关于Pythonnumpy模块-str_()实例源码和python中numpy模块的问题就给大家分享到这里,感谢你花时间阅读本站内容,更多关于+不支持的操作数类型:“float”和“numpy.str
关于Python numpy 模块-str_() 实例源码和python中numpy模块的问题就给大家分享到这里,感谢你花时间阅读本站内容,更多关于+ 不支持的操作数类型:“float”和“numpy.str_”、Jupyter 中的 Numpy 在打印时出错(Python 版本 3.8.8):TypeError: 'numpy.ndarray' object is not callable、numpy.random.random & numpy.ndarray.astype & numpy.arange、numpy.ravel()/numpy.flatten()/numpy.squeeze()等相关知识的信息别忘了在本站进行查找喔。
本文目录一览:- Python numpy 模块-str_() 实例源码(python中numpy模块)
- + 不支持的操作数类型:“float”和“numpy.str_”
- Jupyter 中的 Numpy 在打印时出错(Python 版本 3.8.8):TypeError: 'numpy.ndarray' object is not callable
- numpy.random.random & numpy.ndarray.astype & numpy.arange
- numpy.ravel()/numpy.flatten()/numpy.squeeze()

Python numpy 模块-str_() 实例源码(python中numpy模块)
Python numpy 模块,str_() 实例源码
我们从Python开源项目中,提取了以下45个代码示例,用于说明如何使用numpy.str_()。
- def test_scalar_none_comparison(self):
- # Scalars should still just return False and not give a warnings.
- # The comparisons are flagged by pep8,ignore that.
- with warnings.catch_warnings(record=True) as w:
- warnings.filterwarnings(''always'', '''', FutureWarning)
- assert_(not np.float32(1) == None)
- assert_(not np.str_(''test'') == None)
- # This is dubIoUs (see below):
- assert_(not np.datetime64(''NaT'') == None)
- assert_(np.float32(1) != None)
- assert_(np.str_(''test'') != None)
- # This is dubIoUs (see below):
- assert_(np.datetime64(''NaT'') != None)
- assert_(len(w) == 0)
- # For documentation purposes,this is why the datetime is dubIoUs.
- # At the time of deprecation this was no behavIoUr change,but
- # it has to be considered when the deprecations are done.
- assert_(np.equal(np.datetime64(''NaT''), None))
- def test_scalar_none_comparison(self):
- # Scalars should still just return False and not give a warnings.
- # The comparisons are flagged by pep8, None))
- def test_stratified_batches():
- data = np.array([(''a'', -1), (''b'', 0), (''c'', 1), (''d'', (''e'', -1)],
- dtype=[(''x'', np.str_, 8), (''y'', np.int32)])
- assert list(data[''x'']) == [''a'', ''b'', ''c'', ''d'', ''e'']
- assert list(data[''y'']) == [-1, 0, 1, -1, -1]
- batch_generator = training_batches(data, batch_size=3, n_labeled_per_batch=1)
- first_ten_batches = list(islice(batch_generator, 10))
- labeled_batch_portions = [batch[:1] for batch in first_ten_batches]
- unlabeled_batch_portions = [batch[1:] for batch in first_ten_batches]
- labeled_epochs = np.split(np.concatenate(labeled_batch_portions), 5)
- unlabeled_epochs = np.split(np.concatenate(unlabeled_batch_portions), 4)
- assert ([sorted(items[''x''].tolist()) for items in labeled_epochs] ==
- [[''b'', ''c'']] * 5)
- assert ([sorted(items[''y''].tolist()) for items in labeled_epochs] ==
- [[0, 1]] * 5)
- assert ([sorted(items[''x''].tolist()) for items in unlabeled_epochs] ==
- [[''a'', ''e'']] * 4)
- assert ([sorted(items[''y''].tolist()) for items in unlabeled_epochs] ==
- [[-1, -1]] * 4)
- def discrete(self, x, bin=5):
- #res = np.array([0] * x.shape[-1],dtype=int)
- #?????????????????????woe?????????????<=?woe??
- x_copy = pd.Series.copy(x)
- x_copy = x_copy.astype(str)
- #x_copy = x_copy.astype(np.str_)
- #x_copy = x
- x_gt0 = x[x>=0]
- #if x.name == ''TD_pltF_CNT_1M'':
- #bin = 5
- #x_gt0 = x[(x>=0) & (x<=24)]
- for i in range(bin):
- point1 = stats.scoreatpercentile(x_gt0, i * (100.0/bin))
- point2 = stats.scoreatpercentile(x_gt0, (i + 1) * (100.0/bin))
- x1 = x[(x >= point1) & (x <= point2)]
- mask = np.in1d(x, x1)
- #x_copy[mask] = i + 1
- x_copy[mask] = ''%s-%s'' % (point1,point2)
- #x_copy[mask] = point1
- #print x_copy[mask]
- #print x
- #print x
- return x_copy
- def grade(self,dtype=int)
- #?????????????????????woe?????????????<=?woe??
- x_copy = np.copy(x)
- #x_copy = x_copy.astype(str)
- #x_copy = x_copy.astype(np.str_)
- #x_copy = x
- x_gt0 = x[x>=0]
- for i in range(bin):
- point1 = stats.scoreatpercentile(x_gt0, x1)
- #x_copy[mask] = i + 1
- x_copy[mask] = i + 1
- #x_copy[mask] = point1
- #print x_copy[mask]
- #print x
- print point1,point2
- #print x
- return x_copy
- def test_scalar_none_comparison(self):
- # Scalars should still just return false and not give a warnings.
