本篇文章给大家谈谈SpringMVC--上传文件,以及springmvc上传文件大小限制的知识点,同时本文还将给你拓展AjaxSpringMVC上传文件、jQueryFileUpload结合Sprin
本篇文章给大家谈谈Spring MVC -- 上传文件,以及springmvc上传文件大小限制的知识点,同时本文还将给你拓展Ajax SpringMVC 上传文件、jQuery File Upload 结合 Spring MVC 批量上传文件,如何获取当前上传文件索引?、Spring MVC 上传文件 --- 依赖引用、spring mvc 上传文件三种方式等相关知识,希望对各位有所帮助,不要忘了收藏本站喔。
本文目录一览:- Spring MVC -- 上传文件(springmvc上传文件大小限制)
- Ajax SpringMVC 上传文件
- jQuery File Upload 结合 Spring MVC 批量上传文件,如何获取当前上传文件索引?
- Spring MVC 上传文件 --- 依赖引用
- spring mvc 上传文件三种方式

Spring MVC -- 上传文件(springmvc上传文件大小限制)
Servlet技术出现以前,文件上传的编程仍然是一项很困难的任务,它涉及在服务器端解析原始的HTTP响应。为了减轻编程的痛苦,开发人员借助于商业的文件上传组件。值得庆幸的是,2003年,Apache Software Foundation发布了开源的Commons FileUpload组件,它很快成为了Java Web应用程序员的利器。
经过很多年,Servlet的设计人员才意识到文件文件上传的重要性,并终于成为Servlet 3.0的内置特性。Servlet 3.0的开发人员不再需要将Commons FileUpload组件导入到他们的项目中去。
为此,在Spring MVC中处理文件上传有两种情况:
- 在Servlet 3.0版本以下,使用Apache Commons FileUpload组件;
- 在Servlet 30.版本以上,利用Servlet 3.0及其更高版本的内置支持。
无论使用哪个版本的Servlet,都要利用相同的API来处理已经上传的文件。本篇博客将会介绍如何在需要支持文件上传的Spring MVC应用中使用Commons FileUpload和Servlet 3.0文件上传特性。
一 前端编程
为了上传文件,必须将HTML表格enctype属性值设置为multipart/form-data,像下面这样:
<form action="action" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
select a file <input type="file" name="fieldName"/>
<input type="submit" value="Upload"/>
</form>表格中必须包含类型为file的一个input元素,它会显示成一个按钮,单击时,它会打开一个对话框,用来选择文件。
在HTML 5之前,如果想要上传多个文件,必须使用多个类型为file的input元素。但是在HTML 5中,通过在input元素中引入multiple属性,使得多个文件的上传变得更加简单。在HTML 5中编写以下任意一行代码,便可以生成一个按钮来选择多个文件:
<input type="file" name="fieldName" multiple/>
<input type="file" name="fieldName" multiple="multiple"/>
<input type="file" name="fieldName" multiple=""/>二 MultipartFile接口
在Spring MVC中处理已经上传的文件十分容易。上传到Spring MVC应用程序中的文件会被包含在一个MultipartFile对象中。我们唯一的任务就是,用类型MultipartFile的属性编写一个domain类。
org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile接口源代码如下:


/*
* Copyright 2002-2018 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.web.multipart;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import org.springframework.core.io.InputStreamSource;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
import org.springframework.util.FileCopyUtils;
/**
* A representation of an uploaded file received in a multipart request.
*
* <p>The file contents are either stored in memory or temporarily on disk.
* In either case, the user is responsible for copying file contents to a
* session-level or persistent store as and if desired. The temporary storage
* will be cleared at the end of request processing.
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Trevor D. Cook
* @since 29.09.2003
* @see org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartHttpServletRequest
* @see org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartResolver
*/
public interface MultipartFile extends InputStreamSource {
/**
* Return the name of the parameter in the multipart form.
* @return the name of the parameter (never {@code null} or empty)
*/
String getName();
/**
* Return the original filename in the client''s filesystem.
* <p>This may contain path information depending on the browser used,
* but it typically will not with any other than Opera.
* @return the original filename, or the empty String if no file has been chosen
* in the multipart form, or {@code null} if not defined or not available
* @see org.apache.commons.fileupload.FileItem#getName()
* @see org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartFile#setPreserveFilename
*/
@Nullable
String getOriginalFilename();
/**
* Return the content type of the file.
* @return the content type, or {@code null} if not defined
* (or no file has been chosen in the multipart form)
*/
@Nullable
String getContentType();
/**
* Return whether the uploaded file is empty, that is, either no file has
* been chosen in the multipart form or the chosen file has no content.
*/
boolean isEmpty();
/**
* Return the size of the file in bytes.
* @return the size of the file, or 0 if empty
*/
long getSize();
/**
* Return the contents of the file as an array of bytes.
* @return the contents of the file as bytes, or an empty byte array if empty
* @throws IOException in case of access errors (if the temporary store fails)
*/
byte[] getBytes() throws IOException;
/**
* Return an InputStream to read the contents of the file from.
* <p>The user is responsible for closing the returned stream.
* @return the contents of the file as stream, or an empty stream if empty
* @throws IOException in case of access errors (if the temporary store fails)
*/
@Override
InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException;
/**
* Return a Resource representation of this MultipartFile. This can be used
* as input to the {@code RestTemplate} or the {@code WebClient} to expose
* content length and the filename along with the InputStream.
* @return this MultipartFile adapted to the Resource contract
* @since 5.1
*/
default Resource getResource() {
return new MultipartFileResource(this);
}
/**
* Transfer the received file to the given destination file.
* <p>This may either move the file in the filesystem, copy the file in the
* filesystem, or save memory-held contents to the destination file. If the
* destination file already exists, it will be deleted first.
* <p>If the target file has been moved in the filesystem, this operation
* cannot be invoked again afterwards. Therefore, call this method just once
* in order to work with any storage mechanism.
* <p><b>NOTE:</b> Depending on the underlying provider, temporary storage
* may be container-dependent, including the base directory for relative
* destinations specified here (e.g. with Servlet 3.0 multipart handling).
* For absolute destinations, the target file may get renamed/moved from its
* temporary location or newly copied, even if a temporary copy already exists.
* @param dest the destination file (typically absolute)
* @throws IOException in case of reading or writing errors
* @throws IllegalStateException if the file has already been moved
* in the filesystem and is not available anymore for another transfer
* @see org.apache.commons.fileupload.FileItem#write(File)
* @see javax.servlet.http.Part#write(String)
*/
void transferTo(File dest) throws IOException, IllegalStateException;
/**
* Transfer the received file to the given destination file.
* <p>The default implementation simply copies the file input stream.
* @since 5.1
* @see #getInputStream()
* @see #transferTo(File)
*/
default void transferTo(Path dest) throws IOException, IllegalStateException {
FileCopyUtils.copy(getInputStream(), Files.newOutputStream(dest));
}
}该接口具有以下方法:
/**
* Return the contents of the file as an array of bytes.
* @return the contents of the file as bytes, or an empty byte array if empty
* @throws IOException in case of access errors (if the temporary store fails)
*/
byte[] getBytes() throws IOException;它以字节数组的形式返回文件的内容。
/**
* Return the content type of the file.
* @return the content type, or {@code null} if not defined
* (or no file has been chosen in the multipart form)
*/
@Nullable
String getContentType();它返回文件的内容类型。
/**
* Return an InputStream to read the contents of the file from.
