess:
@Override
public void onLoginSuccess(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
Authentication successfulAuthentication) {
String username = retrieveUserName(successfulAuthentication);
String password = retrievePassword(successfulAuthentication);
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(password)) {
UserDetails user = getUserDetailsService().loadUserByUsername(username);
password = user.getPassword();
}
int tokenLifetime = calculateLoginLifetime(request, successfulAuthentication);
long expiryTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
expiryTime += 1000L * (tokenLifetime < 0 ? TWO_WEEKS_S : tokenLifetime);
String signatureValue = makeTokenSignature(expiryTime, username, password);
setCookie(new String[] { username, Long.toString(expiryTime), signatureValue },
tokenLifetime, request, response);
}
protected String makeTokenSignature(long tokenExpiryTime, String username,
String password) {
String data = username + ":" + tokenExpiryTime + ":" + password + ":" + getKey();
MessageDigest digest;
digest = MessageDigest.getInstance("MD5");
return new String(Hex.encode(digest.digest(data.getBytes())));
}
这段方法的逻辑其实很好理解:
-
首先从登录成功的 Authentication 中提取出用户名/密码。 -
由于登录成功之后,密码可能被擦除了,所以,如果一开始没有拿到密码,就再从 UserDetailsService 中重新加载用户并重新获取密码。 -
再接下来去获取令牌的有效期,令牌有效期默认就是两周。 -
再接下来调用 makeTokenSignature 方法去计算散列值,实际上就是根据 username、令牌有效期以及 password、key 一起计算一个散列值。如果我们没有自己去设置这个 key,默认是在 RememberMeConfigurer#getKey 方法中进行设置的,它的值是一个 UUID 字符串。 -
最后,将用户名、令牌有效期以及计算得到的散列值放入 Cookie 中。
关于第四点,我这里再说一下。
由于我们自己没有设置 key,key 默认值是一个 UUID 字符串,这样会带来一个问题,就是如果服务端重启,这个 key 会变,这样就导致之前派发出去的所有 remember-me 自动登录令牌失效,所以,我们可以指定这个 key。指定方式如下:
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.and()
.rememberMe()
.key("javaboy")
.and()
.csrf().disable();
}
如果自己配置了 key,「即使服务端重启,即使浏览器打开再关闭」,也依然能够访问到 hello 接口。
这是 remember-me 令牌生成的过程。至于是如何走到 onLoginSuccess 方法的,大家可以参考松哥之前的文章:松哥手把手带你捋一遍 Spring Security 登录流程。这里可以给大家稍微提醒一下思路:
AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter#doFilter -> AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter#successfulAuthentication -> AbstractRememberMeServices#loginSuccess -> TokenBasedRememberMeServices#onLoginSuccess。
3.2 解析
那么当用户关掉并打开浏览器之后,重新访问 /hello 接口,此时的认证流程又是怎么样的呢?
我们之前说过,Spring Security 中的一系列功能都是通过一个过滤器链实现的,RememberMe 这个功能当然也不例外。
Spring Security 中提供了 RememberMeAuthenticationFilter 类专门用来做相关的事情,我们来看下 RememberMeAuthenticationFilter 的 doFilter 方法:
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
if (SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication() == null) {
Authentication rememberMeAuth = rememberMeServices.autoLogin(request,
response);
if (rememberMeAuth != null) {
rememberMeAuth = authenticationManager.authenticate(rememberMeAuth);
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(rememberMeAuth);
onSuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, rememberMeAuth);
if (this.eventPublisher != null) {
eventPublisher
.publishEvent(new InteractiveAuthenticationSuccessEvent(
SecurityContextHolder.getContext()
.getAuthentication(), this.getClass()));
}
if (successHandler != null) {
successHandler.onAuthenticationSuccess(request, response,
rememberMeAuth);
return;
}
}
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
else {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
}
可以看到,就是在这里实现的。