- # The comparisons are flagged by pep8, FutureWarning)
- assert_(not np.float32(1) == None)
- assert_(not np.str_(''test'') == None)
- # This is dubIoUs (see below):
- assert_(not np.datetime64(''NaT'') == None)
- assert_(np.float32(1) != None)
- assert_(np.str_(''test'') != None)
- # This is dubIoUs (see below):
- assert_(np.datetime64(''NaT'') != None)
- assert_(len(w) == 0)
- # For documentaiton purpose,but
- # it has to be considered when the deprecations is done.
- assert_(np.equal(np.datetime64(''NaT''), None))
- def test_scalar_none_comparison(self):
- # Scalars should still just return false and not give a warnings.
- # The comparisons are flagged by pep8, None))
- def test_scalar_none_comparison(self):
- # Scalars should still just return False and not give a warnings.
- # The comparisons are flagged by pep8, None))
- def test_scalar_none_comparison(self):
- # Scalars should still just return False and not give a warnings.
- # The comparisons are flagged by pep8, None))
- def normalize_attr_strings(a: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
- """
- Take an np.ndarray of all kinds of string-like elements,and return an array of ascii (np.string_) objects
- """
- if np.issubdtype(a.dtype, np.object_):
- if np.all([type(x) is str for x in a]) or np.all([type(x) is np.str_ for x in a]) or np.all([type(x) is np.unicode_ for x in a]):
- return np.array([x.encode(''ascii'', ''xmlcharrefreplace'') for x in a])
- elif np.all([type(x) is np.string_ for x in a]) or np.all([type(x) is np.bytes_ for x in a]):
- return a.astype("string_")
- else:
- print(type(a[0]))
- raise ValueError("Arbitrary numpy object arrays not supported (all elements must be string objects).")
- elif np.issubdtype(a.dtype, np.string_) or np.issubdtype(a.dtype, np.object_):
- return a
- elif np.issubdtype(a.dtype, np.str_) or np.issubdtype(a.dtype, np.unicode_):
- return np.array([x.encode(''ascii'', ''xmlcharrefreplace'') for x in a])
- else:
- raise ValueError("String values must be object,ascii or unicode.")
- def materialize_attr_values(a: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
- scalar = False
- if np.isscalar(a):
- scalar = True
- a = np.array([a])
- result: np.ndarray = None
- if np.issubdtype(a.dtype, np.string_):
- # First ensure that what we load is valid ascii (i.e. ignore anything outside 7-bit range)
- temp = np.array([x.decode(''ascii'', ''ignore'') for x in a])
- # Then unescape XML entities and convert to unicode
- result = np.array([html.unescape(x) for x in temp.astype(str)], dtype=np.str_)
- elif np.issubdtype(a.dtype, np.unicode_):
- result = np.array(a.astype(str), dtype=np.str_)
- else:
- result = a
- if scalar:
- return result[0]
- else:
- return result
- def npy2py_type(npy_type):
- int_types = [
- np.int_, np.intc, np.intp, np.int8, np.int16, np.int32, np.int64,
- np.uint8, np.uint16, np.uint32, np.uint64
- ]
- float_types = [np.float_, np.float16, np.float32, np.float64]
- bytes_types = [np.str_, np.string_]
- if npy_type in int_types:
- return int
- if npy_type in float_types:
- return float
- if npy_type in bytes_types:
- return bytes
- if hasattr(npy_type, ''char''):
- if npy_type.char in [''S'', ''a'']:
- return bytes
- raise TypeError
- return npy_type
- def test_scalar_none_comparison(self):
- # Scalars should still just return False and not give a warnings.
- # The comparisons are flagged by pep8, None))
- def initialize(self):
- """Initialize FixPandasDataFrame"""
- self.check_arg_types(read_key=str, store_key=str)
- self.check_arg_types(recurse=True, allow_none=True, original_columns=str)
- self.check_arg_vals(''read_key'')
- if not isinstance(self.cleanup_string_columns, list) and not isinstance(self.cleanup_string_columns, bool):
- raise AssertionError(''cleanup_string_columns should be a list of column names or boolean.'')
- if self.read_key == self.store_key:
- self.inplace = True
- self.log().debug(''store_key equals read_key; inplace has been set to "True"'')
- if self.inplace:
- self.store_key = self.read_key
- self.log().debug(''store_key has been set to read_key "%s"'', self.store_key)
- if not self.store_key:
- self.store_key = self.read_key + ''_fix''
- self.log().debug(''store_key has been set to "%s"'', self.store_key)
- # check data types
- for k in self.var_dtype.keys():
- if k not in self.contaminated_columns:
- self.contaminated_columns.append(k)
- try:
- # convert to consistent types
- dt = np.dtype(self.var_dtype[k]).type
- if dt is np.str_ or dt is np.object_:
- dt = str
- self.var_dtype[k] = dt
- except BaseException:
- raise TypeError(''unkNown assigned datatype to variable "%s"'' % k)
- return StatusCode.Success
- def test_object_array_to_fixed_string(self):
- # Ticket #1235.
- a = np.array([''abcdefgh'', ''ijklmnop''], dtype=np.object_)
- b = np.array(a, dtype=(np.str_, 8))
- assert_equal(a, b)
- c = np.array(a, 5))
- assert_equal(c, np.array([''abcde'', ''ijklm'']))
- d = np.array(a, 12))
- assert_equal(a, d)
- e = np.empty((2, ), 8))
- e[:] = a[:]
- assert_equal(a, e)
- def test_string(self):
- lr = LogisticRegression()
- for col in [''features'', u''features'', np.str_(''features'')]:
- lr.setFeaturesCol(col)
- self.assertEqual(lr.getFeaturesCol(), ''features'')
- self.assertRaises(TypeError, lambda: LogisticRegression(featuresCol=2.3))
- def _can_convert_to_string(value):
- vtype = type(value)
- return isinstance(value, basestring) or vtype in [np.unicode_, np.string_, np.str_]
- def toString(value):
- """
- Convert a value to a string,if possible.