* <p>The user is responsible for closing the returned stream.
* @return the contents of the file as stream, or an empty stream if empty
* @throws IOException in case of access errors (if the temporary store fails)
*/
@Override
InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException;它返回一个InputStream ,从中读取文件的内容。
/**
* Return the name of the parameter in the multipart form.
* @return the name of the parameter (never {@code null} or empty)
*/
String getName();它以多部分的形式返回参数的名称。
/**
* Return the original filename in the client''s filesystem.
* <p>This may contain path information depending on the browser used,
* but it typically will not with any other than Opera.
* @return the original filename, or the empty String if no file has been chosen
* in the multipart form, or {@code null} if not defined or not available
* @see org.apache.commons.fileupload.FileItem#getName()
* @see org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartFile#setPreserveFilename
*/
@Nullable
String getOriginalFilename();它返回客户端文件系统中文件的原始文件名称。
/**
* Return the size of the file in bytes.
* @return the size of the file, or 0 if empty
*/
long getSize();它以字节为单位,返回文件的大小。
/**
* Transfer the received file to the given destination file.
* <p>This may either move the file in the filesystem, copy the file in the
* filesystem, or save memory-held contents to the destination file. If the
* destination file already exists, it will be deleted first.
* <p>If the target file has been moved in the filesystem, this operation
* cannot be invoked again afterwards. Therefore, call this method just once
* in order to work with any storage mechanism.
* <p><b>NOTE:</b> Depending on the underlying provider, temporary storage
* may be container-dependent, including the base directory for relative
* destinations specified here (e.g. with Servlet 3.0 multipart handling).
* For absolute destinations, the target file may get renamed/moved from its
* temporary location or newly copied, even if a temporary copy already exists.
* @param dest the destination file (typically absolute)
* @throws IOException in case of reading or writing errors
* @throws IllegalStateException if the file has already been moved
* in the filesystem and is not available anymore for another transfer
* @see org.apache.commons.fileupload.FileItem#write(File)
* @see javax.servlet.http.Part#write(String)
*/
void transferTo(File dest) throws IOException, IllegalStateException;它将上传的文件保存到目标目录下。
/**
* Return whether the uploaded file is empty, that is, either no file has
* been chosen in the multipart form or the chosen file has no content.
*/
boolean isEmpty();它表示被上传的文件是否为空(没有上传文件、或者文件内容为空)。
三 使用Commons Fileupload组件上传文件
只有实现了Servlet 3.0及其更高版本规范的Servlet容器,才支持文件上传。对于版本低于Servlet 3.0的容器,则需要Apache Commons Fileupload组件,commons-fileupload.jar包的下载路径如下:https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/commons-fileupload/commons-fileupload。
这是一个开源项目,因此是免费的,它会提供了源代码。为了让Commons Fileupload能够运行,还需要一个Apache Commins组件commons-io.jar,commons-io.jar包的下载路径如下:https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/commons-io/commons-io。
下载完这两个JAR包,我们还需要做以下工作:
- 将这两个JAR文件复制到应用程序的/WEB-INF/lib路径下;
- 在Spring MVC配置文件中定义multipartResolver bean;
<bean id="multipartResolver"
class="org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartResolver">
<property name="maxUploadSize" value="5000000000"/>
</bean>CommonsMultipartResolver类,实际上就是将org.apache.commons.fileupload.servlet.ServletFileUpload类和org.apache.commons.fileupload.disk.DiskFileItemFactory的功能进行了整合,具体代码如下:


/*
* Copyright 2002-2018 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.web.multipart.commons;
import java.util.List;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import org.apache.commons.fileupload.FileItem;
import org.apache.commons.fileupload.FileItemFactory;
import org.apache.commons.fileupload.FileUpload;
import org.apache.commons.fileupload.FileUploadBase;
import org.apache.commons.fileupload.FileUploadException;
import org.apache.commons.fileupload.servlet.ServletFileUpload;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
import org.springframework.web.context.ServletContextAware;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MaxUploadSizeExceededException;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartException;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartHttpServletRequest;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartResolver;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.support.AbstractMultipartHttpServletRequest;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.support.DefaultMultipartHttpServletRequest;
import org.springframework.web.util.WebUtils;
/**
* Servlet-based {@link MultipartResolver} implementation for
* <a href="https://commons.apache.org/proper/commons-fileupload">Apache Commons FileUpload</a>
* 1.2 or above.
*
* <p>Provides "maxUploadSize", "maxInMemorySize" and "defaultEncoding" settings as
* bean properties (inherited from {@link CommonsFileUploadSupport}). See corresponding
* ServletFileUpload / DiskFileItemFactory properties ("sizeMax", "sizeThreshold",
* "headerEncoding") for details in terms of defaults and accepted values.
*
* <p>Saves temporary files to the servlet container''s temporary directory.
* Needs to be initialized <i>either</i> by an application context <i>or</i>
* via the constructor that takes a ServletContext (for standalone usage).
*
* @author Trevor D. Cook
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 29.09.2003
* @see #CommonsMultipartResolver(ServletContext)
* @see #setResolveLazily
* @see org.apache.commons.fileupload.servlet.ServletFileUpload
* @see org.apache.commons.fileupload.disk.DiskFileItemFactory
*/
public class CommonsMultipartResolver extends CommonsFileUploadSupport
implements MultipartResolver, ServletContextAware {
private boolean resolveLazily = false;
/**
* Constructor for use as bean. Determines the servlet container''s
* temporary directory via the ServletContext passed in as through the
* ServletContextAware interface (typically by a WebApplicationContext).
* @see #setServletContext
* @see org.springframework.web.context.ServletContextAware
* @see org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext
*/
public CommonsMultipartResolver() {
super();
}
/**
* Constructor for standalone usage. Determines the servlet container''s
* temporary directory via the given ServletContext.
* @param servletContext the ServletContext to use
*/
public CommonsMultipartResolver(ServletContext servletContext) {
this();
setServletContext(servletContext);
}
/**
* Set whether to resolve the multipart request lazily at the time of
* file or parameter access.
* <p>Default is "false", resolving the multipart elements immediately, throwing
* corresponding exceptions at the time of the {@link #resolveMultipart} call.
* Switch this to "true" for lazy multipart parsing, throwing parse exceptions
* once the application attempts to obtain multipart files or parameters.
*/
public void setResolveLazily(boolean resolveLazily) {
this.resolveLazily = resolveLazily;
}
/**
* Initialize the underlying {@code org.apache.commons.fileupload.servlet.ServletFileUpload}
* instance. Can be overridden to use a custom subclass, e.g. for testing purposes.
* @param fileItemFactory the Commons FileItemFactory to use
* @return the new ServletFileUpload instance
*/
@Override
protected FileUpload newFileUpload(FileItemFactory fileItemFactory) {
return new ServletFileUpload(fileItemFactory);
}
@Override
public void setServletContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
if (!isUploadTempDirSpecified()) {
getFileItemFactory().setRepository(WebUtils.getTempDir(servletContext));
}
}
@Override
public boolean isMultipart(HttpServletRequest request) {
return ServletFileUpload.isMultipartContent(request);
}
@Override
public MultipartHttpServletRequest resolveMultipart(final HttpServletRequest request) throws MultipartException {
Assert.notNull(request, "Request must not be null");
if (this.resolveLazily) {
return new DefaultMultipartHttpServletRequest(request) {
@Override
protected void initializeMultipart() {
MultipartParsingResult parsingResult = parseRequest(request);
setMultipartFiles(parsingResult.getMultipartFiles());
setMultipartParameters(parsingResult.getMultipartParameters());
setMultipartParameterContentTypes(parsingResult.getMultipartParameterContentTypes());
}
};
}
else {
MultipartParsingResult parsingResult = parseRequest(request);
return new DefaultMultipartHttpServletRequest(request, parsingResult.getMultipartFiles(),
parsingResult.getMultipartParameters(), parsingResult.getMultipartParameterContentTypes());
}
}
/**
* Parse the given servlet request, resolving its multipart elements.
