本文将带您了解关于Spring配置多个数据源,并实现数据源的动态切换转载)的新内容,同时我们还将为您解释spring怎么配置多个数据源的相关知识,另外,我们还将为您提供关于037.[转]springb
本文将带您了解关于Spring 配置多个数据源,并实现数据源的动态切换转载)的新内容,同时我们还将为您解释spring怎么配置多个数据源的相关知识,另外,我们还将为您提供关于037.[转] springboot 配置多个数据源、20. Spring Boot 默认、自定义数据源 、配置多个数据源 jdbcTemplate操作DB、JAVA中使用代码创建多数据源,并实现动态切换、JAVA中使用代码创建多数据源,并实现动态切换(一)的实用信息。
本文目录一览:- Spring 配置多个数据源,并实现数据源的动态切换转载)(spring怎么配置多个数据源)
- 037.[转] springboot 配置多个数据源
- 20. Spring Boot 默认、自定义数据源 、配置多个数据源 jdbcTemplate操作DB
- JAVA中使用代码创建多数据源,并实现动态切换
- JAVA中使用代码创建多数据源,并实现动态切换(一)

Spring 配置多个数据源,并实现数据源的动态切换转载)(spring怎么配置多个数据源)
1. 首先在 config.properties 文件中配置两个数据库连接的基本数据。这个省略了
2. 在 spring 配置文件中配置这两个数据源:
数据源 1
<!-- initialSize初始化时建立物理连接的个数0 maxActive最大连接池数量8 minIdle最小连接池数量0-->
<bean id="dataSource1" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" scope="singleton">
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" />
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}" />
<property name="initialSize" value="${jdbc.init}" />
<property name="maxActive" value="${jdbc.max}" />
<property name="minIdle" value="${jdbc.min}" />
</bean>数据源 2
<bean id="dataSource2" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" scope="singleton">
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username2}" />
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password2}" />
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url2}" />
<property name="initialSize" value="${jdbc.init2}" />
<property name="maxActive" value="${jdbc.max2}" />
<property name="minIdle" value="${jdbc.min2}" />
</bean>3. 自定义一个数据源类,该类继承 org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.lookup.AbstractRoutingDataSource
并重写 determineCurrentLookupKey()方法
3.1 代码如下
public class RoutingDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource {
@Override
protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() {
return DataSourceHolder.getDataSourceType();
}
}
3.2 将该类交由 sping 管理,其在 spring 配置文件中配置如下
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.coe.exp.core.dataSource.RoutingDataSource">
<!-- 为targetDataSources注入两个数据源 -->
<property name="targetDataSources">
<map key-type="java.lang.String">
<entry key="ds1" value-ref="dataSource1"/>
<entry key="ds2" value-ref="dataSource2"/>
</map>
</property>
<!-- 为指定数据源RoutingDataSource注入默认的数据源-->
<property name="defaultTargetDataSource" ref="dataSource1"/>
</bean>
3.3spring 其他的配置如下
<!-- MyBatis配置 -->
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<!-- 把dataSource注入给sqlSessionFactory -->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
<property name="typeAliasesPackage" value="com.coe.exp.core.ent" />
<!-- 指定mapper.xml的位置 -->
<property name="mapperLocations" >
<array>
<value>classpath:com/coe/exp/core/xml/**/*.xml</value>
<value>classpath:com/coe/exp/xml/**/*.xml</value>
</array>
</property>
<!-- 指定myBatis配置文件的位置 -->
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:mybatis/sqlmapconfig.xml" />
</bean>
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="basePackage" value="com.coe.exp.core.mapper,com.coe.exp.mapper" />
<property name="sqlSessionFactoryBeanName" value="sqlSessionFactory" />
</bean>
<!-- 配置事务管理器 -->
<bean id="transactionManager"
class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
</bean>
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="insert*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="save*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="update*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="delete*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="remove*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="add*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="find*" propagation="SUPPORTS"/>
<tx:method name="get*" propagation="SUPPORTS"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<aop:config>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut="execution(* com.coe.exp.dao..*Impl.*(..))" order="2"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut="execution(* com.coe.exp.core.dao..*Impl.*(..))" order="3"/>
</aop:config>
<!-- 注解方式配置事物 -->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager" />
<!-- 引入属性文件 -->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:config.properties" />
<!-- 自动扫描(自动注入) -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.coe.exp,mm" annotation-config="true">
<context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/>
</context:component-scan>
<context:component-scan base-package="com.coe,mm"/>
<!-- 自动扫描定时任务 -->
<task:annotation-driven/>
<!-- spring自动创建代理,植入切面,proxy-target-class属性,默认为false,表示使用jdk动态代理织入增强,当配为<aop:aspectj-autoproxy
poxy-target-/>时,表示使用CGLib动态代理技术织入增强。不过即使proxy-target-class设置为false,如果目标类没有声明接口,则spring将自动使用CGLib动态代理。 -->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy proxy-target-class="true"/>
<import resource="../shiro/spring-shiro.xml"/>4. 编写一个数据源持有类 DataSourceHolder
public class DataSourceHolder {
private static final ThreadLocal<String> contextHolder = new ThreadLocal<String>();
/**
* @Description: 设置数据源类型
* @param dataSourceType 数据库类型
* @return void
* @throws
*/
public static void setDataSourceType(String dataSourceType) {
contextHolder.set(dataSourceType);
}
/**
* @Description: 获取数据源类型
* @param
* @return String
* @throws
*/
public static String getDataSourceType() {
return contextHolder.get();
}
/**
* @Description: 清除数据源类型
* @param
* @return void
* @throws
*/
public static void clearDataSourceType() {
contextHolder.remove();
}
}5. 自定义注解
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* 数据源
*
* @author llb 2017-03-30
*
*/
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Component
public @interface DataSource {
String value() default "";
}6. 动态切换数据源
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import com.coe.exp.core.dataSource.DataSourceHolder;
@Order(1)
@Aspect
@Repository
public class DataSourceAspect {
@Pointcut("execution(* com..dao..*Impl.*(..))")
private void anyMethod() {
}
@AfterReturning(value = "anyMethod()", returning = "result")
public void afterReturning(JoinPoint joinPoint,Object result){
DataSourceHolder.clearDataSourceType();
}
@Before(value="anyMethod()")
public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
MethodSignature methodSignature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();
Method method = methodSignature.getMethod();
//如果方法体上使用了DataSource注解
if (method.isAnnotationPresent(DataSource.class)) {
//获取该方法上的注解名
DataSource datasource = method.getAnnotation(DataSource.class);
//将方法体上的注解的值赋予给DataSourceHolder数据源持有类
DataSourceHolder.setDataSourceType(datasource.value());
}
}
}7. 若方法体上没有注解,则都是使用默认数据源,如果有以下注解,则使用指定的数据源
/**
* 查询哲盟数据库中所有状态正常的客户余额
* @return
* @author mxl
* @version 2017年8月16日下午1:30:06
*/
@DataSource("ds2")
public List<CustomerBalanceEnt> getAllCustBalanceByZm(){
return customerBalanceMapper.getAllCustBalanceByZm();
}上面这个方法就是使用 “ds2”;
---------------------
作者:苹果树上的你
来源:CSDN
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/ll535299/article/details/78203634
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,转载请附上博文链接!