- """
- if isinstance(value, basestring):
- return value
- elif type(value) in [np.string_, np.str_]:
- return str(value)
- elif type(value) == np.unicode_:
- return unicode(value)
- else:
- raise TypeError("Could not convert %s to string type" % type(value))
- def symbols_to_numbers(symbols):
- """Given element symbol(s),return the atomic number(s) (number of protons).
- Args:
- symbols (str or list of str): Atomic symbol(s).
- Returns:
- ndarray: Atomic number(s) (number of protons).
- Raises:
- ValueError: If a given atomic symbol is invalid and doesn''t have a
- corresponding number.
- """
- single_value = False
- if isinstance(symbols, (str, np.str_)):
- symbols = [symbols]
- single_value = True
- numbers = []
- for symbol in symbols:
- number = SYMBOL_TO_NUMBER_MAP.get(symbol)
- if number is None:
- raise ValueError(
- "Given atomic symbol {} is invalid and doesn''t have a number "
- "associated with it.".format(symbol)
- )
- numbers.append(number)
- return numbers[0] if single_value else np.array(numbers)
- def init_list(self):
- if self.fname is '''' or not os.path.isfile(self.fname):
- sys.stderr.write(''Initializing empty class list\\n'')
- self.clist = np.zeros((self.num_frames,), dtype=np.str_)
- else:
- self.clist = self.load()
- self.key, self.key_pos, self.key_counts = np.unique(self.clist, return_inverse=True, return_counts=True)
- def main():
- net = caffe.Net(MODEL_DEF, MODEL_WEIGHT, caffe.TRAIN)
- mat = []
- for i in range(len(net.layers)):
- mat_type = net.layers[i].type
- mat_data = []
- for j in range(len(net.layers[i].blobs)):
- mat_data.append(net.layers[i].blobs[j].data)
- mat.append((mat_type, mat_data))
- dt = np.dtype([(''type'', 16), (''data'', np.ndarray)])
- results = np.array(mat, dtype=dt)
- results.dump(MAT_RESULT)
- def test_object_array_to_fixed_string(self):
- # Ticket #1235.
- a = np.array([''abcdefgh'', e)
- def encode_ascii(s):
- if isinstance(s, str):
- return s.encode(''ascii'')
- elif isinstance(s, numpy.ndarray) and \\
- issubclass(s.dtype.type, numpy.str_):
- ns = numpy.char.encode(s, ''ascii'').view(type(s))
- if ns.dtype.itemsize != s.dtype.itemsize / 4:
- ns = ns.astype((numpy.bytes_, s.dtype.itemsize / 4))
- return ns
- return s
- def decode_ascii(s):
- if isinstance(s, bytes):
- return s.decode(''ascii'')
- elif (isinstance(s, numpy.ndarray) and
- issubclass(s.dtype.type, numpy.bytes_)):
- # np.char.encode/decode annoyingly don''t preserve the type of the
- # array,hence the view() call
- # It also doesn''t necessarily preserve widths of the strings,
- # hence the astype()
- ns = numpy.char.decode(s, ''ascii'').view(type(s))
- if ns.dtype.itemsize / 4 != s.dtype.itemsize:
- ns = ns.astype((numpy.str_, s.dtype.itemsize))
- return ns
- return s
- def regroup(df,column,split_points):
- for i in range(len(split_points)-1):
- df[column][(df[column]>=split_points[i]) & (df[column]<=split_points[i+1])] = ''%s-%s'' % (split_points[i],split_points[i+1])
- df[column] = df[column].astype(np.str_)
- def test_astype_str(self):
- # GH4405
- digits = string.digits
- s1 = Series([digits * 10, tm.rands(63), tm.rands(64), tm.rands(1000)])
- s2 = Series([digits * 10, nan, 1.0])
- types = (compat.text_type, np.str_)
- for typ in types:
- for s in (s1, s2):
- res = s.astype(typ)
- expec = s.map(compat.text_type)
- assert_series_equal(res, expec)
- # GH9757
- # Test str and unicode on python 2.x and just str on python 3.x
- for tt in set([str, compat.text_type]):
- ts = Series([Timestamp(''2010-01-04 00:00:00'')])
- s = ts.astype(tt)
- expected = Series([tt(''2010-01-04'')])
- assert_series_equal(s, expected)
- ts = Series([Timestamp(''2010-01-04 00:00:00'', tz=''US/Eastern'')])
- s = ts.astype(tt)
- expected = Series([tt(''2010-01-04 00:00:00-05:00'')])
- assert_series_equal(s, expected)
- td = Series([timedelta(1, unit=''d'')])
- s = td.astype(tt)
- expected = Series([tt(''1 days 00:00:00.000000000'')])
- assert_series_equal(s, expected)
- def test_constructor_empty_with_string_dtype(self):
- # GH 9428
- expected = DataFrame(index=[0, 1], columns=[0, dtype=object)
- df = DataFrame(index=[0, dtype=str)
- assert_frame_equal(df, expected)
- df = DataFrame(index=[0, dtype=np.str_)
- assert_frame_equal(df, dtype=np.unicode_)
- assert_frame_equal(df, dtype=''U5'')
- assert_frame_equal(df, expected)
- def test_numpy_informed(self):
- # np.dtype doesn''t kNow about our new dtype
- def f():
- np.dtype(self.dtype)
- self.assertRaises(TypeError, f)
- self.assertNotEqual(self.dtype, np.str_)
- self.assertNotEqual(np.str_, self.dtype)
- def test_isscalar_numpy_array_scalars(self):
- self.assertTrue(lib.isscalar(np.int64(1)))
- self.assertTrue(lib.isscalar(np.float64(1.)))