* @param request the request to parse
* @return the parsing result
* @throws MultipartException if multipart resolution failed.
*/
protected MultipartParsingResult parseRequest(HttpServletRequest request) throws MultipartException {
String encoding = determineEncoding(request);
FileUpload fileUpload = prepareFileUpload(encoding);
try {
List<FileItem> fileItems = ((ServletFileUpload) fileUpload).parseRequest(request);
return parseFileItems(fileItems, encoding);
}
catch (FileUploadBase.SizeLimitExceededException ex) {
throw new MaxUploadSizeExceededException(fileUpload.getSizeMax(), ex);
}
catch (FileUploadBase.FileSizeLimitExceededException ex) {
throw new MaxUploadSizeExceededException(fileUpload.getFileSizeMax(), ex);
}
catch (FileUploadException ex) {
throw new MultipartException("Failed to parse multipart servlet request", ex);
}
}
/**
* Determine the encoding for the given request.
* Can be overridden in subclasses.
* <p>The default implementation checks the request encoding,
* falling back to the default encoding specified for this resolver.
* @param request current HTTP request
* @return the encoding for the request (never {@code null})
* @see javax.servlet.ServletRequest#getCharacterEncoding
* @see #setDefaultEncoding
*/
protected String determineEncoding(HttpServletRequest request) {
String encoding = request.getCharacterEncoding();
if (encoding == null) {
encoding = getDefaultEncoding();
}
return encoding;
}
@Override
public void cleanupMultipart(MultipartHttpServletRequest request) {
if (!(request instanceof AbstractMultipartHttpServletRequest) ||
((AbstractMultipartHttpServletRequest) request).isResolved()) {
try {
cleanupFileItems(request.getMultiFileMap());
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
logger.warn("Failed to perform multipart cleanup for servlet request", ex);
}
}
}
}multipartResolver 对象则通过配置property元素来调用setter方法以设置属性值。我们可以通过setter方式注入的属性有:
- maxUploadSize:控制上传单个文件的大小,单位是字节;
- maxInMemorySize:设置上传文件时用到的临时文件的大小,单位是字节;
- defaultEncoding:请求参数的默认编码方式。
这些属性被用来对上传文件进行设置。
此外,CommonsMultipartResolver类的还有一个非常重要的函数:
/**
* Parse the given servlet request, resolving its multipart elements.
* @param request the request to parse
* @return the parsing result
* @throws MultipartException if multipart resolution failed.
*/
protected MultipartParsingResult parseRequest(HttpServletRequest request) throws MultipartException {
String encoding = determineEncoding(request);
FileUpload fileUpload = prepareFileUpload(encoding);
try {
List<FileItem> fileItems = ((ServletFileUpload) fileUpload).parseRequest(request);
return parseFileItems(fileItems, encoding);
}
catch (FileUploadBase.SizeLimitExceededException ex) {
throw new MaxUploadSizeExceededException(fileUpload.getSizeMax(), ex);
}
catch (FileUploadBase.FileSizeLimitExceededException ex) {
throw new MaxUploadSizeExceededException(fileUpload.getFileSizeMax(), ex);
}
catch (FileUploadException ex) {
throw new MultipartException("Failed to parse multipart servlet request", ex);
}
}通过parseRequest()函数解析form中的所有请求字段,并保存到List<FileItem>集合中,然后将集合转换为MultipartParsingResult类型返回:


/**
* Holder for a Map of Spring MultipartFiles and a Map of
* multipart parameters.
*/
protected static class MultipartParsingResult {
private final MultiValueMap<String, MultipartFile> multipartFiles;
private final Map<String, String[]> multipartParameters;
private final Map<String, String> multipartParameterContentTypes;
public MultipartParsingResult(MultiValueMap<String, MultipartFile> mpFiles,
Map<String, String[]> mpParams, Map<String, String> mpParamContentTypes) {
this.multipartFiles = mpFiles;
this.multipartParameters = mpParams;
this.multipartParameterContentTypes = mpParamContentTypes;
}
public MultiValueMap<String, MultipartFile> getMultipartFiles() {
return this.multipartFiles;
}
public Map<String, String[]> getMultipartParameters() {
return this.multipartParameters;
}
public Map<String, String> getMultipartParameterContentTypes() {
return this.multipartParameterContentTypes;
}
}MultipartParsingResult类有个重要的属性:
private final MultiValueMap<String, MultipartFile> multipartFiles;该Map的键值为String类型,保存的是表单类型为file的input元素的name属性值,值为MultipartFile接口类型,该类型保存了该input元素对应的上传文件。
四 Servlet 3.0以下版本文件上传示例
范例upload1展示了如何利用Apache Commons FileUpload处理已经上传的文件。这个范例在Servlet 3.0容器中也是有效的。upload1有一个domain包,包含Procudt类,它包含了一个MultipartFile对象列表。该示例介绍了如何进行产品图片的上传。
1、目录结构
下面展示upload1应用的目录结构:
注意:在lib中我们需要导入Apache Commons FileUpload组件。
2、Product类
Product类具有类型为List<MultipartFile>的imagea属性,这个属性用来保存上传的产品图片文件(可以是多个图片文件):
package domain;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.util.List;
import javax.validation.constraints.NotNull;
import javax.validation.constraints.Size;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
public class Product implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1;
@NotNull
@Size(min=1, max=10)
private String name;
private String description;
private BigDecimal price;
private List<MultipartFile> images;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
public void setDescription(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
public BigDecimal getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(BigDecimal price) {
this.price = price;
}
public List<MultipartFile> getImages() {
return images;
}
public void setImages(List<MultipartFile> images) {
this.images = images;
}
}3、控制器
package controller;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.validation.BindingResult;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ModelAttribute;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
import domain.Product;
@Controller
public class ProductController {
private static final Log logger = LogFactory
.getLog(ProductController.class);
//请求URL:/input-product
@RequestMapping(value = "/input-product")
public String inputProduct(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("product", new Product());
return "ProductForm";
}
//请求URL:/save-product
@RequestMapping(value = "/save-product")
public String saveProduct(HttpServletRequest servletRequest,
@ModelAttribute Product product, BindingResult bindingResult,
Model model) {
//获取上传的图片文件(可以多个文件)
List<MultipartFile> files = product.getImages();
//用于保存所有文件名
List<String> fileNames = new ArrayList<String>();
//检验是否有文件?