这个方法最关键的地方在于,如果从 SecurityContextHolder 中无法获取到当前登录用户实例,那么就调用 rememberMeServices.autoLogin 逻辑进行登录,我们来看下这个方法:
public final Authentication autoLogin(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) {
String rememberMeCookie = extractRememberMeCookie(request);
if (rememberMeCookie == null) {
return null;
}
logger.debug("Remember-me cookie detected");
if (rememberMeCookie.length() == 0) {
logger.debug("Cookie was empty");
cancelCookie(request, response);
return null;
}
UserDetails user = null;
try {
String[] cookieTokens = decodeCookie(rememberMeCookie);
user = processAutoLoginCookie(cookieTokens, request, response);
userDetailsChecker.check(user);
logger.debug("Remember-me cookie accepted");
return createSuccessfulAuthentication(request, user);
}
catch (CookieTheftException cte) {
throw cte;
}
cancelCookie(request, response);
return null;
}
可以看到,这里就是提取出 cookie 信息,并对 cookie 信息进行解码,解码之后,再调用 processAutoLoginCookie 方法去做校验,processAutoLoginCookie 方法的代码我就不贴了,核心流程就是首先获取用户名和过期时间,再根据用户名查询到用户密码,然后通过 MD5 散列函数计算出散列值,再将拿到的散列值和浏览器传递来的散列值进行对比,就能确认这个令牌是否有效,进而确认登录是否有效。
好了,这里的流程我也根据大家大致上梳理了一下。
4.总结
看了上面的文章,大家可能已经发现,如果我们开启了 RememberMe 功能,最最核心的东西就是放在 cookie 中的令牌了,这个令牌突破了 session 的限制,即使服务器重启、即使浏览器关闭又重新打开,只要这个令牌没有过期,就能访问到数据。
一旦令牌丢失,别人就可以拿着这个令牌随意登录我们的系统了,这是一个非常危险的操作。
但是实际上这是一段悖论,为了提高用户体验(少登录),我们的系统不可避免的引出了一些安全问题,不过我们可以通过技术将安全风险降低到最小。
那么如何让我们的 RememberMe 功能更加安全呢?松哥下篇文章来和大家继续分享--持久化令牌方案。
小伙伴们要是觉得看懂了,不妨点个在看鼓励下松哥~
今日干货

公众号后台回复 2TB,免费获取 2TB Java 学习资料。
本文分享自微信公众号 - 江南一点雨(a_javaboy)。
如有侵权,请联系 support@oschina.cn 删除。
本文参与“OSC源创计划”,欢迎正在阅读的你也加入,一起分享。

Spring Boot + Spring Security自定义用户认证
- 引入依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
- 自定义认证过程 自定义认证的过程需要实现Spring Security提供的UserDetailService接口 ,源码如下:
public interface UserDetailsService {
UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException;
}
loadUserByUsername方法返回一个UserDetail对象,该对象也是一个接口,包含一些用于描述用户信息的方法,源码如下:
public interface UserDetails extends Serializable {
// 获取用户包含的权限,返回权限集合,权限是一个继承了GrantedAuthority的对象;
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities();
// 获取密码
String getPassword();
// 获取账号/用户名
String getUsername();
// 账户是否过期
boolean isAccountNonExpired();
//账户是否被锁定
boolean isAccountNonLocked();
//用户凭证是否过期
boolean isCredentialsNonExpired();
//用户是否可用
boolean isEnabled();
}
- 创建实现自定义认证接口的类:
@Configuration
public class UserDetailService implements UserDetailsService {
@Autowired
private PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
// 模拟一个用户,实际项目中应为: 根据用户名查找数据库,如果没有记录则会返回null,有则返回UserDetails对象
MyUser user = new MyUser();
user.setUserName(username);
user.setPassword(this.passwordEncoder.encode("123456"));
// 输出加密后的密码
System.out.println(user.getPassword());
// 返回对象之后 会在内部进行认证(密码/盐/加密过密码等)
return new User(username, user.getPassword(), user.isEnabled(),
user.isAccountNonExpired(), user.isCredentialsNonExpired(),
user.isAccountNonLocked(), AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList("admin"));
}
}
- 创建用户类
@Data
public class MyUser implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 3497935890426858541L;
private String userName;
private String password;
private boolean accountNonExpired = true;
private boolean accountNonLocked= true;
private boolean credentialsNonExpired= true;
private boolean enabled= true;
}
- 配置类:
@Configuration
public class MySecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
...