![037.[转] springboot 配置多个数据源 037.[转] springboot 配置多个数据源](http://www.gvkun.com/zb_users/upload/2025/02/4b13d0e8-1aa8-44a5-ab6c-15ee93d71cba1739065721691.jpg)
037.[转] springboot 配置多个数据源
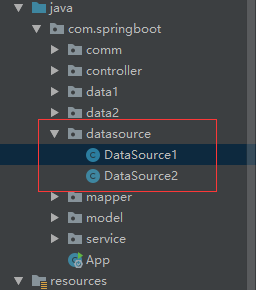
1、在 application.properties 文件 配置两个数据源
#默认使用 tomcat-jdbc
spring.datasource.type=org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSource
spring.datasource.data1.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/mysql-boot
spring.datasource.data1.username=root
spring.datasource.data1.password=123123
spring.datasource.data1.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.data2.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/mysql-confswh
spring.datasource.data2.username=root
spring.datasource.data2.password=123123
spring.datasource.data2.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
2、创建一个 datasource 包,新建 DataSource1,DataSource2 两个文件,通过注解来配置数据源
DataSource1
package com.springboot.datasource;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceBuilder;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
@Configuration//注解到spring容器中
@MapperScan(basePackages = "com.springboot.data1.mapper",sqlSessionFactoryRef = "data1SqlSessionFactory")
public class DataSource1 {
/**
* 返回data1数据库的数据源
* @return
*/
@Bean(name="data1Source")
@Primary//主数据源
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.data1")
public DataSource dataSource(){
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
/**
* 返回data1数据库的会话工厂
* @param ds
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
@Bean(name = "data1SqlSessionFactory")
@Primary
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory(@Qualifier("data1Source") DataSource ds) throws Exception{
SqlSessionFactoryBean bean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
bean.setDataSource(ds);
return bean.getObject();
}
/**
* 返回data1数据库的会话模板
* @param sessionFactory
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
@Bean(name = "data1SqlSessionTemplate")
@Primary
public SqlSessionTemplate sqlSessionTemplate(@Qualifier("data1SqlSessionFactory") SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory) throws Exception{
return new SqlSessionTemplate(sessionFactory);
}
/**
* 返回data1数据库的事务
* @param ds
* @return
*/
@Bean(name = "data1TransactionManager")
@Primary
public DataSourceTransactionManager transactionManager(@Qualifier("data1Source") DataSource ds){
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(ds);
}
}
DataSource2:
package com.springboot.datasource;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceBuilder;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
@Configuration//注解到spring容器中
@MapperScan(basePackages = "com.springboot.data2.mapper",sqlSessionFactoryRef = "data2SqlSessionFactory")
public class DataSource2 {
/**
* 返回data2数据库的数据源
* @return
*/
@Bean(name="data2Source")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.data2")
public DataSource dataSource(){
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
/**
* 返回data2数据库的会话工厂
* @param ds
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
@Bean(name = "data2SqlSessionFactory")
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory(@Qualifier("data2Source") DataSource ds) throws Exception{
SqlSessionFactoryBean bean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
bean.setDataSource(ds);
return bean.getObject();
}
/**
* 返回data2数据库的会话模板
* @param sessionFactory
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
@Bean(name = "data2SqlSessionTemplate")
public SqlSessionTemplate sqlSessionTemplate(@Qualifier("data2SqlSessionFactory") SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory) throws Exception{
return new SqlSessionTemplate(sessionFactory);
}
/**
* 返回data2数据库的事务
* @param ds
* @return
*/
@Bean(name = "data2TransactionManager")
public DataSourceTransactionManager transactionManager(@Qualifier("data2Source") DataSource ds){
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(ds);
}
}
3、测试 Service&Mapper
@RequestMapping("getTopicList")
public List<Map<String,Object>> getTopicList(){
List<Map<String,Object>> list1 = userServiceData1.getTopicListData1();
List<Map<String,Object>> list2 = userServiceData2.getTopicListData2();
return list1;
}
https://www.cnblogs.com/lijianda/p/11022892.html
附:
http://www.demodashi.com/demo/14622.html
20. Spring Boot 默认、自定义数据源 、配置多个数据源 jdbcTemplate操作DB
Spring-Boot-2.0.0-M1版本将默认的数据库连接池从tomcat jdbc pool改为了hikari,这里主要研究下hikari的默认配置
0. 创建Spring Boot项目,选中 Web、MySQL、JDBC 依赖
1. 启动类默认加载了DataSourceAutoConfiguration,默认数据源是HikariDataSource
@SpringBootApplicationpublic class SpringBootJdbcApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootJdbcApplication.class, args);
}
}
2. 数据源配置文件属性
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot //系统自带的默认数据源配置中,用 url,若是自定义的HikariDataSource,用jdbcUrl (自定义的其它类型数据源名称取什么待测)
username: root
password: xiaochao
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver //老版本用com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
name: hikari
3. 测试
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class SpringBootJdbcApplicationTests {
@Autowired
DataSource dataSource;
@Test
public void contextLoads() throws SQLException {
System.out.println(dataSource.getClass().getName());
System.out.println(dataSource.getConnection());
}
}
结果:
HikariProxyConnection@265939934 wrapping com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ConnectionImpl@14982a82
com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource
4. 自定义数据源
4.1 首先排除掉系统默认数据源
- exclude:排除,不包括,祛除,赶出,反义词 : include
@SpringBootApplication(exclude = {DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class})public class SpringBootJdbcApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SpringBootJdbcApplication.class, args); } }
4.2 在配置类中加入自定义的线程池
-
@Bean @ConfigurationProperties("spring.datasource") //此配置项名称是自定义的,只要和配置文件中的各项名称对应上就好 public HikariDataSource dataSource() { return DataSourceBuilder.create().type(HikariDataSource.class).build(); } -
4.3 把配置文件中的spring.datasource.url 改为spring.datasource.jdbcUrl
- 4.4 自动以tomcat jdbc 数据源 首先引入tomcat-jdbc依赖
-
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.tomcat</groupId> <artifactId>tomcat-jdbc</artifactId> <version>9.0.13</version> </dependency> -
配置tomcat数据源Bean
@Configuration
public class MyConfig {
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties("spring.datasource") //此配置项名称是自定义的,只要能和配置文件中的各项名称对应上就好
public org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSource dataSource() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().type(org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSource.class).build();
}
}
自定义其它类型的数据源方式同理
配置多个数据源

5. 数据源自动配置 源码解析
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by Fernflower decompiler)
//
package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc;
import com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.apache.commons.dbcp2.BasicDataSource;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnClass;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnMissingBean;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnProperty;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.jdbc.DatabaseDriver;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
abstract class DataSourceConfiguration {
DataSourceConfiguration() {
}
protected static <T> T createDataSource(DataSourceProperties properties, Class<? extends DataSource> type) {
return properties.initializeDataSourceBuilder().type(type).build();
}
@ConditionalOnMissingBean({DataSource.class})
@ConditionalOnProperty(
name = {"spring.datasource.type"}
)
static class Generic {
Generic() {
}
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource(DataSourceProperties properties) {
return properties.initializeDataSourceBuilder().build();
}
}
@ConditionalOnClass({BasicDataSource.class})
@ConditionalOnMissingBean({DataSource.class})
@ConditionalOnProperty(
name = {"spring.datasource.type"},