if (null != files && files.size() > 0) {
//遍历
for (MultipartFile multipartFile : files) {
//获取文件名
String fileName = multipartFile.getOriginalFilename();
fileNames.add(fileName);
//获取应用/image虚拟路径在文件系统上对应的真实路径 + 文件名 并创建File对象
File imageFile = new File(servletRequest.getServletContext()
.getRealPath("/image"), fileName);
try {
//将上传的文件保存到目标目录下
multipartFile.transferTo(imageFile);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
// save product here
model.addAttribute("product", product);
return "ProductDetails";
}
}ProductController类有inputProduct()和saveProduct()两个请求处理方法。inputProduct()方法向浏览器发出一个产品表单,saveProduct()方法将已经上传的图片文件保存到应用程序的image目录下,文件名不改变。
注意:必须先创建好image文件夹。
4、配置文件
下面给出springmvc-config.xml文件的所有内容:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="controller" />
<mvc:annotation-driven />
<mvc:resources mapping="/css/**" location="/css/" />
<mvc:resources mapping="/*.html" location="/" />
<mvc:resources mapping="/image/**" location="/image/" />
<bean id="viewResolver"
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/jsp/" />
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp" />
</bean>
<bean id="multipartResolver"
class="org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartResolver">
<property name="maxUploadSize" value="5000000000"/>
</bean>
</beans>利用multipartResolver bean的maxUploadSize属性,可以设置能够接受的最大文件容量。如果没有设置这个属性,则没有最大文件容量限制。没有设置文件容量限制,并不意味着可以上传任意大小的文件。上传过大的文件时需要花费很长的时间,这样会导致服务器超时,为了处理超大文件的问题,可以利用HTML 5 File API将文件切片,然后再分别上传这些文件。
如果想对上传的文件类型进行过滤,那么我们可以需要先获取上传文件的名称,然后检测其扩展名。此外,我们也可以在前端使用js代码检测上传文件的扩展名。
部署描述符(web.xml文件):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app version="3.1"
xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee
http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd">
<!-- 配置编码方式过滤器,注意一点:要配置在所有过滤器的前面 -->
<filter>
<filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>encoding</param-name>
<param-value>utf-8</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/config/springmvc-config.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>注意,web.xml文件中我们配置了编码方式过滤器,将所有http请求的参数编码为UTF-8方式,与jsp中页面编码一致。
5、视图
用于上传图片文件的ProductForm.jsp页面如下所示:
<%@ taglib prefix="form" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags/form" %>
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c" %>
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Add Product Form</title>
<style type="text/css">@import url("<c:url value="/css/main.css"/>");</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="global">
<form:form modelAttribute="product" action="save-product" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<fieldset>
<legend>Add a product</legend>
<p>
<label for="name">Product Name: </label>
<form:input id="name" path="name" cssErrorClass="error"/>
<form:errors path="name" cssClass="error"/>
</p>
<p>
<label for="description">Description: </label>
<form:input id="description" path="description"/>
</p>
<p>
<label for="price">Price: </label>
<form:input id="price" path="price" cssErrorClass="error"/>
</p>
<p>
<label for="image">Product Image: </label>
<input type="file" name="images[0]"/>
</p>
<p id="buttons">
<input id="reset" type="reset" tabindex="4">
<input id="submit" type="submit" tabindex="5"
value="Add Product">
</p>
</fieldset>
</form:form>
</div>
</body>
</html>注意表单中类型为file的input元素,它将显示为一个按钮,用于选择要上传的文件。并且input元素的name属性指定为"images[0]",即绑定到表单支持对象product的images属性(List<MultipartFile>类型>)的第一个元素上。
如果想支持多个文件同时上传,只需将 <input type="file" name="images[0]"/>替换成如下:
<input type="file" name="images" multiple/>提交Product表单,将会调用saveProduct()方法,如果这个方法能够顺利执行,用户将会跳转到ProductDetails.jsp页面:
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c" %>
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Save Product</title>
<style type="text/css">@import url("<c:url value="/css/main.css"/>");</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="global">
<h4>The product has been saved.</h4>
<p>
<h5>Details:</h5>
Product Name: ${product.name}<br/>
Description: ${product.description}<br/>
Price: $${product.price}
<p>Following files are uploaded successfully.</p>
<ol>
<c:forEach items="${product.images}" var="image">
<li>${image.originalFilename}
<img width="100" src="<c:url value="/image/"/>
${image.originalFilename}"/>
</li>
</c:forEach>
</ol>
</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>该页面将会显示已经保存的Product的详细信息及其图片。
6、测试
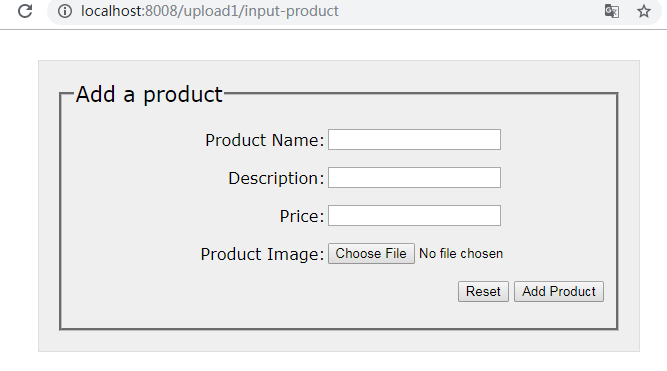
将应用程序部署到tomcat服务器,并在网页输入以下URL:
http://localhost:8008/upload1/input-product将会看到一个如图所示的Add Product表单,试着输入一些产品信息,并选择一个要上传的文件:
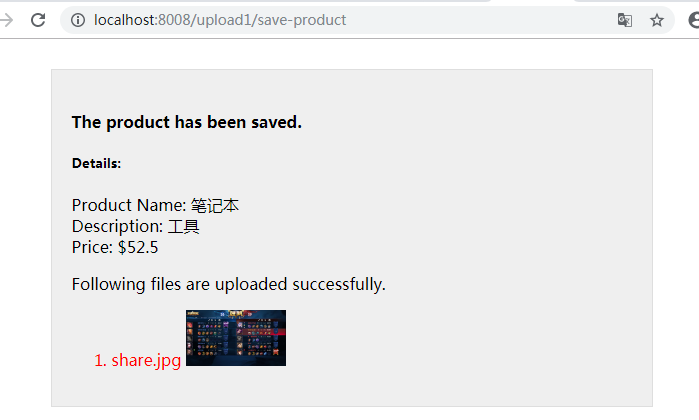
单击"Add Product"按钮,就可以看到如下所示的网页:
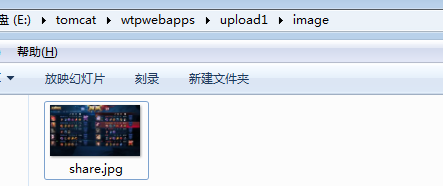