}
注:PasswordEncoder是一个密码加密接口,而BCryptPasswordEncoder是Spring Security提供的一个实现方法,我们也可以自己实现PasswordEncoder。
不过Spring Security实现的BCryptPasswordEncoder已经足够强大,它对相同的密码进行加密后可以生成不同的结果
启动项目:访问http://localhost:8080/login, 便可以使用任意用户名以及123456作为密码登录系统
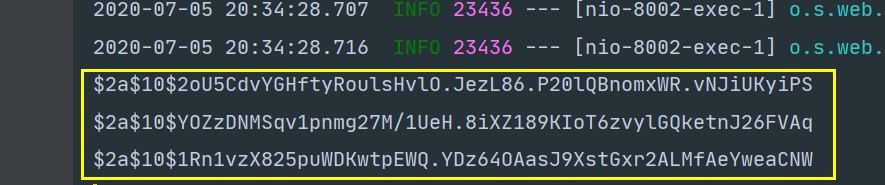
BCryptPasswordEncoder对相同的密码生成的结果每次都是不一样的
- 替换默认登录页 直接在src/main/resources/resources目录下定义一个login.html(不需要Controller跳转)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>登录</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/login.css" type="text/css">
</head>
<body>
<formaction="/login" method="post">
<div>
<h3>账户登录</h3>
<input type="text" placeholder="用户名" name="username" required="required" />
<input type="password" placeholder="密码" name="password" required="required" />
<button type="submit">登录</button>
</div>
</form>
</body>
</html>
在MySecurityConfig中添加:
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.formLogin() // 表单登录
// http.httpBasic() // HTTP Basic
.loginPage("/login.html") //指定了跳转到登录页面的请求URL
.loginProcessingUrl("/login") //对应登录页面form表单的action="/login"
.and()
.authorizeRequests() // 授权配置
//.antMatchers("/login.html").permitAll()表示跳转到登录页面的请求不被拦截,否则会进入无限循环
.antMatchers("/login.html").permitAll()
.anyRequest() // 所有请求
.authenticated()// 都需要认证
.and().csrf().disable(); // 关闭csrf防御
}
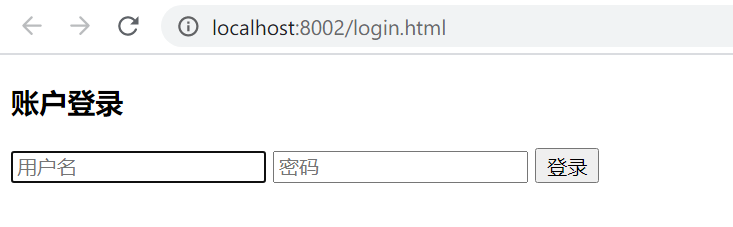
访问http://localhost:8080/hello ,会看到页面已经被重定向到了http://localhost:8080/login.html 使用任意用户名+密码123456登录
在未登录的情况下,当用户访问html资源的时候,如果已经登陆则返回JSON数据,否则直接跳转到登录页,状态码为401。
要实现这个功能我们将loginPage的URL改为/authentication/require,并且在antMatchers方法中加入该URL,让其免拦截:
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.formLogin() // 表单登录
// http.httpBasic() // HTTP Basic
.loginPage("/authentication/require") // 登录跳转 URL
.loginProcessingUrl("/login") // 处理表单登录 URL
.and()
.authorizeRequests() // 授权配置
.antMatchers("/authentication/require", "/login.html").permitAll() // 登录跳转 URL 无需认证
.anyRequest() // 所有请求
.authenticated() // 都需要认证
.and().csrf().disable();
}
创建控制器MySecurityController,处理这个请求:
@RestController
public class MySecurityController {
//RequestCache requestCache是Spring Security提供的用于缓存请求的对象
private RequestCache requestCache = new HttpSessionRequestCache();
//DefaultRedirectStrategy是Spring Security提供的重定向策略
private RedirectStrategy redirectStrategy = new DefaultRedirectStrategy();
@GetMapping("/authentication/require")
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED) //HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED 未认证 状态码401
public String requireAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
//getRequest方法可以获取到本次请求的HTTP信息
SavedRequest savedRequest = requestCache.getRequest(request, response);
if (savedRequest != null) {
String targetUrl = savedRequest.getRedirectUrl();
if (StringUtils.endsWithIgnoreCase(targetUrl, ".html"))
//sendRedirect为Spring Security提供的用于处理重定向的方法
redirectStrategy.sendRedirect(request, response, "/login.html");
}