- self.assertTrue(lib.isscalar(np.int32(1)))
- self.assertTrue(lib.isscalar(np.object_(''foobar'')))
- self.assertTrue(lib.isscalar(np.str_(''foobar'')))
- self.assertTrue(lib.isscalar(np.unicode_(u(''foobar''))))
- self.assertTrue(lib.isscalar(np.bytes_(b''foobar'')))
- self.assertTrue(lib.isscalar(np.datetime64(''2014-01-01'')))
- self.assertTrue(lib.isscalar(np.timedelta64(1, ''h'')))
- def test_object_array_to_fixed_string(self):
- # Ticket #1235.
- a = np.array([''abcdefgh'', e)
- def test_object_array_to_fixed_string(self):
- # Ticket #1235.
- a = np.array([''abcdefgh'', e)
- def set_format(self, data, digits, scientific):
- """data: object with a dtype attribute"""
- type = data.dtype.type
- if type in (np.str, np.bool_, np.bool, np.object_):
- fmt = ''%s''
- else:
- # XXX: use self.digits_spinBox.getValue() and instead?
- # XXX: use self.digits_spinBox.getValue() instead?
- format_letter = ''e'' if scientific else ''f''
- fmt = ''%%.%d%s'' % (digits, format_letter)
- # this does not call model_data.reset() so it should be called by the caller
- self.model_data._set_format(fmt)
- def to_excel(self):
- """View selection in Excel"""
- if xw is None:
- QMessageBox.critical(self, "Error", "to_excel() is not available because xlwings is not installed")
- data = self._selection_data()
- if data is None:
- return
- # convert (row) generators to lists then array
- # Todo: the conversion to array is currently necessary even though xlwings will translate it back to a list
- # anyway. The problem is that our lists contains numpy types and especially np.str_ crashes xlwings.
- # unsure how we should fix this properly: in xlwings,or change _selection_data to return only standard
- # Python types.
- xw.view(np.array([list(r) for r in data]))
- def test_object_array_to_fixed_string(self):
- # Ticket #1235.
- a = np.array([''abcdefgh'', e)
- def get_data(lst,preproc):
- data = []
- result = []
- for path in lst:
- f = dicom.read_file(path)
- img = preproc(f.pixel_array.astype(float) / np.max(f.pixel_array))
- dst_path = path.rsplit(".", 1)[0] + ".64x64.jpg"
- scipy.misc.imsave(dst_path, img)
- result.append(dst_path)
- data.append(img)
- data = np.array(data, dtype=np.uint8)
- data = data.reshape(data.size)
- data = np.array(data,dtype=np.str_)
- data = data.reshape(data.size)
- return [data,result]
- def test_object_array_to_fixed_string(self):
- # Ticket #1235.
- a = np.array([''abcdefgh'', e)
- def test_structure_format(self):
- dt = np.dtype([(''name'', (''grades'', np.float64, (2,))])
- x = np.array([(''Sarah'', (8.0, 7.0)), (''John'', (6.0, 7.0))], dtype=dt)
- assert_equal(np.array2string(x),
- "[(''Sarah'',[ 8.,7.]) (''John'',[ 6.,7.])]")
- # for issue #5692
- A = np.zeros(shape=10, dtype=[("A", "M8[s]")])
- A[5:].fill(np.nan)
- assert_equal(np.array2string(A),
- "[(''1970-01-01T00:00:00'',) (''1970-01-01T00:00:00'',) " +
- "(''1970-01-01T00:00:00'',)\\n (''1970-01-01T00:00:00'',) (''NaT'',)\\n " +
- "(''NaT'',)]")
- # See #8160
- struct_int = np.array([([1, -1], ([123,)], dtype=[(''B'', ''i4'', 2)])
- assert_equal(np.array2string(struct_int),
- "[([ 1,-1],) ([123,1],)]")
- struct_2dint = np.array([([[0, [2, 3]], ([[12, 0], [0, 0]],
- dtype=[(''B'', 2))])
- assert_equal(np.array2string(struct_2dint),
- "[([[ 0,[ 2,3]],) ([[12,0],[ 0,0]],)]")
- # See #8172
- array_scalar = np.array(
- (1., 2.1234567890123456789, 3.), dtype=(''f8,f8,f8''))
- assert_equal(np.array2string(array_scalar), "( 1.,2.12345679,3.)")
- def store_data(self, store_loc, **kwargs):
- """Put arrays to store
- """
- #print(store_loc)
- g = self.store.create_group(store_loc)
- for k, v, in kwargs.items():
- #print(type(v[0]))
- #print(k)
- if type(v) == list:
- if len(v) != 0:
- if type(v[0]) is np.str_ or type(v[0]) is str:
- v = [a.encode(''utf8'') for a in v]
- g.create_dataset(k, data=v, compression=self.clib, compression_opts=self.clev)
- def test_object_array_to_fixed_string(self):
- # Ticket #1235.