同时我们可以在tomcat服务器,upload1应用下的image目录下看到,已经上传的文件:
如果将ProductForm.jsp中的:<input type="file" name="images[0]"/>更改为如下代码:
<input type="file" name="images" multiple/>那么就可以实现多个文件同时上传:
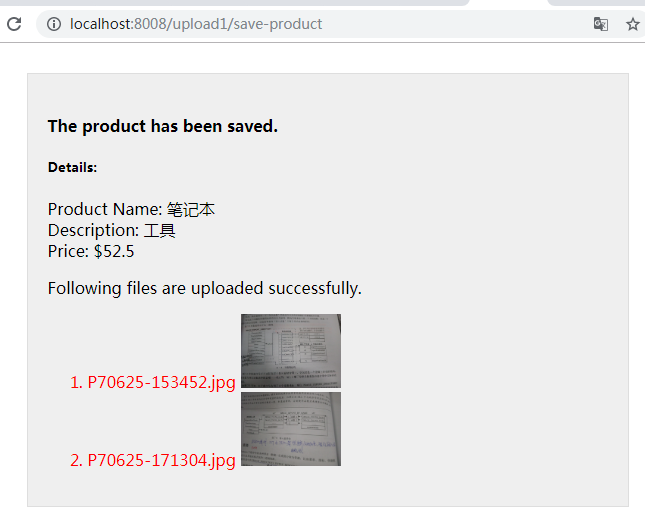
五 Servlet 3.0及其更高版本上传文件
有了Servlet 3.0就不需要Common FileUpload和Common IO JAR包了。在Servlet 3.0及其以上版本的容器进行服务器端文件上传的编程,是围绕着注解类型MultipartConfig和javax.servlet.http.Part接口进行的。处理已上传文件的Servlets必须以@MultipartConfig进行注解。
下列是可能在MultipartConfig注解类型中出现的属性,它们都是可选的:
- maxFileSize:单个上传文件的最大容量,默认值是-1,表示没有限制,大于指定容量的文件将会遭到拒绝;
- maxRequestSize:表示Multipart HTTP请求运行的最大容量,默认值为-1,表示没有限制;
- location:表示在Part调用write()方法时,要将已上传的文件保存到磁盘中的位置;
- fileSizeThreshod:设置上传文件时用到的临时文件的大小;
Spring MVC的DispatcherServlet处理大部分或者所有请求。但是遗憾的是,如果不修改源代码,将无法对Servlet进行注解。但值得庆幸的是,Servlet 3.0中有一种比较容易的方法,能使一个Servlet变成一个MultipartConfig Servlet,即给部署描述符(web.xml)中的Servlet声明赋值。以下代码与用@MultipartConfig给DispatcherServlet进行注解的效果一样:
<servlet>
<servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/config/springmvc-config.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
<multipart-config>
<max-file-size>20848820</max-file-size>
<max-request-size>418018841</max-request-size>
<file-size-threshold>1048576</file-size-threshold>
</multipart-config>
</servlet>此外,还需要在Spring MVC配置文件中使用一个StandardServletMultipartResolver,如下:
<bean id="multipartResolver"
class="org.springframework.web.multipart.support.StandardServletMultipartResolver">
</bean>upload2应用程序展示了如何在Servlet 3.0以及更改版本的容器中处理文件上传问题,这是从upload1中改写过来的,upload2和upload1相似部分不再做详细介绍。主要的区别在于,现在的web.xml文件中包含了一个multipart-config元素。upload2应用的目录结构如下:
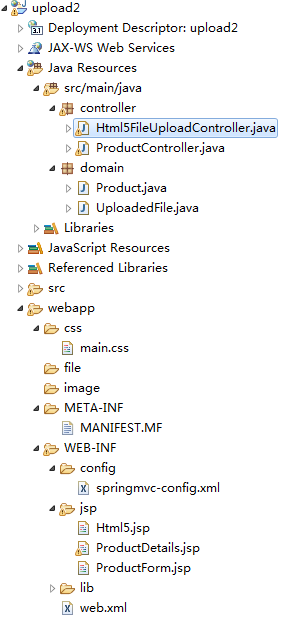
1、配置文件
下面是upload2应用的部署描述符(web.xml文件):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app version="3.1"
xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee
http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd">
<servlet>
<servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/config/springmvc-config.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
<multipart-config>
<max-file-size>20848820</max-file-size>
<max-request-size>418018841</max-request-size>
<file-size-threshold>1048576</file-size-threshold>
</multipart-config>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>Spring MVC配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="controller" />
<mvc:annotation-driven />
<mvc:resources mapping="/css/**" location="/css/" />
<mvc:resources mapping="/*.html" location="/" />
<mvc:resources mapping="/image/**" location="/image/" />
<mvc:resources mapping="/file/**" location="/file/" />
<bean id="viewResolver"
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/jsp/" />
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp" />
</bean>
<bean id="multipartResolver"
class="org.springframework.web.multipart.support.StandardServletMultipartResolver">
</bean>
</beans>2、Produtct类
package domain;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.util.List;
import javax.validation.constraints.NotNull;
import javax.validation.constraints.Size;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
public class Product implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 78L;
@NotNull
@Size(min=1, max=10)
private String name;
private String description;
private BigDecimal price;
private List<MultipartFile> images;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
public void setDescription(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
public BigDecimal getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(BigDecimal price) {
this.price = price;
}
public List<MultipartFile> getImages() {
return images;
}
public void setImages(List<MultipartFile> images) {
this.images = images;
}
}3、ProductController类
package controller;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.validation.BindingResult;
import org.springframework.validation.FieldError;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ModelAttribute;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
import domain.Product;
@Controller
public class ProductController {
private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ProductController.class);
//请求URL:/input-product
@RequestMapping(value="/input-product")
public String inputProduct(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("product", new Product());
return "ProductForm";
}
//请求URL:/save-product
@RequestMapping(value = "/save-product")
public String saveProduct(HttpServletRequest servletRequest,
@ModelAttribute Product product, BindingResult bindingResult,
Model model) {
//获取上传的图片文件(可以多个文件)
List<MultipartFile> files = product.getImages();
//用于保存所有文件名
List<String> fileNames = new ArrayList<String>();
//检验是否有文件?