return "访问的资源需要身份认证!";
}
}
上面代码获取了引发跳转的请求,根据请求是否以.html为结尾来对应不同的处理方法。如果是以.html结尾,那么重定向到登录页面,否则返回”访问的资源需要身份认证!”信息,并且HTTP状态码为401(HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED)。
这样当我们访问http://localhost:8080/hello 的时候页面便会跳转到http://localhost:8080/authentication/require,
 ,
,
当我们访问http://localhost:8080/hello.html 的时候,页面将会跳转到登录页面。
- 处理成功和失败 Spring Security有一套默认的处理登录成功和失败的方法:当用户登录成功时,页面会跳转会引发登录的请求,比如在未登录的情况下访问http://localhost:8080/hello, 页面会跳转到登录页,登录成功后再跳转回来;登录失败时则是跳转到Spring Security默认的错误提示页面。下面 通过一些自定义配置来替换这套默认的处理机制。
自定义登录成功逻辑 要改变默认的处理成功逻辑很简单,只需要实现org.springframework.security.web.authentication.AuthenticationSuccessHandler接口的onAuthenticationSuccess方法即可:
@Component
public class MyAuthenticationSucessHandler implements AuthenticationSuccessHandler {
@Autowired
private ObjectMapper mapper;
@Override
public void onAuthenticationSuccess(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
Authentication authentication) throws IOException, ServletException {
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
// 将认证信息转换成jsonString写入response
response.getWriter().write(mapper.writeValueAsString(authentication));
}
}
其中Authentication参数既包含了认证请求的一些信息,比如IP,请求的SessionId等,也包含了用户信息,即前面提到的User对象。通过上面这个配置,用户登录成功后页面将打印出Authentication对象的信息。
要使这个配置生效,我们还在MySecurityConfig的configure中配置它:
@Configuration
public class MySecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private MyAuthenticationSucessHandler authenticationSucessHandler;
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.formLogin() // 表单登录
// http.httpBasic() // HTTP Basic
.loginPage("/authentication/require") // 登录跳转 URL
.loginProcessingUrl("/login") // 处理表单登录 URL
.successHandler(authenticationSucessHandler) // 处理登录成功
.and()
.authorizeRequests() // 授权配置
.antMatchers("/authentication/require", "/login.html").permitAll() // 登录跳转 URL 无需认证
.anyRequest() // 所有请求
.authenticated() // 都需要认证
.and().csrf().disable();
}
}
我们将MyAuthenticationSucessHandler注入进来,并通过successHandler方法进行配置。
这时候重启项目登录后页面将会输出如下JSON信息:
像password,credentials这些敏感信息,Spring Security已经将其屏蔽。
除此之外,我们也可以在登录成功后做页面的跳转,修改MyAuthenticationSucessHandler:
@Component
public class MyAuthenticationSucessHandler implements AuthenticationSuccessHandler {
private RequestCache requestCache = new HttpSessionRequestCache();
private RedirectStrategy redirectStrategy = new DefaultRedirectStrategy();
@Override
public void onAuthenticationSuccess(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
Authentication authentication) throws IOException {
SavedRequest savedRequest = requestCache.getRequest(request, response);
redirectStrategy.sendRedirect(request, response, savedRequest.getRedirectUrl());
}
}
通过上面配置,登录成功后页面将跳转回引发跳转的页面。如果想指定跳转的页面,比如跳转到/index,可以将savedRequest.getRedirectUrl()修改为/index:
@Component
public class MyAuthenticationSucessHandler implements AuthenticationSuccessHandler {
private RedirectStrategy redirectStrategy = new DefaultRedirectStrategy();