havingValue = "org.apache.commons.dbcp2.BasicDataSource",
matchIfMissing = true
)
static class Dbcp2 {
Dbcp2() {
}
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(
prefix = "spring.datasource.dbcp2"
)
public BasicDataSource dataSource(DataSourceProperties properties) {
return (BasicDataSource)DataSourceConfiguration.createDataSource(properties, BasicDataSource.class);
}
}
@ConditionalOnClass({HikariDataSource.class})
@ConditionalOnMissingBean({DataSource.class})
@ConditionalOnProperty(
name = {"spring.datasource.type"},
havingValue = "com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource",
matchIfMissing = true
)
static class Hikari {
Hikari() {
}
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(
prefix = "spring.datasource.hikari"
)
public HikariDataSource dataSource(DataSourceProperties properties) {
HikariDataSource dataSource = (HikariDataSource)DataSourceConfiguration.createDataSource(properties, HikariDataSource.class);
if (StringUtils.hasText(properties.getName())) {
dataSource.setPoolName(properties.getName());
}
return dataSource;
}
}
@ConditionalOnClass({org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSource.class})
@ConditionalOnMissingBean({DataSource.class})
@ConditionalOnProperty(
name = {"spring.datasource.type"},
havingValue = "org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSource",
matchIfMissing = true
)
static class Tomcat {
Tomcat() {
}
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(
prefix = "spring.datasource.tomcat"
)
public org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSource dataSource(DataSourceProperties properties) {
org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSource dataSource = (org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSource)DataSourceConfiguration.createDataSource(properties, org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSource.class);
DatabaseDriver databaseDriver = DatabaseDriver.fromJdbcUrl(properties.determineUrl());
String validationQuery = databaseDriver.getValidationQuery();
if (validationQuery != null) {
dataSource.setTestOnBorrow(true);
dataSource.setValidationQuery(validationQuery);
}
return dataSource;
}
}
}
参考文档:Spring Boot 官方文档 —— 84.1 Configure a Custom DataSource 章节
package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc;
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass({DataSource.class, EmbeddedDatabaseType.class})
@EnableConfigurationProperties({DataSourceProperties.class})
@Import({DataSourcePoolMetadataProvidersConfiguration.class, DataSourceInitializationConfiguration.class})
public class DataSourceAutoConfiguration {
public DataSourceAutoConfiguration() {}
。。。。。。
}
@Configuration
@Import({DataSourceInitializerInvoker.class, DataSourceInitializationConfiguration.Registrar.class})
class DataSourceInitializationConfiguration {
DataSourceInitializationConfiguration() {
}
static class Registrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar {
private static final String BEAN_NAME = "dataSourceInitializerPostProcessor";
Registrar() {
}
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition("dataSourceInitializerPostProcessor")) {
GenericBeanDefinition beanDefinition = new GenericBeanDefinition();
beanDefinition.setBeanClass(DataSourceInitializerPostProcessor.class);
beanDefinition.setRole(2);
beanDefinition.setSynthetic(true);
registry.registerBeanDefinition("dataSourceInitializerPostProcessor", beanDefinition);
}
}
}
}
package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.ObjectProvider;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener; //此类是一个监听器
class DataSourceInitializerInvoker implements ApplicationListener<DataSourceSchemaCreatedEvent>, InitializingBean {
private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(DataSourceInitializerInvoker.class);
private final ObjectProvider<DataSource> dataSource;
private final DataSourceProperties properties;
private final ApplicationContext applicationContext;
private DataSourceInitializer dataSourceInitializer;
private boolean initialized;
DataSourceInitializerInvoker(ObjectProvider<DataSource> dataSource, DataSourceProperties properties, ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
this.dataSource = dataSource;
this.properties = properties;
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
DataSourceInitializer initializer = this.getDataSourceInitializer();
if (initializer != null) {
boolean schemaCreated = this.dataSourceInitializer.createSchema(); //run DDL schema
if (schemaCreated) {
this.initialize(initializer);
}
}
}
private void initialize(DataSourceInitializer initializer) {
try {
this.applicationContext.publishEvent(new DataSourceSchemaCreatedEvent(initializer.getDataSource()));
if (!this.initialized) {
this.dataSourceInitializer.initSchema(); //run init data schema
this.initialized = true;
}
} catch (IllegalStateException var3) {
logger.warn("Could not send event to complete DataSource initialization (" + var3.getMessage() + ")");
}
}
//监听器监听到事件后运行的方法
public void onApplicationEvent(DataSourceSchemaCreatedEvent event) {
DataSourceInitializer initializer = this.getDataSourceInitializer();
if (!this.initialized && initializer != null) {
initializer.initSchema(); //run init data schema
this.initialized = true;
}
}
private DataSourceInitializer getDataSourceInitializer() {
if (this.dataSourceInitializer == null) {
DataSource ds = (DataSource)this.dataSource.getIfUnique();
if (ds != null) {
this.dataSourceInitializer = new DataSourceInitializer(ds, this.properties, this.applicationContext);
}
}
return this.dataSourceInitializer;
}
}
package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc;
import ......;
class DataSourceInitializer { //【初始化程序】
private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(DataSourceInitializer.class);
private final DataSource dataSource;
private final DataSourceProperties properties;
private final ResourceLoader resourceLoader;
DataSourceInitializer(DataSource dataSource, DataSourceProperties properties, ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
this.dataSource = dataSource;
this.properties = properties;
this.resourceLoader = (ResourceLoader)(resourceLoader != null ? resourceLoader : new DefaultResourceLoader());
}
DataSourceInitializer(DataSource dataSource, DataSourceProperties properties) {
this(dataSource, properties, (ResourceLoader)null);
}
public DataSource getDataSource() {
return this.dataSource;
}
//建表SQL,classpath*:schema-*.sql
public boolean createSchema() {
//this.properties.getSchema()即:用户在配置文件中指定的 spring.datasource.schema=xxx
List<Resource> scripts = this.getScripts("spring.datasource.schema", this.properties.getSchema(), "schema");
if (!scripts.isEmpty()) {
if (!this.isEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Initialization disabled (not running DDL scripts)");
return false;
}
String username = this.properties.getSchemaUsername();
String password = this.properties.getSchemaPassword();
this.runScripts(scripts, username, password);
}
return !scripts.isEmpty();
}
//初始化数据SQL ,classpath*:data-*.sql
public void initSchema() {
//this.properties.getData 即:用户在配置文件中自定义的:spring.datasource.data=XXX
List<Resource> scripts = this.getScripts("spring.datasource.data", this.properties.getData(), "data");
if (!scripts.isEmpty()) {
if (!this.isEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Initialization disabled (not running data scripts)");
return;
}
String username = this.properties.getDataUsername();
String password = this.properties.getDataPassword();
this.runScripts(scripts, username, password);
}
}
。。。。。。
//根据特定名称规则获取SQL脚本文件
private List<Resource> getScripts(String propertyName, List<String> resources, String fallback) {
if (resources != null) { //指定名称的脚本文件名字集合
return this.getResources(propertyName, resources, true); //从指定名称的脚本名字文件集合中获取脚本SQL
} else { //若是没有指定的,则在类路径下寻找通配规则的脚本文件
String platform = this.properties.getPlatform(); //平台,纲领
List<String> fallbackResources = new ArrayList();
//这里为啥add() 2个 SQL?