- a = np.array([''abcdefgh'', e)
- def get_datinfo(cutoutid,setupdic):
- """
- Function returning information on file names etc. for both default run and cutout run
- --- INPUT ---
- cutoutid ID to return information for
- setupdic Dictionary containing the setup parameters read from the TDOSE setup file
- """
- if cutoutid == -9999:
- cutstr = None
- imgsize = setupdic[''cutout_sizes'']
- refimg = setupdic[''ref_image'']
- datacube = setupdic[''data_cube'']
- variancecube = setupdic[''noise_cube'']
- sourcecat = setupdic[''source_catalog'']
- else:
- if type(setupdic[''cutout_sizes'']) == np.str_:
- sizeinfo = np.genfromtxt(setupdic[''cutout_sizes''],dtype=None,comments=''#'')
- objent = np.where(sizeinfo[:,0] == cutoutid)[0]
- if len(objent) > 1:
- sys.exit('' ---> More than one match in ''+setupdic[''cutout_sizes'']+'' for object ''+str(cutoutid))
- elif len(objent) == 0:
- sys.exit('' ---> No match in ''+setupdic[''cutout_sizes'']+'' for object ''+str(cutoutid))
- else:
- imgsize = sizeinfo[objent,1:][0].astype(float).tolist()
- else:
- imgsize = setupdic[''cutout_sizes'']
- cutstr = (''_id''+str(int(cutoutid))+''_cutout''+str(imgsize[0])+''x''+str(imgsize[1])+''arcsec'').replace(''.'',''p'')
- img_init_base = setupdic[''ref_image''].split(''/'')[-1]
- cube_init_base = setupdic[''data_cube''].split(''/'')[-1]
- var_init_base = setupdic[''variance_cube''].split(''/'')[-1]
- cut_img = setupdic[''cutout_directory'']+img_init_base.replace(''.fits'',cutstr+''.fits'')
- cut_cube = setupdic[''cutout_directory'']+cube_init_base.replace(''.fits'',cutstr+''.fits'')
- cut_variance = setupdic[''cutout_directory'']+var_init_base.replace(''.fits'',cutstr+''.fits'')
- cut_sourcecat = setupdic[''source_catalog''].replace(''.fits'',cutstr+''.fits'')
- if setupdic[''wht_image''] is None:
- refimg = cut_img
- else:
- wht_init_base = setupdic[''wht_image''].split(''/'')[-1]
- wht_img = setupdic[''cutout_directory'']+wht_init_base.replace(''.fits'',cutstr+''.fits'')
- refimg = [cut_img,wht_img]
- datacube = cut_cube
- variancecube = cut_variance
- sourcecat = cut_sourcecat
- return cutstr, imgsize, refimg, datacube, variancecube, sourcecat
- # = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = =
- def _infer_dtype_from_scalar(val):
- """ interpret the dtype from a scalar """
- dtype = np.object_
- # a 1-element ndarray
- if isinstance(val, np.ndarray):
- if val.ndim != 0:
- raise ValueError(
- "invalid ndarray passed to _infer_dtype_from_scalar")
- dtype = val.dtype
- val = val.item()
- elif isinstance(val, compat.string_types):
- # If we create an empty array using a string to infer
- # the dtype,NumPy will only allocate one character per entry
- # so this is kind of bad. Alternately we Could use np.repeat
- # instead of np.empty (but then you still don''t want things
- # coming out as np.str_!
- dtype = np.object_
- elif isinstance(val, (np.datetime64,
- datetime)) and getattr(val, ''tzinfo'', None) is None:
- val = lib.Timestamp(val).value
- dtype = np.dtype(''M8[ns]'')
- elif isinstance(val, (np.timedelta64, timedelta)):
- val = tslib.convert_to_timedelta(val, ''ns'')
- dtype = np.dtype(''m8[ns]'')
- elif is_bool(val):
- dtype = np.bool_
- elif is_integer(val):
- if isinstance(val, np.integer):
- dtype = type(val)
- else:
- dtype = np.int64
- elif is_float(val):
- if isinstance(val, np.floating):
- dtype = type(val)
- else:
- dtype = np.float64
- elif is_complex(val):
- dtype = np.complex_
- return dtype, val
- def make_dataset(dir, train=True):
- paths = None
- poses = None
- # ??? ? ??? ?
- for target in os.listdir(dir):
- target_dir = os.path.join(dir, target)
- # if not os.path.isdir(target_dir) or target == "Street" or target == "GreatCourt":
- # if not os.path.isdir(target_dir):
- if not target == "KingsCollege":
- continue
- # ?? ??? ?? ??? ?? ???? ??? ? ?
- if train:
- path = np.genfromtxt(os.path.join(target_dir, ''dataset_train.txt''),
- dtype=np.str_, delimiter='' '', skip_header=3,
- usecols=[0])
- pose = np.genfromtxt(os.path.join(target_dir,
- dtype=np.float32,
- usecols=[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7])
- else:
- path = np.genfromtxt(os.path.join(target_dir, ''dataset_test.txt''), 7])
- # order ? path ? ????? ???