@Override
public void onAuthenticationSuccess(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
Authentication authentication) throws IOException {
redirectStrategy.sendRedirect(request, response, "/index");
}
}
在IndexController中定义一个处理该请求的方法:
@RestController
public class IndexController {
@GetMapping("index")
public Object index(){
return SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
}
}
登录成功后,便可以使用SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication()获取到Authentication对象信息。除了通过这种方式获取Authentication对象信息外,也可以使用下面这种方式:
@RestController
public class IndexController {
@GetMapping("index")
public Object index(Authentication authentication) {
return authentication;
}
}
重启项目,登录成功后,页面将跳转到http://localhost:8080/index:
- 自定义登录失败逻辑 和自定义登录成功处理逻辑类似,自定义登录失败处理逻辑需要实现org.springframework.security.web.authentication.AuthenticationFailureHandler的onAuthenticationFailure方法:
@Component
public class MyAuthenticationFailureHandler implements AuthenticationFailureHandler {
@Override
public void onAuthenticationFailure(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
AuthenticationException exception) throws IOException {
}
}
onAuthenticationFailure方法的AuthenticationException参数是一个抽象类,Spring Security根据登录失败的原因封装了许多对应的实现类,
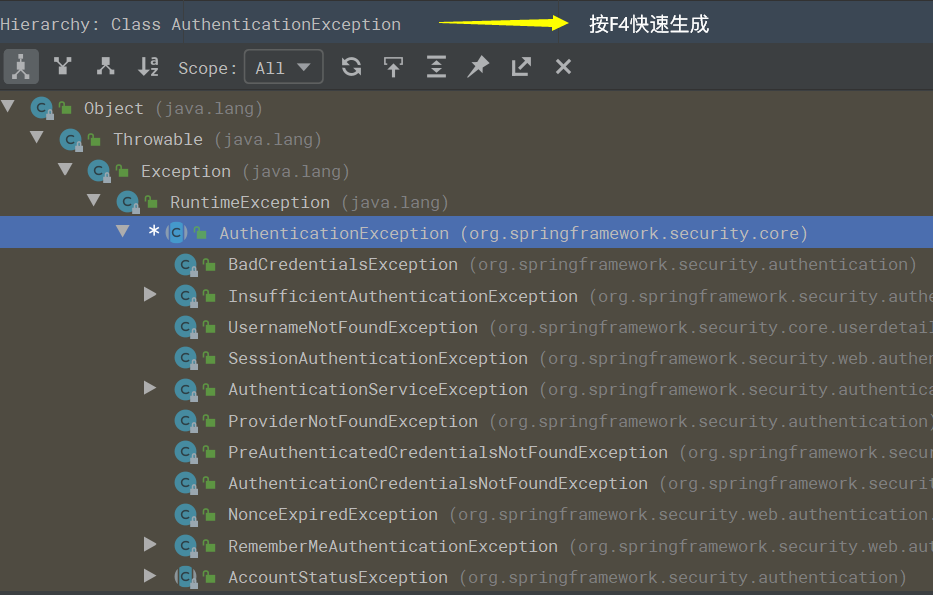
不同的失败原因对应不同的异常,比如用户名或密码错误对应的是BadCredentialsException,用户不存在对应的是UsernameNotFoundException,用户被锁定对应的是LockedException等。
假如我们需要在登录失败的时候返回失败信息,可以这样处理:
@Component
public class MyAuthenticationFailureHandler implements AuthenticationFailureHandler {
@Autowired
private ObjectMapper mapper;
@Override
public void onAuthenticationFailure(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
AuthenticationException exception) throws IOException {
response.setStatus(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.value());
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
response.getWriter().write(mapper.writeValueAsString(exception.getMessage()));
}
}
状态码定义为500(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.value()),即系统内部异常。
同样的,我们需要在BrowserSecurityConfig的configure中配置它:
@Configuration
public class BrowserSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private MyAuthenticationSucessHandler authenticationSucessHandler;
@Autowired
private MyAuthenticationFailureHandler authenticationFailureHandler;
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.formLogin() // 表单登录
// http.httpBasic() // HTTP Basic
.loginPage("/authentication/require") // 登录跳转 URL
.loginProcessingUrl("/login") // 处理表单登录 URL
.successHandler(authenticationSucessHandler) // 处理登录成功
.failureHandler(authenticationFailureHandler) // 处理登录失败
.and()
.authorizeRequests() // 授权配置
.antMatchers("/authentication/require", "/login.html").permitAll() // 登录跳转 URL 无需认证
.anyRequest() // 所有请求
.authenticated() // 都需要认证
.and().csrf().disable();
}
}
重启项目之后,使用错误的密码登录 图示如下:
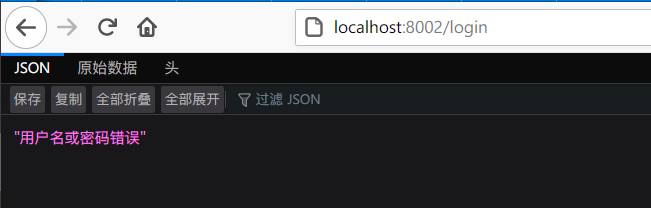
本博文代码均经过测试,可以正常运行!