fallbackResources.add("classpath*:" + fallback + "-" + platform + ".sql"); //DatasourceProperties中的构造器中,platform默认被赋值为 all
fallbackResources.add("classpath*:" + fallback + ".sql");
return this.getResources(propertyName, fallbackResources, false);
}
}
。。。。。。
//运行SQL脚本
private void runScripts(List<Resource> resources, String username, String password) {
if (!resources.isEmpty()) {
ResourceDatabasePopulator populator = new ResourceDatabasePopulator();
populator.setContinueOnError(this.properties.isContinueOnError());
populator.setSeparator(this.properties.getSeparator());
if (this.properties.getSqlScriptEncoding() != null) {
populator.setSqlScriptEncoding(this.properties.getSqlScriptEncoding().name());
}
Iterator var5 = resources.iterator();
while(var5.hasNext()) {
Resource resource = (Resource)var5.next();
populator.addScript(resource);
}
DataSource dataSource = this.dataSource;
if (StringUtils.hasText(username) && StringUtils.hasText(password)) {
dataSource = DataSourceBuilder.create(this.properties.getClassLoader()).driverClassName(this.properties.determineDriverClassName()).url(this.properties.determineUrl()).username(username).password(password).build();
}
DatabasePopulatorUtils.execute(populator, dataSource);
}
}
}
package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc;
@ConfigurationProperties(
prefix = "spring.datasource"
)
public class DataSourceProperties implements BeanClassLoaderAware, InitializingBean {private Class<? extends DataSource> type;
private String driverClassName;
private String url;
private String username;
private String password;private DataSourceInitializationMode initializationMode;
private String platform;
private List<String> schema;private Charset sqlScriptEncoding;
......public DataSourceProperties() {
this.initializationMode = DataSourceInitializationMode.EMBEDDED;
this.platform = "all";
this.continueOnError = false;
this.separator = ";";
this.embeddedDatabaseConnection = EmbeddedDatabaseConnection.NONE;
this.xa = new DataSourceProperties.Xa();
}
}
通配规则:schema‐*.sql、data‐*.sql, 优先级第三高 eg:schema-emp.sql, schema-dept.sql; data-emp.sql ,data-dept.sql
默认规则:schema.sql,schema‐all.sql (或者关系,给用户多个选择); 优先级第二高,
自定义规则:yml中配置,根据上面代码,优先级高
spring:
datasource:
schema:
‐ classpath: department.sql
‐ classpath: user.sql
......
data:
‐ classpath: department_initData.sql
‐ classpath: user_initData.sql
......
自定义指定的SQL文件
经过测验,schema.sql 和schema-all.sql 在resources目录下并没有生效,有待继续查验
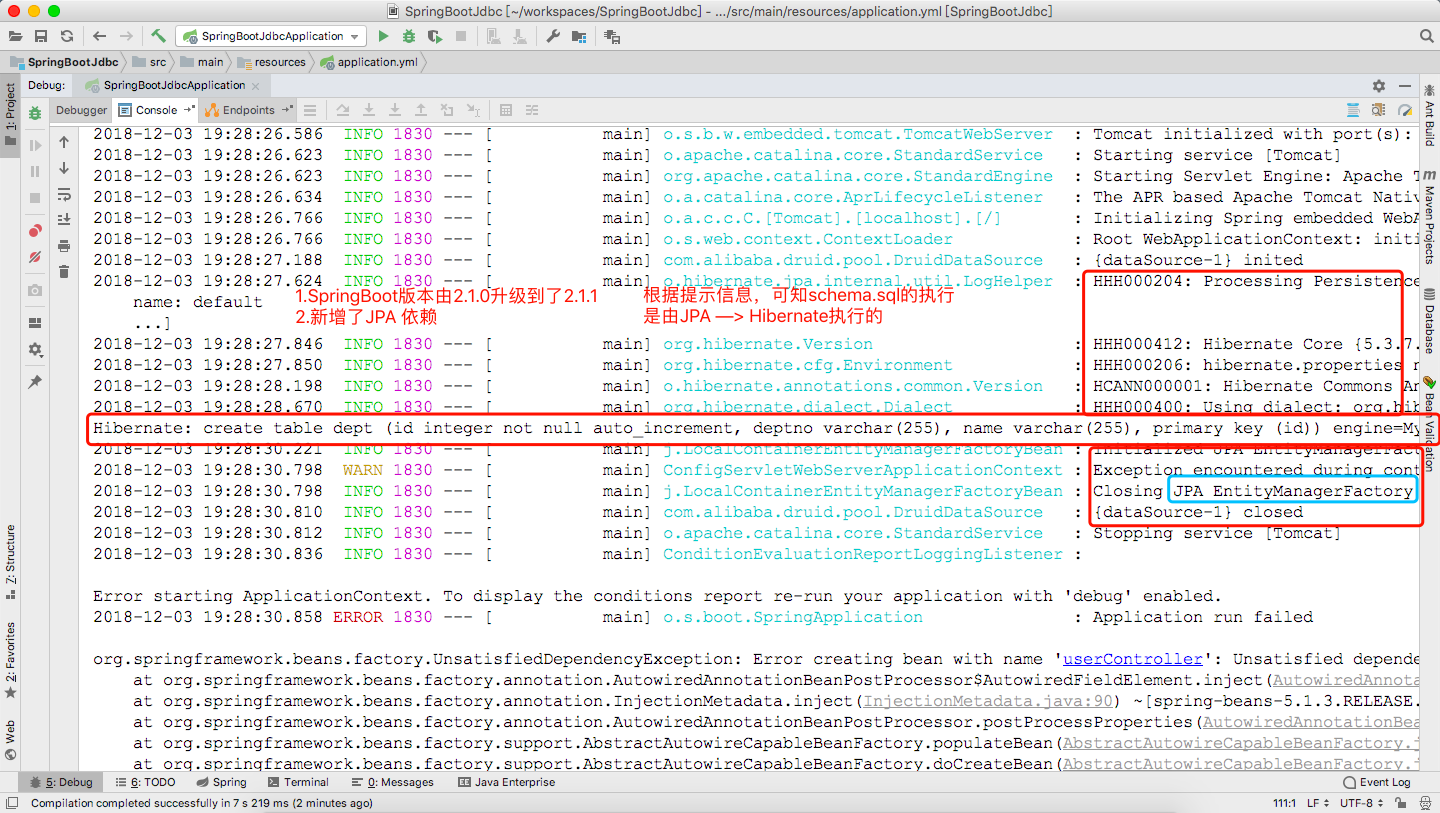
6. jdbcTemplate操作数据库
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/getById2/{id}")
public List<Map<String, Object>> selectByPrimaryKey2(@PathVariable Integer id){
//这种query is OK
List<Map<String, Object>> maps = jdbcTemplate.queryForList("SELECT * FROM USER");
return maps;
//以下几种方式都会产生error,error信息见下文:待查明
// Object[] obj = new Object[1];
// obj[0] = id;
// return jdbcTemplate.queryForList("select * from user where id = ?", obj,User.class);
// return jdbcTemplate.queryForList("SELECT * FROM USER", User.class);
// return jdbcTemplate.queryForObject("select id,name,sex,age from user where id = " + id,User.class);
}
}
org.springframework.jdbc.IncorrectResultSetColumnCountException: Incorrect column count: expected 1, actual 4
at org.springframework.jdbc.core.SingleColumnRowMapper.mapRow(SingleColumnRowMapper.java:110) ~[spring-jdbc-5.1.3.RELEASE.jar:5.1.3.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.jdbc.core.RowMapperResultSetExtractor.extractData(RowMapperResultSetExtractor.java:94) ~[spring-jdbc-5.1.3.RELEASE.jar:5.1.3.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.jdbc.core.RowMapperResultSetExtractor.extractData(RowMapperResultSetExtractor.java:61) ~[spring-jdbc-5.1.3.RELEASE.jar:5.1.3.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate$1QueryStatementCallback.doInStatement(JdbcTemplate.java:440) ~[spring-jdbc-5.1.3.RELEASE.jar:5.1.3.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate.execute(JdbcTemplate.java:376) ~[spring-jdbc-5.1.3.RELEASE.jar:5.1.3.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate.query(JdbcTemplate.java:452) ~[spring-jdbc-5.1.3.RELEASE.jar:5.1.3.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate.query(JdbcTemplate.java:462) ~[spring-jdbc-5.1.3.RELEASE.jar:5.1.3.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate.queryForList(JdbcTemplate.java:485) ~[spring-jdbc-5.1.3.RELEASE.jar:5.1.3.RELEASE]
at com.everjiankang.cache.controller.UserController.selectByPrimaryKey2(UserController.java:53) ~[classes/:na]
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method) ~[na:1.8.0_181]
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:62) ~[na:1.8.0_181]