- order = path.argsort()
- # order ? sorting
- path1 = path[order]
- pose1 = pose[order]
- # reverse order ?? sorting
- path2 = path[order[-2::-1]]
- pose2 = pose[order[-2::-1]]
- # concat
- path = np.hstack((path1, path2))
- pose = np.vstack((pose1, pose2))
- path = np.core.defchararray.add(target + ''/'', path)
- if paths is None:
- paths = path
- poses = pose
- else:
- paths = np.hstack((paths, path))
- poses = np.vstack((poses, pose))
- return paths, poses
- def data(self, index, role=Qt.displayRole):
- """Cell content"""
- if not index.isValid():
- return to_qvariant()
- # if role == Qt.decorationRole:
- # return ima.icon(''editcopy'')
- # if role == Qt.displayRole:
- # return ""
- if role == Qt.TextAlignmentRole:
- return to_qvariant(int(Qt.AlignRight | Qt.AlignVCenter))
- elif role == Qt.FontRole:
- return self.font
- value = self.get_value(index)
- if role == Qt.displayRole:
- if value is np.ma.masked:
- return ''''
- # for headers
- elif isinstance(value, str) and not isinstance(value, np.str_):
- return value
- else:
- return to_qvariant(self._format % value)
- elif role == Qt.BackgroundColorRole:
- if self.bgcolor_possible and self.bg_gradient is not None and value is not np.ma.masked:
- if self.bg_value is None:
- try:
- v = self.color_func(value) if self.color_func is not None else value
- if -np.inf < v < self.vmin:
- # Todo: this is suboptimal,as it can reset many times (though in practice,it is usually
- # ok). When we get buffering,we will need to compute vmin/vmax on the whole buffer
- # at once,eliminating this problem (and we Could even compute final colors directly
- # all at once)
- self.vmin = v
- self.reset()
- elif self.vmax < v < np.inf:
- self.vmax = v
- self.reset()
- v = scale_to_01range(v, self.vmin, self.vmax)
- except TypeError:
- v = np.nan
- else:
- i, j = index.row(), index.column()
- v = self.bg_value[i, j]
- return self.bg_gradient[v]
- # elif role == Qt.ToolTipRole:
- # return to_qvariant("{}\\n{}".format(repr(value),self.get_labels(index)))
- return to_qvariant()
- def main():
- parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
- parser.add_argument(''file'')
- args = parser.parse_args()
- print("Using file %s" % args.file)
- if not os.path.isfile(args.file):
- raise FileNotFoundError("Couldn''t find file at ''%s''" % args.file)
- if args.file.split(''.'')[-1] != ''mat'':
- raise ValueError("File ''%s'' not a valid mat file" % args.file)
- file = args.file
- name = file.split(''.'')[0]
- outfile = ''.''.join([name, ''csv''])
- data = sio.loadmat(file)
- keys = [''classification_id'', ''user_name'',''user_id'',\\
- ''annotation'',''gold_label'',''machine_score'', \\
- ''diff'',''object_id'',''subject_id'',''mag'',''mag_err'']
- count = 0
- with open(outfile, ''w'') as csvfile:
- writer = csv.DictWriter(csvfile, fieldnames=keys)
- writer.writeheader()
- for index in range(len(data[''classification_id''][0])):
- d = {}
- for key in keys:
- #print(key,data[key],type(data[key][0]))
- if type(data[key][0]) is numpy.str_:
- d[key] = data[key][index].strip()
- else:
- d[key] = data[key][0][index]
- writer.writerow(d)
- sys.stdout.write("%d records processed\\r" % count)
- sys.stdout.flush()
- count += 1
- def get_wqp_results(self, service, **kwargs):
- """Bring data from WQP site into a Pandas DataFrame for analysis"""
- # set data types
- Rdtypes = {"OrganizationIdentifier": np.str_, "OrganizationFormalName": np.str_, "ActivityIdentifier": np.str_,
- "ActivityStartTime/Time": np.str_,
- "ActivityTypeCode": np.str_, "ActivityMediaName": np.str_, "ActivityMediaSubdivisionName": np.str_,
- "ActivityStartDate": np.str_, "ActivityStartTime/TimeZoneCode": np.str_,
- "ActivityEndDate": np.str_, "ActivityEndTime/Time": np.str_, "ActivityEndTime/TimeZoneCode": np.str_,
- "ActivityDepthHeightMeasure/MeasureValue": np.float16,
- "ActivityDepthHeightMeasure/MeasureUnitCode": np.str_,
- "ActivityDepthAltitudeReferencePointText": np.str_,
- "ActivityTopDepthHeightMeasure/MeasureValue": np.float16,
- "ActivityTopDepthHeightMeasure/MeasureUnitCode": np.str_,
- "ActivityBottomDepthHeightMeasure/MeasureValue": np.float16,
- "ActivityBottomDepthHeightMeasure/MeasureUnitCode": np.str_,
- "ProjectIdentifier": np.str_, "ActivityConductingOrganizationText": np.str_,
- "MonitoringLocationIdentifier": np.str_, "ActivityCommentText": np.str_,
- "SampleAquifer": np.str_, "HydrologicCondition": np.str_, "HydrologicEvent": np.str_,
- "SampleCollectionMethod/MethodIdentifier": np.str_,
- "SampleCollectionMethod/MethodIdentifierContext": np.str_,
- "SampleCollectionMethod/MethodName": np.str_, "SampleCollectionEquipmentName": np.str_,
- "ResultDetectionConditionText": np.str_, "CharacteristicName": np.str_,
- "ResultSampleFractionText": np.str_,
- "ResultMeasureValue": np.str_, "ResultMeasure/MeasureUnitCode": np.str_,
- "MeasureQualifierCode": np.str_,
- "ResultStatusIdentifier": np.str_, "StatisticalBaseCode": np.str_, "ResultValueTypeName": np.str_,
- "ResultWeightBasisText": np.str_, "ResultTimeBasisText": np.str_,