源码地址: https://github.com/ttdys/springboot/tree/master/springboot_security/02_custom_authentication

Spring Boot 整合 Spring Security + JWT(实现无状态登录)
学习在 Spring Boot 中整合 Spring Security 和 JWT ,实现无状态登录,可做为前后端分离时的解决方案,技术上没问题,但实际上还是推荐使用 OAuth2 中的 password 模式。
1 登录概述
1.1 有状态登录
有状态服务,即服务端需要记录每次会话的客户端信息,从而识别客户端身份,根据用户身份进行请求的处理,如 Tomcat 中的 Session 。例如:用户登录后,我们把用户的信息保存在服务端 session 中,并且给用户一个 cookie 值,记录对应的 session ,然后下次请求,用户携带 cookie 值来(这一步由浏览器自动完成),我们就能识别到对应 session ,从而找到用户的信息。这种方式目前来看最方便,但是也有一些缺陷,如下:
- 服务端保存大量数据,增加服务端压力。
- 服务端保存用户状态,不支持集群化部署。
1.2 无状态登录
微服务集群中的每个服务,对外提供的都使用 RESTful 风格的接口。而 RESTful 风格的一个最重要的规范就是:服务的无状态性,即:
- 服务端不保存任何客户端请求者信息。
- 客户端的每次请求必须具备自描述信息,通过这些信息识别客户端身份。
优势:
- 客户端请求不依赖服务端的信息,多次请求不需要必须访问到同一台服务器。
- 服务端的集群和状态对客户端透明。
- 服务端可以任意的迁移和伸缩(可以方便的进行集群化部署)。
- 减小服务端存储压力。
1.3 无状态登录的流程
无状态登录的流程:
- 首先客户端发送账户名/密码到服务端进行认证。
- 认证通过后,服务端将用户信息加密并且编码成一个 token ,返回给客户端。
- 以后客户端每次发送请求,都需要携带认证的 token 。
- 服务端对客户端发送来的 token 进行解密,判断是否有效,并且获取用户登录信息。
2 JWT 概述
2.1 JWT 简介
JWT (Json Web Token),是一种 JSON 风格的轻量级的授权和身份认证规范,可实现无状态、分布式的 Web 应用授权。官网:https://jwt.io/

JWT 作为一种规范,并没有和某一种语言绑定在一起,常用的 Java 实现是 GitHub 上的开源项目 jjwt ,地址如下:https://github.com/jwtk/jjwt
2.2 JWT 数据格式
JWT 包含三部分数据:
-
Header:头部,通常头部有两部分信息:- 声明类型,这里是 JWT 。
- 加密算法,自定义。
我们会对头部进行 Base64 编码(可解码),得到第一部分数据。
-
Payload:载荷,就是有效数据,在官方文档中(RFC7519),这里给了 7 个示例信息:- iss (issuer):表示签发人。
- exp (expiration time):表示token过期时间。
- sub (subject):主题。
- aud (audience):受众。
- nbf (Not Before):生效时间。
- iat (Issued At):签发时间。
- jti (JWT ID):编号。
这部分也会采用 Base64 编码,得到第二部分数据。
-
Signature:签名,是整个数据的认证信息。一般根据前两步的数据,再加上服务端的密钥 secret (密钥保存在服务端,不能泄露给客户端),通过 Header 中配置的加密算法生成,用于验证整个数据的完整性和可靠性。
比如,生成的数据格式:
eyJhbGciOiJIUzUxMiJ9.eyJhdXRob3JpdGllcyI6IlJPTEVfdXNlciwiLCJzdWIiOiJ1c2VyIiwiZXhwIjoxNTc0NzczNTkyfQ.FuPIltzXi5j14t_gSL1GoIMUZxTHKK0FvB3gds6eTZFDkQr1ZxWVxdqZ5YFbCxdkwQ_VXtPK-GgcW5Kzzx3wvw
注意,这里的数据通过 . 隔开成了三部分,分别对应前面提到的三部分:
- Header :头部(声明类型、加密算法),采用 Base64 编码,如:
eyJhbGciOiJIUzUxMiJ9。 - Payload :载荷,就是有效数据,采用 Base64 编码,如:
eyJhdXRob3JpdGllcyI6IlJPTEVfdXNlciwiLCJzdWIiOiJ1c2VyIiwiZXhwIjoxNTc0NzczNTkyfQ - Signature :签名,如:
FuPIltzXi5j14t_gSL1GoIMUZxTHKK0FvB3gds6eTZFDkQr1ZxWVxdqZ5YFbCxdkwQ_VXtPK-GgcW5Kzzx3wvw。
2.3 JWT 交互流程
- 应用程序或客户端向授权服务器请求授权。
- 获取到授权后,授权服务器会向应用程序返回访问令牌。
- 应用程序使用访问令牌来访问受保护资源(如 API )。
因为 JWT 签发的 token 中已经包含了用户的身份信息,并且每次请求都会携带,这样服务端就无需保存用户信息,甚至无需去数据库查询,这样就完全符合了 RESTful 的无状态规范。
2.4 JWT 问题
说了这么多, JWT 也不是天衣无缝,由客户端维护登录状态带来的一些问题在这里依然存在,如下:
- 续签问题,这是被很多人诟病的问题之一,传统的 cookie + session 的方案天然的支持续签,但是 JWT 由于服务端不保存用户状态,因此很难完美解决续签问题,如果引入 Redis ,虽然可以解决问题,但是 JWT 也变得不伦不类了。
- 注销问题,由于服务端不再保存用户信息,所以一般可以通过修改 secret 来实现注销,服务端 secret 修改后,已经颁发的未过期的 token 就会认证失败,进而实现注销,不过毕竟没有传统的注销方便。
- 密码重置,密码重置后,原本的 token 依然可以访问系统,这时候也需要强制修改 secret 。
- 基于第 2 点和第 3 点,一般建议不同用户取不同 secret 。
3 实战
3.1 创建工程
创建 Spring Boot 项目 spring-boot-springsecurity-jwt ,添加 Web/Spring Security 依赖,如下:

之后手动在 pom 文件中添加 jjwt 依赖,最终的依赖如下:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.jsonwebtoken</groupId>
<artifactId>jjwt</artifactId>
<version>0.9.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
3.2 创建接口
新建实体类 User 实现 UserDetails 接口,如下:
public class User implements UserDetails {
private String username;
private String password;
private List<GrantedAuthority> authorities;
@Override
public Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities() {
return authorities;
}
@Override
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
@Override