at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:43) ~[na:1.8.0_181]
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:498) ~[na:1.8.0_181]
at org.springframework.web.method.support.InvocableHandlerMethod.doInvoke(InvocableHandlerMethod.java:189) ~[spring-web-5.1.3.RELEASE.jar:5.1.3.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.web.method.support.InvocableHandlerMethod.invokeForRequest(InvocableHandlerMethod.java:138) ~[spring-web-5.1.3.RELEASE.jar:5.1.3.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ServletInvocableHandlerMethod.invokeAndHandle(ServletInvocableHandlerMethod.java:102) ~[spring-webmvc-5.1.3.RELEASE.jar:5.1.3.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter.invokeHandlerMethod(RequestMappingHandlerAdapter.java:895) ~[spring-webmvc-5.1.3.RELEASE.jar:5.1.3.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter.handleInternal(RequestMappingHandlerAdapter.java:800) ~[spring-webmvc-5.1.3.RELEASE.jar:5.1.3.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter.handle(AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter.java:87) ~[spring-webmvc-5.1.3.RELEASE.jar:5.1.3.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet.doDispatch(DispatcherServlet.java:1038) ~[spring-webmvc-5.1.3.RELEASE.jar:5.1.3.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet.doService(DispatcherServlet.java:942) ~[spring-webmvc-5.1.3.RELEASE.jar:5.1.3.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet.processRequest(FrameworkServlet.java:1005) ~[spring-webmvc-5.1.3.RELEASE.jar:5.1.3.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet.doGet(FrameworkServlet.java:897) ~[spring-webmvc-5.1.3.RELEASE.jar:5.1.3.RELEASE]
at javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet.service(HttpServlet.java:634) ~[tomcat-embed-core-9.0.13.jar:9.0.13]
at org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet.service(FrameworkServlet.java:882) ~[spring-webmvc-5.1.3.RELEASE.jar:5.1.3.RELEASE]
at javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet.service(HttpServlet.java:741) ~[tomcat-embed-core-9.0.13.jar:9.0.13]
at org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain.internalDoFilter(ApplicationFilterChain.java:231) ~[tomcat-embed-core-9.0.13.jar:9.0.13]
at org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain.doFilter(ApplicationFilterChain.java:166) ~[tomcat-embed-core-9.0.13.jar:9.0.13]
at org.apache.tomcat.websocket.server.WsFilter.doFilter(WsFilter.java:53) ~[tomcat-embed-websocket-9.0.13.jar:9.0.13]
at org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain.internalDoFilter(ApplicationFilterChain.java:193) ~[tomcat-embed-core-9.0.13.jar:9.0.13]
at org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain.doFilter(ApplicationFilterChain.java:166) ~[tomcat-embed-core-9.0.13.jar:9.0.13]
at org.springframework.web.filter.RequestContextFilter.doFilterInternal(RequestContextFilter.java:99) ~[spring-web-5.1.3.RELEASE.jar:5.1.3.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.web.filter.OncePerRequestFilter.doFilter(OncePerRequestFilter.java:107) ~[spring-web-5.1.3.RELEASE.jar:5.1.3.RELEASE]
at org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain.internalDoFilter(ApplicationFilterChain.java:193) ~[tomcat-embed-core-9.0.13.jar:9.0.13]
at org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain.doFilter(ApplicationFilterChain.java:166) ~[tomcat-embed-core-9.0.13.jar:9.0.13]
at org.springframework.web.filter.FormContentFilter.doFilterInternal(FormContentFilter.java:92) ~[spring-web-5.1.3.RELEASE.jar:5.1.3.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.web.filter.OncePerRequestFilter.doFilter(OncePerRequestFilter.java:107) ~[spring-web-5.1.3.RELEASE.jar:5.1.3.RELEASE]
at org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain.internalDoFilter(ApplicationFilterChain.java:193) ~[tomcat-embed-core-9.0.13.jar:9.0.13]
at org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain.doFilter(ApplicationFilterChain.java:166) ~[tomcat-embed-core-9.0.13.jar:9.0.13]
at org.springframework.web.filter.HiddenHttpMethodFilter.doFilterInternal(HiddenHttpMethodFilter.java:93) ~[spring-web-5.1.3.RELEASE.jar:5.1.3.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.web.filter.OncePerRequestFilter.doFilter(OncePerRequestFilter.java:107) ~[spring-web-5.1.3.RELEASE.jar:5.1.3.RELEASE]
at org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain.internalDoFilter(ApplicationFilterChain.java:193) ~[tomcat-embed-core-9.0.13.jar:9.0.13]
at org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain.doFilter(ApplicationFilterChain.java:166) ~[tomcat-embed-core-9.0.13.jar:9.0.13]