- "ResultTemperatureBasisText": np.str_,
- "ResultParticleSizeBasisText": np.str_, "PrecisionValue": np.str_, "ResultCommentText": np.str_,
- "USGSPCode": np.str_, "ResultDepthHeightMeasure/MeasureValue": np.float16,
- "ResultDepthHeightMeasure/MeasureUnitCode": np.str_,
- "ResultDepthAltitudeReferencePointText": np.str_,
- "SubjectTaxonomicName": np.str_, "SampleTissueAnatomyName": np.str_,
- "ResultAnalyticalMethod/MethodIdentifier": np.str_,
- "ResultAnalyticalMethod/MethodIdentifierContext": np.str_,
- "ResultAnalyticalMethod/MethodName": np.str_, "MethodDescriptionText": np.str_,
- "LaboratoryName": np.str_,
- "AnalysisstartDate": np.str_, "ResultLaboratoryCommentText": np.str_,
- "DetectionQuantitationLimitTypeName": np.str_,
- "DetectionQuantitationLimitMeasure/MeasureValue": np.str_,
- "DetectionQuantitationLimitMeasure/MeasureUnitCode": np.str_, "PreparationStartDate": np.str_,
- "ProviderName": np.str_}
- # define date field indices
- dt = [6, 56, 61]
- csv = self.get_response(service, **kwargs).url
- print(csv)
- # read csv into DataFrame
- df = pd.read_csv(csv, dtype=Rdtypes, parse_dates=dt)
- return df

+ 不支持的操作数类型:“float”和“numpy.str_”
如何解决+ 不支持的操作数类型:“float”和“numpy.str_”
我有以下 2 个列表。
[''4794447'',''1132804'',''1392609'',''9512999'',''2041520'',''7233323'',''2853077'',''4297617'',''1321426'',''2155664'',''13310447'',''6066387'',''3551036'',''4098927'',''1865298'',''20153634'',''1323783'',''6070500'',''4661537'',''2342299'',''1302946'',''6657982'',''2807002'',''3032171'',''5928040'',''2463431'',''6131977'',''778489''][0.7142857142857143,0.35714285714285715,0.5138888888888888,0.4583333333333333,0.6,0.5675675675675675,0.589041095890411,0.43478260869565216,0.47368421052631576,0.68,0.622894633764199,0.5945945945945946,0.6338028169014085,0.42028985507246375,0.7464788732394366,0.47593226788432264,0.39436619718309857,0.6176470588235294,0.4142857142857143,0.618421052631579,0.5070422535211268,0.625,0.5789473684210527,0.7012987012987013,0.6533333333333333,0.43661971830985913,0.7222222222222222]
我需要计算相关性,所以我这样做了:
population_by_region = result[''Population''].tolist()win_loss_by_region = result[''wl_ratio''].tolist()corr,val = stats.pearsonr(population_by_region,win_loss_by_region)
但是我得到这个不是很清楚的错误:
---------------------------------------------------------------------------TypeError Traceback (most recent call last)<ipython-input-28-37cd29ba1516> in <module>66 print(win_loss_by_region)67 #print(cities)---> 68 corr,win_loss_by_region)6970 print(corr)/opt/conda/lib/python3.7/site-packages/scipy/stats/stats.py in pearsonr(x,y)3403 # that the data type is at least 64 bit floating point. It might have3404 # more precision if the input is,for example,np.longdouble.-> 3405 dtype = type(1.0 + x[0] + y[0])34063407 if n == 2:TypeError: unsupported operand type(s) for +: ''float'' and ''numpy.str_''
两个列表的长度相同!
解决方法
我认为需要两个数字,所以使用:
population_by_region = result[''Population''].astype(int).tolist()
也不需要转换为列表,传递两列,如:
corr,val = stats.pearsonr(result[''Population''].astype(int),result[''wl_ratio''])print (corr,val)-0.04027318804589655 0.8387661496942489

Jupyter 中的 Numpy 在打印时出错(Python 版本 3.8.8):TypeError: 'numpy.ndarray' object is not callable
如何解决Jupyter 中的 Numpy 在打印时出错(Python 版本 3.8.8):TypeError: ''numpy.ndarray'' object is not callable?
晚安, 尝试打印以下内容时,我在 jupyter 中遇到了 numpy 问题,并且得到了一个 错误: 需要注意的是python版本是3.8.8。 我先用 spyder 测试它,它运行正确,它给了我预期的结果
使用 Spyder:
import numpy as np
for i in range (5):
n = np.random.rand ()
print (n)
Results
0.6604903457995978
0.8236300859753154
0.16067650689842816
0.6967868357083673
0.4231597934445466
现在有了 jupyter
import numpy as np
for i in range (5):
n = np.random.rand ()
print (n)
-------------------------------------------------- ------
TypeError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-78-0c6a801b3ea9> in <module>
2 for i in range (5):
3 n = np.random.rand ()
----> 4 print (n)
TypeError: ''numpy.ndarray'' object is not callable
感谢您对我如何在 Jupyter 中解决此问题的帮助。
非常感谢您抽出宝贵时间。
阿特,约翰”
解决方法
暂无找到可以解决该程序问题的有效方法,小编努力寻找整理中!
如果你已经找到好的解决方法,欢迎将解决方案带上本链接一起发送给小编。
小编邮箱:dio#foxmail.com (将#修改为@)

numpy.random.random & numpy.ndarray.astype & numpy.arange
今天看到这样一句代码:
xb = np.random.random((nb, d)).astype(''float32'') #创建一个二维随机数矩阵(nb行d列)
xb[:, 0] += np.arange(nb) / 1000. #将矩阵第一列的每个数加上一个值要理解这两句代码需要理解三个函数
1、生成随机数
numpy.random.random(size=None)
size为None时,返回float。
size不为None时,返回numpy.ndarray。例如numpy.random.random((1,2)),返回1行2列的numpy数组
2、对numpy数组中每一个元素进行类型转换
numpy.ndarray.astype(dtype)
返回numpy.ndarray。例如 numpy.array([1, 2, 2.5]).astype(int),返回numpy数组 [1, 2, 2]
3、获取等差数列
numpy.arange([start,]stop,[step,]dtype=None)
功能类似python中自带的range()和numpy中的numpy.linspace
返回numpy数组。例如numpy.arange(3),返回numpy数组[0, 1, 2]

numpy.ravel()/numpy.flatten()/numpy.squeeze()
numpy.ravel(a, order=''C'')
Return a flattened array
numpy.chararray.flatten(order=''C'')
Return a copy of the array collapsed into one dimension
numpy.squeeze(a, axis=None)
Remove single-dimensional entries from the shape of an array.