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
@Override
public boolean isAccountNonExpired() {
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean isAccountNonLocked() {
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean isCredentialsNonExpired() {
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean isEnabled() {
return true;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public void setAuthorities(List<GrantedAuthority> authorities) {
this.authorities = authorities;
}
}
新建 HelloController ,如下:
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
return "hello";
}
@GetMapping("/admin/hello")
public String admin() {
return "hello admin";
}
@GetMapping("/user/hello")
public String user() {
return "hello user";
}
}
3.3 配置过滤器
这里主要配置两个过滤器:
- 用户登录的过滤器
// 过滤器1:用户登录的过滤器,在用户的登录的过滤器中校验用户是否登录成功,
// 如果登录成功,则生成一个 token 返回给客户端,登录失败则给前端一个登录失败的提示
public class JwtLoginFilter extends AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter {
public JwtLoginFilter(String defaultFilterProcessesUrl, AuthenticationManager authenticationManager) {
super(new AntPathRequestMatcher(defaultFilterProcessesUrl));
setAuthenticationManager(authenticationManager);
}
@Override
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse) throws AuthenticationException, IOException {
// 这里只支持 JSON 的登录方式
// 如果想表单方式也支持,可参考 spring-boot-springsecurity-loginbyjson 中的 MyAuthenticationFilter
// 获取输入参数,如 {"username":"user","password":"123456"}
User user = new ObjectMapper().readValue(req.getInputStream(), User.class);
// 进行登录校验,如果校验成功,会到 successfulAuthentication 的回调中,否则到 unsuccessfulAuthentication 的回调中
return getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(user.getUsername(), user.getPassword()));
}
@Override
protected void successfulAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse resp, FilterChain chain, Authentication authResult) throws IOException, ServletException {
// 获取登录用户的角色
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities = authResult.getAuthorities();
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
for (GrantedAuthority authority : authorities) {
sb.append(authority.getAuthority()).append(",");
}
// 生成 token 并返回
// 数据格式:分 3 部分用 . 隔开,如:eyJhbGciOiJIUzUxMiJ9.eyJhdXRob3JpdGllcyI6IlJPTEVfdXNlciwiLCJzdWIiOiJ1c2VyIiwiZXhwIjoxNTc0NzczNTkyfQ.FuPIltzXi5j14t_gSL1GoIMUZxTHKK0FvB3gds6eTZFDkQr1ZxWVxdqZ5YFbCxdkwQ_VXtPK-GgcW5Kzzx3wvw
// 1.Header:头部(声明类型、加密算法),采用 Base64 编码,如:eyJhbGciOiJIUzUxMiJ9
// 2.Payload:载荷,就是有效数据,采用 Base64 编码,如:eyJhdXRob3JpdGllcyI6IlJPTEVfdXNlciwiLCJzdWIiOiJ1c2VyIiwiZXhwIjoxNTc0NzczNTkyfQ
// 3.Signature:签名,是整个数据的认证信息。一般根据前两步的数据,再加上服务的的密钥 secret (密钥保存在服务端,不能泄露给客户端),通过 Header 中配置的加密算法生成。用于验证整个数据完整和可靠性。
String jwt = Jwts.builder()
.claim("authorities", sb) // 配置用户角色
.setSubject(authResult.getName()) // 配置主题
.setExpiration(new Date(System.currentTimeMillis() + 60 * 60 * 1000)) // 配置过期时间
.signWith(SignatureAlgorithm.HS512, "abc@123") // 配置加密算法和密钥
.compact();
resp.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("token", jwt);
map.put("msg", "登录成功");
PrintWriter out = resp.getWriter();
out.write(new ObjectMapper().writeValueAsString(map));
out.flush();
out.close();
}
@Override
protected void unsuccessfulAuthentication(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp, AuthenticationException failed) throws IOException, ServletException {
resp.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("msg", "登录失败");