if (null != files && files.size() > 0) {
//遍历
for (MultipartFile multipartFile : files) {
//获取文件名
String fileName = multipartFile.getOriginalFilename();
fileNames.add(fileName);
//获取应用/image虚拟路径在文件系统上对应的真实路径 + 文件名 并创建File对象
File imageFile = new File(servletRequest.getServletContext()
.getRealPath("/image"), fileName);
try {
//将上传的文件保存到目标目录下
multipartFile.transferTo(imageFile);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
// save product here
model.addAttribute("product", product);
return "ProductDetails";
}
}4、视图
ProductForm.jsp:
<%@ taglib prefix="form" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags/form" %>
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Add Product Form</title>
<style type="text/css">@import url("<c:url value="/css/main.css"/>");</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="global">
<form:form modelAttribute="product" action="save-product" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<fieldset>
<legend>Add a product</legend>
<p>
<label for="name">Product Name: </label>
<form:input id="name" path="name" cssErrorClass="error"/>
<form:errors path="name" cssClass="error"/>
</p>
<p>
<label for="description">Description: </label>
<form:input id="description" path="description"/>
</p>
<p>
<label for="price">Price: </label>
<form:input id="price" path="price" cssErrorClass="error"/>
</p>
<p>
<label for="image">Product Image: </label>
<!-- <input type="file" name="images[0]"/> -->
<input type="file" name="images" multiple/>
</p>
<p id="buttons">
<input id="reset" type="reset" tabindex="4">
<input id="submit" type="submit" tabindex="5"
value="Add Product">
</p>
</fieldset>
</form:form>
</div>
</body>
</html>ProductDetails:


<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Save Product</title>
<style type="text/css">@import url("<c:url value="/css/main.css"/>");</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="global">
<h4>The product has been saved.</h4>
<p>
<h5>Details:</h5>
Product Name: ${product.name}<br/>
Description: ${product.description}<br/>
Price: $${product.price}
<p>Following files are uploaded successfully.</p>
<ol>
<c:forEach items="${product.images}" var="image">
<li>${image.originalFilename}
<img width="100" src="<c:url value="/image/"/>${image.originalFilename}"/>
</li>
</c:forEach>
</ol>
</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>main.css:


#global {
text-align: left;
border: 1px solid #dedede;
background: #efefef;
width: 560px;
padding: 20px;
margin: 30px auto;
}
form {
font:100% verdana;
min-width: 500px;
max-width: 600px;
width: 560px;
}
form fieldset {
border-color: #bdbebf;
border-width: 3px;
margin: 0;
}
legend {
font-size: 1.3em;
}
form label {
width: 250px;
display: block;
float: left;
text-align: right;
padding: 2px;
}
#buttons {
text-align: right;
}
#errors, li {
color: red;
}
.error {
color: red;
font-size: 9pt;
}5、测试
将应用程序部署到tomcat服务器,并在网页输入以下URL:
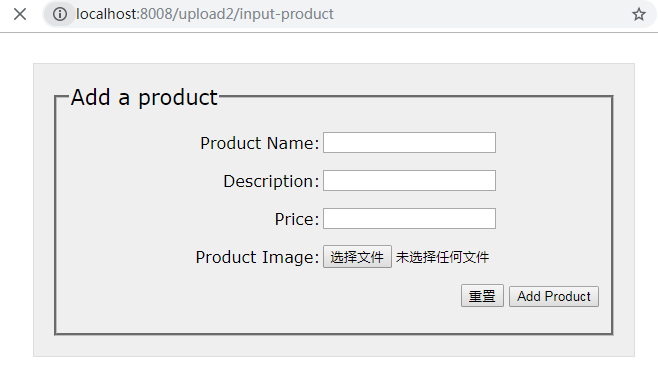
http://localhost:8008/upload2/input-product将会看到一个如图所示的Add Product表单,试着输入一些产品信息,并选择一个要上传的文件:
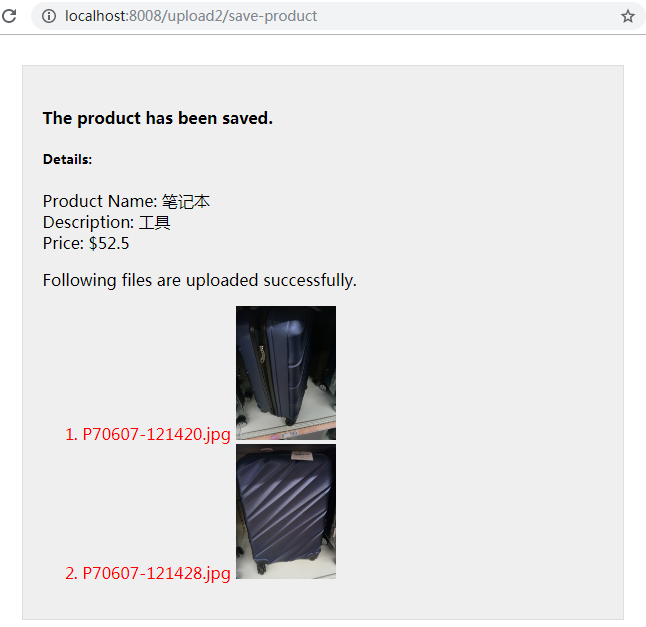
单击"Add Product"按钮,就可以看到如下所示的网页:
六 upload2应用HTML 5进行文件上传
虽然Servlet 3.0中的文件上传特性使文件上传变得十分容器,只需在服务器端编程即可,但是这对提升用户体验毫无帮助。单独一个HTML表单并不能显示进度条,或者显示已经成功上传的文件数量。开发人员采用了各种不同的技术来改善用户界面,例如,单独用一个浏览器线程对服务器发出请求,以便报告上传进度,或者利用像Java applets、Adobe Flash、Microsoft Silverlight这样的第三方技术。
这些第三方技术可以工作,但都在一定程度上存在限制。今天Java applets和Microsoft Silverlight几乎过时了,Chrome不在允许Java applets和Microsoft Silverlight,Microsoft取代Internet Explorer的新浏览器Edge根本不需要插件。
我们仍然可以使用Flash、因为Chrome仍然可以运行它,Edge已经集成了它,然而,现在越来越多的人选择使用HTML 5。
HTML 5在其DOM中添加了一个File API,它允许访问本地文件。与Java applets、Adobe Flash、Microsoft Silverlight相比,HTML 5似乎是针对客户端文件上传局限性的最佳解决方案。
为了验证HTML 5的性能,upload2中的html5页面采用了JavaScript和HTML 5 File API来提供报告上传进度的进度条。upload2应用程序中也创建了一个UploadedFile 类,用于在服务器中保存已上传的文件。
1、UploadedFile类
upload2的UploadedFile类只包含一个属性multipartFile,用来保存已经上传的文件:
package domain;
import java.io.Serializable;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
public class UploadedFile implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
//用来保存已经上传的文件
private MultipartFile multipartFile;
public MultipartFile getMultipartFile() {
return multipartFile;
}
public void setMultipartFile(MultipartFile multipartFile) {
this.multipartFile = multipartFile;
}
}2、Html5FileUploadController类
upload2中的Html5FileUploadController类能够将已经上传的文件保存到应用程序的file目录下:
package controller;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.validation.BindingResult;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ModelAttribute;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
import domain.UploadedFile;
@Controller
public class Html5FileUploadController {
private static final Log logger = LogFactory
.getLog(Html5FileUploadController.class);
//请求URL:/html5
@RequestMapping(value = "/html5")
public String inputProduct() {
return "Html5";
}
//请求URL:/upload-file
@RequestMapping(value = "/upload-file")
public void saveFile(HttpServletRequest servletRequest,
@ModelAttribute UploadedFile uploadedFile,
BindingResult bindingResult, Model model) {
//获取已经上传的文件
MultipartFile multipartFile = uploadedFile.getMultipartFile();
//获取上传的文件名
String fileName = multipartFile.getOriginalFilename();
try {
//获取应用/file虚拟路径在文件系统上对应的真实路径 + 文件名 并创建File对象
File file = new File(servletRequest.getServletContext()
.getRealPath("/file"), fileName);
//将上传的文件保存到目标目录下
multipartFile.transferTo(file);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}3、html5.jsp页面
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script>
var totalFileLength, totalUploaded, fileCount, filesUploaded;
// show uoload file information use element of id="debug"
function debug(s) {
var debug = document.getElementById(''debug'');
if (debug) {
debug.innerHTML = debug.innerHTML + ''<br/>'' + s;
}
}
//load event of XMLHttpRequest object
function onUploadComplete(e) {
totalUploaded += document.getElementById(''files'').