相同点: 将多维数组 降为 一维数组
不同点:
ravel() 返回的是视图(view),意味着改变元素的值会影响原始数组元素的值;
flatten() 返回的是拷贝,意味着改变元素的值不会影响原始数组;
squeeze()返回的是视图(view),仅仅是将shape中dimension为1的维度去掉;
ravel()示例:
1 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
2 import numpy as np
3
4 def log_type(name,arr):
5 print("数组{}的大小:{}".format(name,arr.size))
6 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.shape))
7 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.ndim))
8 print("数组{}元素的数据类型:{}".format(name,arr.dtype))
9 #print("数组:{}".format(arr.data))
10
11 a = np.floor(10*np.random.random((3,4)))
12 print(a)
13 log_type(''a'',a)
14
15 a1 = a.ravel()
16 print("a1:{}".format(a1))
17 log_type(''a1'',a1)
18 a1[2] = 100
19
20 print(a)
21 log_type(''a'',a)
flatten()示例
1 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
2 import numpy as np
3
4 def log_type(name,arr):
5 print("数组{}的大小:{}".format(name,arr.size))
6 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.shape))
7 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.ndim))
8 print("数组{}元素的数据类型:{}".format(name,arr.dtype))
9 #print("数组:{}".format(arr.data))
10
11 a = np.floor(10*np.random.random((3,4)))
12 print(a)
13 log_type(''a'',a)
14
15 a1 = a.flatten()
16 print("修改前a1:{}".format(a1))
17 log_type(''a1'',a1)
18 a1[2] = 100
19 print("修改后a1:{}".format(a1))
20
21 print("a:{}".format(a))
22 log_type(''a'',a)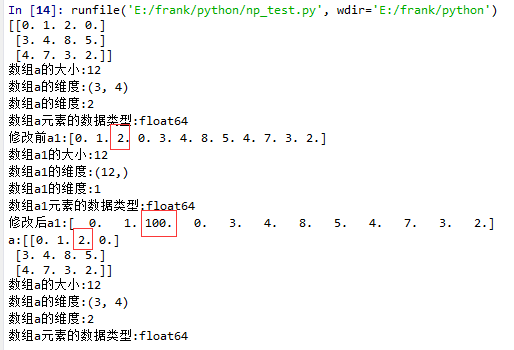
squeeze()示例:
1. 没有single-dimensional entries的情况
1 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
2 import numpy as np
3
4 def log_type(name,arr):
5 print("数组{}的大小:{}".format(name,arr.size))
6 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.shape))
7 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.ndim))
8 print("数组{}元素的数据类型:{}".format(name,arr.dtype))
9 #print("数组:{}".format(arr.data))
10
11 a = np.floor(10*np.random.random((3,4)))
12 print(a)
13 log_type(''a'',a)
14
15 a1 = a.squeeze()
16 print("修改前a1:{}".format(a1))
17 log_type(''a1'',a1)
18 a1[2] = 100
19 print("修改后a1:{}".format(a1))
20
21 print("a:{}".format(a))
22 log_type(''a'',a)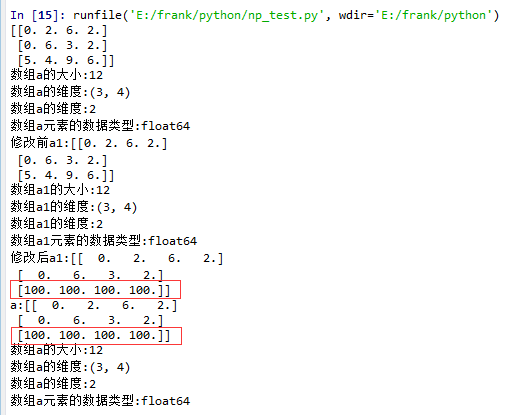
从结果中可以看到,当没有single-dimensional entries时,squeeze()返回额数组对象是一个view,而不是copy。
2. 有single-dimentional entries 的情况
1 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
2 import numpy as np
3
4 def log_type(name,arr):
5 print("数组{}的大小:{}".format(name,arr.size))
6 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.shape))
7 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.ndim))
8 print("数组{}元素的数据类型:{}".format(name,arr.dtype))
9 #print("数组:{}".format(arr.data))
10
11 a = np.floor(10*np.random.random((1,3,4)))
12 print(a)
13 log_type(''a'',a)
14
15 a1 = a.squeeze()
16 print("修改前a1:{}".format(a1))
17 log_type(''a1'',a1)
18 a1[2] = 100
19 print("修改后a1:{}".format(a1))
20
21 print("a:{}".format(a))
22 log_type(''a'',a)
关于Python numpy 模块-str_() 实例源码和python中numpy模块的问题就给大家分享到这里,感谢你花时间阅读本站内容,更多关于+ 不支持的操作数类型:“float”和“numpy.str_”、Jupyter 中的 Numpy 在打印时出错(Python 版本 3.8.8):TypeError: 'numpy.ndarray' object is not callable、numpy.random.random & numpy.ndarray.astype & numpy.arange、numpy.ravel()/numpy.flatten()/numpy.squeeze()等相关知识的信息别忘了在本站进行查找喔。
本文标签:



![[转帖]Ubuntu 安装 Wine方法(ubuntu如何安装wine)](https://www.gvkun.com/zb_users/cache/thumbs/4c83df0e2303284d68480d1b1378581d-180-120-1.jpg)