at org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter.doFilterInternal(CharacterEncodingFilter.java:200) ~[spring-web-5.1.3.RELEASE.jar:5.1.3.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.web.filter.OncePerRequestFilter.doFilter(OncePerRequestFilter.java:107) ~[spring-web-5.1.3.RELEASE.jar:5.1.3.RELEASE]
at org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain.internalDoFilter(ApplicationFilterChain.java:193) ~[tomcat-embed-core-9.0.13.jar:9.0.13]
at org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain.doFilter(ApplicationFilterChain.java:166) ~[tomcat-embed-core-9.0.13.jar:9.0.13]
at org.apache.catalina.core.StandardWrapperValve.invoke(StandardWrapperValve.java:199) ~[tomcat-embed-core-9.0.13.jar:9.0.13]
at org.apache.catalina.core.StandardContextValve.invoke(StandardContextValve.java:96) [tomcat-embed-core-9.0.13.jar:9.0.13]
at org.apache.catalina.authenticator.AuthenticatorBase.invoke(AuthenticatorBase.java:490) [tomcat-embed-core-9.0.13.jar:9.0.13]
at org.apache.catalina.core.StandardHostValve.invoke(StandardHostValve.java:139) [tomcat-embed-core-9.0.13.jar:9.0.13]
at org.apache.catalina.valves.ErrorReportValve.invoke(ErrorReportValve.java:92) [tomcat-embed-core-9.0.13.jar:9.0.13]
at org.apache.catalina.core.StandardEngineValve.invoke(StandardEngineValve.java:74) [tomcat-embed-core-9.0.13.jar:9.0.13]
at org.apache.catalina.connector.CoyoteAdapter.service(CoyoteAdapter.java:343) [tomcat-embed-core-9.0.13.jar:9.0.13]
at org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11Processor.service(Http11Processor.java:408) [tomcat-embed-core-9.0.13.jar:9.0.13]
at org.apache.coyote.AbstractProcessorLight.process(AbstractProcessorLight.java:66) [tomcat-embed-core-9.0.13.jar:9.0.13]
at org.apache.coyote.AbstractProtocol$ConnectionHandler.process(AbstractProtocol.java:791) [tomcat-embed-core-9.0.13.jar:9.0.13]
at org.apache.tomcat.util.net.NioEndpoint$SocketProcessor.doRun(NioEndpoint.java:1417) [tomcat-embed-core-9.0.13.jar:9.0.13]
at org.apache.tomcat.util.net.SocketProcessorBase.run(SocketProcessorBase.java:49) [tomcat-embed-core-9.0.13.jar:9.0.13]
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.runWorker(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1149) [na:1.8.0_181]
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.run(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:624) [na:1.8.0_181]
at org.apache.tomcat.util.threads.TaskThread$WrappingRunnable.run(TaskThread.java:61) [tomcat-embed-core-9.0.13.jar:9.0.13]
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:748) [na:1.8.0_181]

JAVA中使用代码创建多数据源,并实现动态切换
业务需求,就是根据数据库存储的不同数据源信息,动态创建数据源并实现业务不同而转到不同的数据源上处理。
数据库存储起来的数据源信息是不确定的,可以删除和添加,这些是业务前提。
在网上找了下相关资料,对于使用Spring配置,直接配置多套数据源,使用AOP动态切换的方式居多,这种方式博主以前也使用过,很强大。不过有个前提就是多个数据源的信息是预先就确定的。那么对于不确定数据源信息的业务需求,就只有使用代码动态实现数据源初始化和销毁操作了。

JAVA中使用代码创建多数据源,并实现动态切换(一)
近日,博主有个业务需求,就是根据数据库存储的不同数据源信息,动态创建数据源并实现业务不同而转到不同的数据源上处理。
数据库存储起来的数据源信息是不确定的,可以删除和添加,这些是业务前提。
在网上找了下相关资料,对于使用Spring配置,直接配置多套数据源,使用AOP动态切换的方式居多,这种方式博主以前也使用过,很强大。不过有个前提就是多个数据源的信息是预先就确定的。那么对于不确定数据源信息的业务需求,就只有使用代码动态实现数据源初始化和销毁操作了。
好了,有了这些思路,可以开始准备写代码了。
1、创建一个线程上下文对象(使用ThreadLocal,保证线程安全)。上下文对象中主要维护了数据源的KEY和数据源的地址等信息,当KEY对应的数据源找不到时,根据数据源地址、驱动和用户名等创建 一个数据源,这里也是业务中需要解决的一个核心问题(JAVA动态创建数据源)。
/**
* Copyright (c) 2015 - 2016 eay Inc.
* All rights reserved.
*/
package com.eya.pubservice.datasource;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 当前正在使用的数据源信息的线程上线文
* @create ll
* @createDate 2017年3月27日 下午2:37:07
* @update
* @updateDate
*/
public class DBContextHolder {
/** 数据源的KEY */
public static final String DATASOURCE_KEY = "DATASOURCE_KEY";
/** 数据源的URL */
public static final String DATASOURCE_URL = "DATASOURCE_URL";
/** 数据源的驱动 */
public static final String DATASOURCE_DRIVER = "DATASOURCE_DRIVER";
/** 数据源的用户名 */
public static final String DATASOURCE_USERNAME = "DATASOURCE_USERNAME";
/** 数据源的密码 */
public static final String DATASOURCE_PASSWORD = "DATASOURCE_PASSWORD";
private static final ThreadLocal<Map<String, Object>> contextHolder = new ThreadLocal<Map<String, Object>>();
public static void setDBType(Map<String, Object> dataSourceConfigMap) {
contextHolder.set(dataSourceConfigMap);
}
public static Map<String, Object> getDBType() {
Map<String, Object> dataSourceConfigMap = contextHolder.get();
if (dataSourceConfigMap == null) {
dataSourceConfigMap = new HashMap<String, Object>();
}
return dataSourceConfigMap;
}
public static void clearDBType() {
contextHolder.remove();
}
}2、创建一个AbstractRoutingDataSource的子类,实现其determineCurrentLookupKey方法,用于决定使用哪一个数据源。说明一下,这里实现了ApplicationContextAware接口,用于在Spring加载完成后,注入Spring上下文对象,用于获取Bean。
/**
* Copyright (c) 2015 - 2016 eya Inc.