files[filesUploaded].size;
filesUploaded++;
debug(''complete '' + filesUploaded + " of " + fileCount);
debug(''totalUploaded: '' + totalUploaded);
if (filesUploaded < fileCount) {
uploadNext();
} else {
var bar = document.getElementById(''bar'');
bar.style.width = ''100%'';
bar.innerHTML = ''100% complete'';
alert(''Finished uploading file(s)'');
}
}
//trigger when selecting file change
function onFileSelect(e) {
var files = e.target.files; // FileList object
var output = [];
//get upload file count
fileCount = files.length;
totalFileLength = 0;
for (var i=0; i<fileCount; i++) {
var file = files[i];
output.push(file.name, '' ('',
file.size, '' bytes, '',
file.lastModifiedDate.toLocaleDateString(), '') ''
);
output.push(''<br/>'');
debug(''add '' + file.name + '' (''+ file.size + ''bytes'' + '') '' );
totalFileLength += file.size;
}
//show selecting file information
document.getElementById(''selectedFiles'').innerHTML =
output.join('''');
debug(''totalFileLength: '' + totalFileLength + ''bytes'');
}
//progress event of XMLHttpRequest object
function onUploadProgress(e) {
if (e.lengthComputable) {
var percentComplete = parseInt(
(e.loaded + totalUploaded) * 100
/ totalFileLength);
var bar = document.getElementById(''bar'');
bar.style.width = percentComplete + ''%'';
bar.innerHTML = percentComplete + '' % complete'';
} else {
debug(''unable to compute'');
}
}
//error event of XMLHttpRequest object
function onUploadFailed(e) {
alert("Error uploading file");
}
//upload next file
function uploadNext() {
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
var fd = new FormData();
var file = document.getElementById(''files'').
files[filesUploaded];
fd.append("multipartFile", file);
xhr.upload.addEventListener(
"progress", onUploadProgress, false);
xhr.addEventListener("load", onUploadComplete, false);
xhr.addEventListener("error", onUploadFailed, false);
xhr.open("POST", "upload-file");
debug(''uploading '' + file.name);
xhr.send(fd);
}
//trigger when click Upload button
function startUpload() {
totalUploaded = filesUploaded = 0;
uploadNext();
}
//trigger when window load
window.onload = function() {
document.getElementById(''files'').addEventListener(
''change'', onFileSelect, false);
document.getElementById(''uploadButton'').
addEventListener(''click'', startUpload, false);
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Multiple file uploads with progress bar</h1>
<div id=''progressBar'' style=''height:20px;border:2px solid green''>
<div id=''bar''
style=''height:100%;background:#33dd33;width:0%''>
</div>
</div>
<form>
<input type="file" id="files" multiple/>
<br/>
<output id="selectedFiles"></output>
<input id="uploadButton" type="button" value="Upload"/>
</form>
<div id=''debug''
style=''height:300px;border:2px solid green;overflow:auto''>
</div>
</body>
</html>html5.jsp页面主要包含以下三部分:
- 一个id为progressBar的div元素:用于展示上传进度;
- 一个表单:表单中有一个类型为file的input元素和一个按钮,用于上传文件;
- 一个id为debug的div元素,用来显示调试信息,主要包括上传文件信息;
这个表单有两点需要注意:
<form>
<input type="file" id="files" multiple/>
<br/>
<output id="selectedFiles"></output>
<input id="uploadButton" type="button" value="Upload"/>
</form>- id为files的input元素,它有一个multiple属性,用于支持多文件选择;
- 这个按钮不是一个提交按钮,因此单击它不会提交表单,事实上,脚本是利用XMLHttpRequest对象来上传的;
下面来看JavaScript代码。执行脚本时,它做的第一件事就是为这4个变量分配空间:
var totalFileLength, totalUploaded, fileCount, filesUploaded;(1) totalFileLength变量保存要上传的文件总长度;
(2) totalUploaded是指目前已经上传的字节数;
(3) fileCount:要上传的文件数量;
(4) filesUploaded:表示已经上传的文件数量;
随后,当html5.jsp页面完全加载后,便触发window.onload事件:
window.onload = function() {
document.getElementById(''files'').addEventListener(
''change'', onFileSelect, false);
document.getElementById(''uploadButton'').
addEventListener(''click'', startUpload, false);
}这段代码将id为files的input元素的change事件映射到onFileSelect()函数,将按钮的click事件映射到startUpload()函数。
每当用户从本地目录中修改了不同的文件时,都会触发change事件。与该事件相关的事件处理器onFileSelect()函数只是在一个id为selectedFiles的output元素中输出已选中的文件的名称和数量:
//trigger when selecting file change
function onFileSelect(e) {
var files = e.target.files; // FileList object
var output = [];
//get upload file count
fileCount = files.length;
totalFileLength = 0;
for (var i=0; i<fileCount; i++) {
var file = files[i];
output.push(file.name, '' ('',
file.size, '' bytes, '',
file.lastModifiedDate.toLocaleDateString(), '') ''
);
output.push(''<br/>'');
debug(''add '' + file.name + '' (''+ file.size + ''bytes'' + '') '' );
totalFileLength += file.size;
}
//show selecting file information
document.getElementById(''selectedFiles'').innerHTML =
output.join('''');
debug(''totalFileLength: '' + totalFileLength + ''bytes'');
}当用户点击Upload按钮时,就会调用startUpload()函数:
//trigger when click Upload button
function startUpload() {
totalUploaded = filesUploaded = 0;
uploadNext();
}并随着调用uploadNext()函数,uploadNext()函数上传已选文件列表中的下一个文件。它首先创建一个XMLHttpRequest对象和一个FormData对象(表单对象),并将接下来通过document.getElementById(''files'')获取一个FileList对象,并将要上传的文件添加到属性multipartFile上:
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
var fd = new FormData();
var file = document.getElementById(''files'').
files[filesUploaded];
fd.append("multipartFile", file);
随后,uploadNext()函数将XMLHttpRequest对象的progress事件绑定添加到onUploadProgress(),并将load事件和error时间分别添加到onUploadComplete()和onUploadFalied:
xhr.upload.addEventListener(
"progress", onUploadProgress, false);
xhr.addEventListener("load", onUploadComplete, false);
xhr.addEventListener("error", onUploadFailed, false);接下来,打开一个服务器连接,请求/upload-file页面,并发出FormData:
xhr.open("POST", "upload-file");
debug(''uploading '' + file.name);
xhr.send(fd);fd是一个表单对象,该对象的各个属性会被绑定到/upload-file页面对应的请求处理方法saveFile()的模型参数uploadedFile的各个属性上:
public void saveFile(HttpServletRequest servletRequest,
@ModelAttribute UploadedFile uploadedFile,
BindingResult bindingResult, Model model)在上传期间,会重复的调用onUploadProgress()函数,让它有机会更新进度条。更新包括计算已经上传的总字节比率,计算已选择文件的字节数,拓宽progressBar div元素里面的div元素:
//progress event of XMLHttpRequest object
function onUploadProgress(e) {
if (e.lengthComputable) {
var percentComplete = parseInt(
(e.loaded + totalUploaded) * 100
/ totalFileLength);
var bar = document.getElementById(''bar'');
bar.style.width = percentComplete + ''%'';
bar.innerHTML = percentComplete + '' % complete'';
} else {
debug(''unable to compute'');
}
}上传完成时,调用onUploadComplete()函数。这个事件处理器会添加totalUploaded,即已经完成上传的文件容量,并添加filesUploaded值。随后,它会查看已经选中的所有文件是否都已经上传,如果是,则会显示一条消息,告诉用户文件上传已经成功完成,如果不是,则再次调用uploadNext():
//load event of XMLHttpRequest object
function onUploadComplete(e) {
totalUploaded += document.getElementById(''files'').