PrintWriter out = resp.getWriter();
out.write(new ObjectMapper().writeValueAsString(map));
out.flush();
out.close();
}
}
- 校验 token 的过滤器
// 过滤器2:当其他请求发送来,校验 token 的过滤器,如果校验成功,就让请求继续执行
// 请求时注意认证方式选择 Bearer Token
public class JwtFilter extends GenericFilterBean {
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest req = (HttpServletRequest) servletRequest;
// 获取 token ,注意获取方式要跟前台传的方式保持一致
// 这里请求时注意认证方式选择 Bearer Token,会用 header 传递
String jwtToken = req.getHeader("authorization");
// 注意 "abc@123" 要与生成 token 时的保持一致
Jws<Claims> jws = Jwts.parser().setSigningKey("abc@123")
.parseClaimsJws(jwtToken.replace("Bearer", ""));
Claims claims = jws.getBody();
// 获取用户名
String username = claims.getSubject();
// 获取用户角色,注意 "authorities" 要与生成 token 时的保持一致
List<GrantedAuthority> authorities = AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList((String) claims.get("authorities"));
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken token = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(username, null, authorities);
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(token);
filterChain.doFilter(servletRequest, servletResponse);
}
}
3.4 配置 Spring Security
新增 SecurityConfig 配置类,如下:
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Bean
PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
// return NoOpPasswordEncoder.getInstance();// 密码不加密
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();// 密码加密
}
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
// 在内存中配置2个用户
/*auth.inMemoryAuthentication()
.withUser("admin").password("123456").roles("admin")
.and()
.withUser("user").password("123456").roles("user");// 密码不加密*/
auth.inMemoryAuthentication()
.withUser("admin").password("$2a$10$fB2UU8iJmXsjpdk6T6hGMup8uNcJnOGwo2.QGR.e3qjIsdPYaS4LO").roles("admin")
.and()
.withUser("user").password("$2a$10$3TQ2HO/Xz1bVHw5nlfYTBON2TDJsQ0FMDwAS81uh7D.i9ax5DR46q").roles("user");// 密码加密
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/admin/**").hasRole("admin")
.antMatchers("/user/**").access("hasAnyRole(''user'',''admin'')")
.antMatchers(HttpMethod.POST, "/login").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.addFilterBefore(new JwtLoginFilter("/login", authenticationManager()), UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class)
.addFilterBefore(new JwtFilter(), UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class)
.csrf().disable();
}
}
3.5 测试
项目启动之后,用 Postman 完成测试。

取出 token 的第 1 部分, Base64 解码得到 Header ,如下:

取出 token 的第 2 部分, Base64 解码得到 Payload ,如下:

因为 Base64 是一种编码方案,并不是加密方案,因此不建议将用户的敏感信息放在 token 中。
最后拿着上述 token 访问 /user/hello ,可正常访问。注意:认证方式 Authorization 选择 Bearer Token 。
- Spring Boot 教程合集(微信左下方阅读全文可直达)。
- Spring Boot 教程合集示例代码:https://github.com/cxy35/spring-boot-samples
- 本文示例代码:https://github.com/cxy35/spring-boot-samples/tree/master/spring-boot-security/spring-boot-springsecurity-jwt
扫码关注微信公众号 程序员35 ,获取最新技术干货,畅聊 #程序员的35,35的程序员# 。独立站点:https://cxy35.com
今天关于spring boot 基于 shiro /spring security 实现自定义登录和spring security 自定义登录页面的分享就到这里,希望大家有所收获,若想了解更多关于4. Spring Boot 中 Spring Security 自定义用户认证、Spring Boot + Spring Security 实现自动登录功能、Spring Boot + Spring Security自定义用户认证、Spring Boot 整合 Spring Security + JWT(实现无状态登录)等相关知识,可以在本站进行查询。
本文标签:



![[转帖]Ubuntu 安装 Wine方法(ubuntu如何安装wine)](https://www.gvkun.com/zb_users/cache/thumbs/4c83df0e2303284d68480d1b1378581d-180-120-1.jpg)