* All rights reserved.
*/
package com.eya.pubservice.datasource;
import java.util.Map;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.apache.commons.collections.MapUtils;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.lookup.AbstractRoutingDataSource;
/**
* 动态数据源父类
* @create ll
* @createDate 2017年3月27日 下午2:38:05
* @update
* @updateDate
*/
public abstract class AbstractDynamicDataSource<T extends DataSource> extends AbstractRoutingDataSource
implements
ApplicationContextAware {
/** 日志 */
protected Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass());
/** 默认的数据源KEY */
protected static final String DEFAULT_DATASOURCE_KEY = "defaultDataSource";
/** 数据源KEY-VALUE键值对 */
public Map<Object, Object> targetDataSources;
/** spring容器上下文 */
private static ApplicationContext ctx;
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
ctx = applicationContext;
}
public static ApplicationContext getApplicationContext() {
return ctx;
}
public static Object getBean(String name) {
return ctx.getBean(name);
}
/**
* @param targetDataSources the targetDataSources to set
*/
public void setTargetDataSources(Map<Object, Object> targetDataSources) {
this.targetDataSources = targetDataSources;
super.setTargetDataSources(targetDataSources);
// afterPropertiesSet()方法调用时用来将targetDataSources的属性写入resolvedDataSources中的
super.afterPropertiesSet();
}
/**
* 创建数据源
* @param driverClassName 数据库驱动名称
* @param url 连接地址
* @param username 用户名
* @param password 密码
* @return 数据源{@link T}
* @Author : ll. create at 2017年3月27日 下午2:44:34
*/
public abstract T createDataSource(String driverClassName, String url, String username,
String password);
/**
* 设置系统当前使用的数据源
* <p>数据源为空或者为0时,自动切换至默认数据源,即在配置文件中定义的默认数据源
* @see org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.lookup.AbstractRoutingDataSource#determineCurrentLookupKey()
*/
@Override
protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() {
logger.info("【设置系统当前使用的数据源】");
Map<String, Object> configMap = DBContextHolder.getDBType();
logger.info("【当前数据源配置为:{}】", configMap);
if (MapUtils.isEmpty(configMap)) {
// 使用默认数据源
return DEFAULT_DATASOURCE_KEY;
}
// 判断数据源是否需要初始化
this.verifyAndInitDataSource();
logger.info("【切换至数据源:{}】", configMap);
return configMap.get(DBContextHolder.DATASOURCE_KEY);
}
/**
* 判断数据源是否需要初始化
* @Author : ll. create at 2017年3月27日 下午3:57:43
*/
private void verifyAndInitDataSource() {
Map<String, Object> configMap = DBContextHolder.getDBType();
Object obj = this.targetDataSources.get(configMap.get(DBContextHolder.DATASOURCE_KEY));
if (obj != null) {
return;
}
logger.info("【初始化数据源】");
T datasource = this.createDataSource(configMap.get(DBContextHolder.DATASOURCE_DRIVER)
.toString(), configMap.get(DBContextHolder.DATASOURCE_URL).toString(),
configMap.get(DBContextHolder.DATASOURCE_USERNAME).toString(),
configMap.get(DBContextHolder.DATASOURCE_PASSWORD).toString());
this.addTargetDataSource(configMap.get(DBContextHolder.DATASOURCE_KEY).toString(),
datasource);
}
/**
* 往数据源key-value键值对集合添加新的数据源
* @param key 新的数据源键
* @param dataSource 新的数据源
* @Author : ll. create at 2017年3月27日 下午2:56:49
*/
private void addTargetDataSource(String key, T dataSource) {
this.targetDataSources.put(key, dataSource);
super.setTargetDataSources(this.targetDataSources);
// afterPropertiesSet()方法调用时用来将targetDataSources的属性写入resolvedDataSources中的
super.afterPropertiesSet();
}
}3、编写AbstractDynamicDataSource的实现类,使用com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource数据源。主要实现创建数据源的方法(createDataSource)
/**
* Copyright (c) 2015 - 2016 eya Inc.
* All rights reserved.