files[filesUploaded].size;
filesUploaded++;
debug(''complete '' + filesUploaded + " of " + fileCount);
debug(''totalUploaded: '' + totalUploaded);
if (filesUploaded < fileCount) {
uploadNext();
} else {
var bar = document.getElementById(''bar'');
bar.style.width = ''100%'';
bar.innerHTML = ''100% complete'';
alert(''Finished uploading file(s)'');
}
}如果上传失败,则会调用onUploadFailed()函数,并且显示一条消息:
//error event of XMLHttpRequest object
function onUploadFailed(e) {
alert("Error uploading file");
}4、测试
在浏览器中中输入如下URL:
http://localhost:8008/upload2/html5选中几个文件,并单击Upload按钮,将会看到一个进度条、以及文件上传的信息,如下:
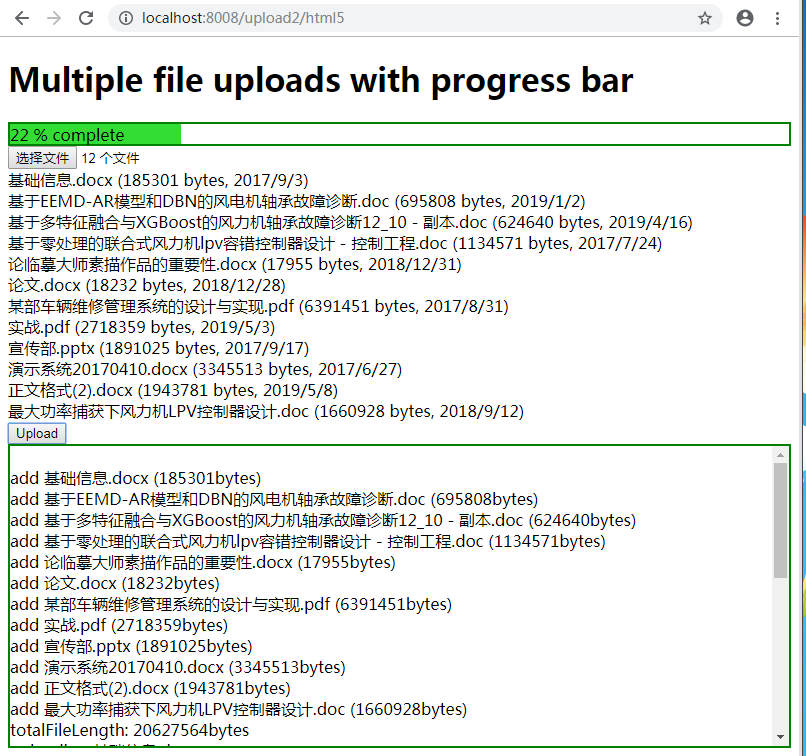
注意:如果有中文,则有必要将整个应用的字符编码设置为UTF-8。
参考文章
[1]彻底解决springMVC中文乱码
[2]Spring MVC学习指南
[3]FormData对象
[4]小记 HTML5 file对象
[5]HTML笔记(HTML5 File API)

Ajax SpringMVC 上传文件
jsp 文件
<form id="uploadForm" method="post" name="fileinfo" enctype="multipart/form-data"> <input type="file" id="image" name="image"> <input type="button"onclick="upload()" value="上传图片"> </form>
Ajax写法
function upload() {
var uploadResult = document.getElementById("upload-result");
uploadResult.style.color = "green";
uploadResult.innerHTML = "正在上传.....";
var formData = new FormData($("uploadForm")[0]);
formData.append('Content-Type','multipart/form-data');
formData.append('image',$('input[type=file]')[0].files[0]);
$.ajax({
url : "${pageContext.request.contextpath}/api/v1/file",type : 'POST',data : formData,dataType : 'json',contentType : false,processData : false,cache : false,//防止缓存
error : function(data) {
alert("请求失败,网络异常")
console.log(data);
},success : function(data) {
console.log(data);
var code = data.status;
if (code == 200) {
uploadResult.style.color = "green";
uploadResult.innerHTML = "上传成功";
imgurl = data.data;
} else {
uploadResult.style.color = "red";
uploadResult.innerHTML = "上传失败";
}
}
});
}
SpringMVC服务器端写法:
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public Object uploadFile(HttpServletRequest request) {
CommonsMultipartResolver multipartResolver = new CommonsMultipartResolver(
request.getSession().getServletContext());
// 先判断request中是否包涵multipart类型的数据,
String fileUrl = "";
if (multipartResolver.isMultipart(request)) {
// 再将request中的数据转化成multipart类型的数据
MultipartHttpServletRequest multiRequest = (MultipartHttpServletRequest) request;
Iterator<String> iter = multiRequest.getFileNames();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
multipartfile file = multiRequest.getFile((String) iter.next());
if (file != null) {
try {
GridFSInputFile inputFile = fileService.save(file.getInputStream(),file.getoriginalFilename());
if (inputFile == null) {
return StatusConfig.FileUploadError;
} else {
fileUrl = inputFile.getId().toString();
System.out.println("fileUrll" + (fileUrl));
}
} catch (IllegalStateException | IOException e) {
return StatusConfig.FileUploadError;
}
}
}
HashMap<String,Object> hashMap = new HashMap<String,Object>();
fileUrl = this.getHttpFilePath() + fileUrl;
hashMap.put(ConstantsKey.STATUS,200);
hashMap.put(ConstantsKey.DATA,fileUrl);
String json = ConvertUtils.as().toJson(hashMap);
System.out.println("photourl:" + json);
return json;
} else {
return StatusConfig.RequestTypeError;
}
}
jQuery File Upload 结合 Spring MVC 批量上传文件,如何获取当前上传文件索引?
jQuery File Upload 结合 Spring MVC 批量上传文件,怎么获取当前上传文件索引?求大神!!!
jQuery File Upload 上传是一个文件上传完后继续另外一个文件上传,往后台发送多次请求,想知道通过后台方式怎么得知是第几个文件的发送。

Spring MVC 上传文件 --- 依赖引用
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.0.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.0.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>2.5</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>jsp-api</artifactId>
<version>2.0</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
<version>5.0.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-fileupload</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-fileupload</artifactId>
<version>1.3.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-io</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-io</artifactId>
<version>2.4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.11</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
spring mvc 上传文件三种方式
直接上代码吧,大伙一看便知
这时:commonsmultipartresolver 的源码,可以研究一下 http://www.verysource.com/code/2337329_1/commonsmultipartresolver.java.html
前台:
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 |
|
配置:
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 |
|
后台:
方式一:
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 |
|
方式二:
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
|
方式三:
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 |
|
我们看看测试上传的时间:
第一次我用一个4M的文件:
fileName:test.rar
方法一的运行时间:14712ms
fileName:test.rar
方法二的运行时间:5ms
方法三的运行时间:4ms
第二次:我用一个50M的文件
方式一进度很慢,估计得要个5分钟
方法二的运行时间:67ms
方法三的运行时间:80ms
从测试结果我们可以看到:用springMVC自带的上传文件的方法要快的多!
对于测试二的结果:可能是方法三得挨个搜索,所以要慢点。不过一般情况下我们是方法三,因为他能提供给我们更多的方法
关于Spring MVC -- 上传文件和springmvc上传文件大小限制的介绍已经告一段落,感谢您的耐心阅读,如果想了解更多关于Ajax SpringMVC 上传文件、jQuery File Upload 结合 Spring MVC 批量上传文件,如何获取当前上传文件索引?、Spring MVC 上传文件 --- 依赖引用、spring mvc 上传文件三种方式的相关信息,请在本站寻找。
本文标签:



![[转帖]Ubuntu 安装 Wine方法(ubuntu如何安装wine)](https://www.gvkun.com/zb_users/cache/thumbs/4c83df0e2303284d68480d1b1378581d-180-120-1.jpg)