*/
package com.eya.pubservice.datasource;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.List;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import com.alibaba.druid.filter.Filter;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
/**
* Druid数据源
* <p>摘抄自http://www.68idc.cn/help/buildlang/java/20160606618505.html
* @create ll
* @createDate 2017年3月27日 下午2:40:17
* @update
* @updateDate
*/
public class DruidDynamicDataSource extends AbstractDynamicDataSource<DruidDataSource> {
private boolean testWhileIdle = true;
private boolean testOnBorrow = false;
private boolean testOnReturn = false;
// 是否打开连接泄露自动检测
private boolean removeAbandoned = false;
// 连接长时间没有使用,被认为发生泄露时长
private long removeAbandonedTimeoutMillis = 300 * 1000;
// 发生泄露时是否需要输出 log,建议在开启连接泄露检测时开启,方便排错
private boolean logAbandoned = false;
// 只要maxPoolPreparedStatementPerConnectionSize>0,poolPreparedStatements就会被自动设定为true,使用oracle时可以设定此值。
// private int maxPoolPreparedStatementPerConnectionSize = -1;
// 配置监控统计拦截的filters
private String filters; // 监控统计:"stat" 防SQL注入:"wall" 组合使用: "stat,wall"
private List<Filter> filterList;
/*
* 创建数据源
* @see com.cdelabcare.pubservice.datasource.IDynamicDataSource#createDataSource(java.lang.String, java.lang.String, java.lang.String, java.lang.String)
*/
@Override
public DruidDataSource createDataSource(String driverClassName, String url, String username,
String password) {
DruidDataSource parent = (DruidDataSource) super.getApplicationContext().getBean(
DEFAULT_DATASOURCE_KEY);
DruidDataSource ds = new DruidDataSource();
ds.setUrl(url);
ds.setUsername(username);
ds.setPassword(password);
ds.setDriverClassName(driverClassName);
ds.setInitialSize(parent.getInitialSize());
ds.setMinIdle(parent.getMinIdle());
ds.setMaxActive(parent.getMaxActive());
ds.setMaxWait(parent.getMaxWait());
ds.setTimeBetweenConnectErrorMillis(parent.getTimeBetweenConnectErrorMillis());
ds.setTimeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis(parent.getTimeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis());
ds.setMinEvictableIdleTimeMillis(parent.getMinEvictableIdleTimeMillis());
ds.setValidationQuery(parent.getValidationQuery());
ds.setTestWhileIdle(testWhileIdle);
ds.setTestOnBorrow(testOnBorrow);
ds.setTestOnReturn(testOnReturn);
ds.setRemoveAbandoned(removeAbandoned);
ds.setRemoveAbandonedTimeoutMillis(removeAbandonedTimeoutMillis);
ds.setLogAbandoned(logAbandoned);
// 只要maxPoolPreparedStatementPerConnectionSize>0,poolPreparedStatements就会被自动设定为true,参照druid的源码
ds.setMaxPoolPreparedStatementPerConnectionSize(parent
.getMaxPoolPreparedStatementPerConnectionSize());
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(filters))
try {
ds.setFilters(filters);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
addFilterList(ds);
return ds;
}
private void addFilterList(DruidDataSource ds) {
if (filterList != null) {
List<Filter> targetList = ds.getProxyFilters();
for (Filter add : filterList) {
boolean found = false;
for (Filter target : targetList) {
if (add.getClass().equals(target.getClass())) {
found = true;
break;
}
}
if (!found)
targetList.add(add);
}
}
}
}4、使用Spring配置默认数据源。系统运行肯定有一套默认的数据源(否则动态创建的数据源信息从哪里来呢?上面提到的,动态创建的数据源信息是存放在数据库中的)。这里我贴出完整的Spring配置。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.2.xsd
">
<bean id="defaultDataSource"init-method="init" destroy-method="close">
<!-- 基本属性driverClassName、 url、user、password -->
<property name="driverClassName" value="${pro.driver}" />
<property name="url" value="${pro.url}" />
<property name="username" value="${pro.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${pro.password}" />
<!-- 配置初始化大小、最小、最大 -->
<property name="initialSize" value="${pro.initialSize}" />
<property name="minIdle" value="${pro.minIdle}" />
<property name="maxActive" value="${pro.maxActive}" />
<!-- 配置获取连接等待超时的时间 -->
<property name="maxWait" value="${pro.maxWait}" />
<!-- 配置间隔多久才进行一次检测,检测需要关闭的空闲连接,单位是毫秒 -->
<property name="timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis" value="${pro.timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis}" />
<!-- 配置一个连接在池中最小生存的时间,单位是毫秒 -->
<property name="minEvictableIdleTimeMillis" value="${pro.minEvictableIdleTimeMillis}" />
<property name="validationQuery" value="SELECT ''x''" />
<property name="testWhileIdle" value="true" />
<property name="testOnBorrow" value="false" />
<property name="testOnReturn" value="false" />
<!-- 打开PSCache,并且指定每个连接上PSCache的大小 -->
<property name="poolPreparedStatements" value="true" />
<property name="maxPoolPreparedStatementPerConnectionSize"
value="20" />
<!-- 配置监控统计拦截的filters,去掉后监控界面sql无法统计 -->
<property name="filters" value="stat" />
</bean>
<bean id="druidDynamicDataSource">
<property name="defaultTargetDataSource" ref="defaultDataSource" />
<property name="targetDataSources">
<map>
<entry key="defaultDataSource" value-ref="defaultDataSource"/>
<!-- 这里还可以加多个dataSource -->
</map>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- 注解事务 -->
<bean id="txManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="druidDynamicDataSource" />
</bean>
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="txManager" />
<!-- 定义SqlSessionFactory -->
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory">
<property name="configLocation">
<value>classpath:config/sqlMapConfig.xml</value>
</property>
<property name="dataSource" ref="druidDynamicDataSource" />
<property name="typeAliasesPackage" value="com.eya.model.domain" />
<property name="mapperLocations" value="classpath:com/eya/dao/**/*.xml" />
<!-- define config location -->
<!-- <property name="configLocation" value="sqlMapConfig.xml"/> -->
</bean>
<!-- 扫描mybatis的接口类 -->
<bean>
<property name="basePackage" value="com.eya.dao,com.eya.pubmapper" />
</bean>
<!-- spring 线程池的配置 -->
<bean id ="taskExecutor">
<!-- 线程池维护线程的最少数量 -->
<property name ="corePoolSize" value ="5" />
<!-- 线程池维护线程所允许的空闲时间 -->
<property name ="keepAliveSeconds" value ="30000" />
<!-- 线程池维护线程的最大数量 -->
<property name ="maxPoolSize" value ="1000" />
<!-- 线程池所使用的缓冲队列 -->
<property name ="queueCapacity" value ="200" />
</bean>
<!-- 配置线程池 -->
<bean id ="dataImportTaskExecutor" parent="taskExecutor" >
<!-- 线程池维护线程的最少数量 -->
<property name ="corePoolSize" value ="1" />
<!-- 线程池维护线程的最大数量 -->
<property name ="maxPoolSize" value ="1" />
</bean>
</beans>5、编写测试类。实际业务中应该使用AOP实现数据源的切换,这里只写了一个测试,AOP相关很简单,就不在这里单独写了。当调用该方法时,可以从日志信息中看到,首先初始化了datasource-2,并且切换到了datasource-2。图片效果不行,勉强看看
/**
* 分页查询
* @return {@link Pagination}
* @Author : ll. create at 2016年04月05日 下午01:43:19
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "/page.do", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public Pagination<CoreRoleView> page(HttpServletRequest request) {
logger.info("【分页查询】");
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map.put(DBContextHolder.DATASOURCE_KEY, "localhost");
map.put(DBContextHolder.DATASOURCE_DRIVER, "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
map.put(DBContextHolder.DATASOURCE_URL,
"jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/test_20170217?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8");
map.put(DBContextHolder.DATASOURCE_USERNAME, "root");
map.put(DBContextHolder.DATASOURCE_PASSWORD, "");
DBContextHolder.setDBType(map);
return super.page(request, false);
}
我们今天的关于Spring 配置多个数据源,并实现数据源的动态切换转载)和spring怎么配置多个数据源的分享就到这里,谢谢您的阅读,如果想了解更多关于037.[转] springboot 配置多个数据源、20. Spring Boot 默认、自定义数据源 、配置多个数据源 jdbcTemplate操作DB、JAVA中使用代码创建多数据源,并实现动态切换、JAVA中使用代码创建多数据源,并实现动态切换(一)的相关信息,可以在本站进行搜索。
本文标签:



![[转帖]Ubuntu 安装 Wine方法(ubuntu如何安装wine)](https://www.gvkun.com/zb_users/cache/thumbs/4c83df0e2303284d68480d1b1378581d-180-120-1.jpg)

